i principi di base - Structural Biology
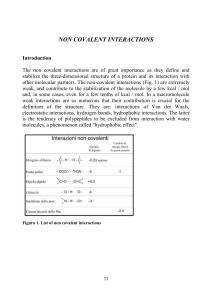
... weak, and contribute to the stabilization of the molecule by a few kcal / mol and, in some cases, even for a few tenths of kcal / mol. In a macromolecule weak interactions are so numerous that their contribution is crucial for the definition of the structure. They are: interactions of Van der Waals, ...
... weak, and contribute to the stabilization of the molecule by a few kcal / mol and, in some cases, even for a few tenths of kcal / mol. In a macromolecule weak interactions are so numerous that their contribution is crucial for the definition of the structure. They are: interactions of Van der Waals, ...
Metallic and nonmetallic double perovskites: A case study of A $ _2
... the Re sublattice. Indeed, because there are two t2g electrons per Re, a large enough splitting would lead to an insulating state. The magnetoresistance of these systems shows an interesting behavior. The Ca compound did not show any significant MR even at high fields. Hence, in Fig. 4, we compare ...
... the Re sublattice. Indeed, because there are two t2g electrons per Re, a large enough splitting would lead to an insulating state. The magnetoresistance of these systems shows an interesting behavior. The Ca compound did not show any significant MR even at high fields. Hence, in Fig. 4, we compare ...
Electron - CoolHub
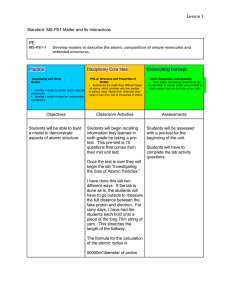
... Tell students that this is the periodic table. Explain that each box contains information about a different atom. The periodic table shows all the atoms that everything in the known universe is made from. It’s kind of like the alphabet in which only 26 letters, in different combinations, make up man ...
... Tell students that this is the periodic table. Explain that each box contains information about a different atom. The periodic table shows all the atoms that everything in the known universe is made from. It’s kind of like the alphabet in which only 26 letters, in different combinations, make up man ...
CP - Supplemental Activities
... of!the!particle!ever!be!zero!inside!the!box?!Why!or!why!not?!! Can!the!energy!of!the!particle!be!any!value!inside!a!given!box?!Why!or!why!not?! 4. Using!the!equation!for!the!energy!of!a!particle!in!a!one!dimensional!box,!please!describe!the! affect!the!changing!the!length!of!box!would!have!on!the!en ...
... of!the!particle!ever!be!zero!inside!the!box?!Why!or!why!not?!! Can!the!energy!of!the!particle!be!any!value!inside!a!given!box?!Why!or!why!not?! 4. Using!the!equation!for!the!energy!of!a!particle!in!a!one!dimensional!box,!please!describe!the! affect!the!changing!the!length!of!box!would!have!on!the!en ...
regents chemistry midterm - irondequoit 2014_entire exam w key
... 3) The forming of the H–Cl bond absorbs energy. 4) The forming of the H–Cl bond releases energy. 26. Which is an empirical formula? 1) C2H2 3) H2O2 2) H2O 4) C6Hl2O6 27. Which symbol represents an atom in the ground state with the most stable valence electron configuration? 1) B 3) Li 2) O 4) Ne 28. ...
... 3) The forming of the H–Cl bond absorbs energy. 4) The forming of the H–Cl bond releases energy. 26. Which is an empirical formula? 1) C2H2 3) H2O2 2) H2O 4) C6Hl2O6 27. Which symbol represents an atom in the ground state with the most stable valence electron configuration? 1) B 3) Li 2) O 4) Ne 28. ...
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... This increase of electropositivitity from Boron to Aluminium is the the usual trend according or associated with increasing size. However, B and Al follows immediately after s block elements, while Ga, In and Tl follows after d block elements. So the extra d-electrons in Ga, In and Tl do not shield ...
... This increase of electropositivitity from Boron to Aluminium is the the usual trend according or associated with increasing size. However, B and Al follows immediately after s block elements, while Ga, In and Tl follows after d block elements. So the extra d-electrons in Ga, In and Tl do not shield ...
Chapter 2 - Chemistry
... ii.) catalyst a substance that speeds up a reaction without undergoing any net change itself - the element symbol of the catalytic substance is often placed over the arrow 2 H2O2 (aq) ...
... ii.) catalyst a substance that speeds up a reaction without undergoing any net change itself - the element symbol of the catalytic substance is often placed over the arrow 2 H2O2 (aq) ...
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
... Solve NaF consists of Na+ and F− ions, CsI of Cs+ and I− ions, and CaO of Ca2+ and O2− ions. Because the product Q1Q2 appears in the numerator of Equation 8.4, the lattice energy increases dramatically when the charges increase. Thus, we expect the lattice energy of CaO, which has 2+ and 2− ions, to ...
... Solve NaF consists of Na+ and F− ions, CsI of Cs+ and I− ions, and CaO of Ca2+ and O2− ions. Because the product Q1Q2 appears in the numerator of Equation 8.4, the lattice energy increases dramatically when the charges increase. Thus, we expect the lattice energy of CaO, which has 2+ and 2− ions, to ...
Lab 1
... If there are 2.62 1022 atoms in 1.00 g of sodium and they are lined up side by side, what is the length of the line of sodium atoms in miles? Assume that the atoms are spheres of radius 0.186 nm. ...
... If there are 2.62 1022 atoms in 1.00 g of sodium and they are lined up side by side, what is the length of the line of sodium atoms in miles? Assume that the atoms are spheres of radius 0.186 nm. ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2
... A) Solid sodium carbonate is heated to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. D) Sodium carbonate is heated to give sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. 20) ...
... A) Solid sodium carbonate is heated to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. D) Sodium carbonate is heated to give sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. 20) ...
CHAPTER 23 THE TRANSITION ELEMENTS AND THEIR
... inner orbitals, they shield (screen) the nuclear charge, making electrons shared between the transition metal and some bonded atom feel a fairly constant effective nuclear charge. ...
... inner orbitals, they shield (screen) the nuclear charge, making electrons shared between the transition metal and some bonded atom feel a fairly constant effective nuclear charge. ...
MISE - Physical Basis of Chemistry
... We are still assuming there to be 100 grams of each element, so this will not give us the “true” Chemical formula. The actual amounts of each element would change the ratio and thus the formula. 3. Deducing the mole … the chemist’s “dozen”… Up to now, we’ve been talking about relative atomic weights ...
... We are still assuming there to be 100 grams of each element, so this will not give us the “true” Chemical formula. The actual amounts of each element would change the ratio and thus the formula. 3. Deducing the mole … the chemist’s “dozen”… Up to now, we’ve been talking about relative atomic weights ...
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical explanations
... mechanics, which may be considered as a theoretical justification of the main chemical ideas.’’ Several interpretative methods have been developed in this spirit: the loge theory (Daudel 1953; Daudel et al. 1954, 1955; Aslangul et al. 1972, 1974), the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) (Ba ...
... mechanics, which may be considered as a theoretical justification of the main chemical ideas.’’ Several interpretative methods have been developed in this spirit: the loge theory (Daudel 1953; Daudel et al. 1954, 1955; Aslangul et al. 1972, 1974), the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) (Ba ...
A) 0% B) 20% C) 50% D) 80% E) 100% 1. Naturally occurring boron
... C) The average speed of the particles in both containers is the same. D) The density of the containers is the same. E) The size of the helium atoms is the same as the size of the oxygen atoms. 54. When a sample of ethane gas in a closed container is cooled so that its absolute temperature halves, wh ...
... C) The average speed of the particles in both containers is the same. D) The density of the containers is the same. E) The size of the helium atoms is the same as the size of the oxygen atoms. 54. When a sample of ethane gas in a closed container is cooled so that its absolute temperature halves, wh ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
... In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are form ...
... In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are form ...
Higher Chemistry - Mobile Resource
... At the higher temperature the total number of collisions does not increase much. However a much higher proportion of the collisions produce the necessary activation energy and so reaction can happen. ...
... At the higher temperature the total number of collisions does not increase much. However a much higher proportion of the collisions produce the necessary activation energy and so reaction can happen. ...
eBook AQA GCSE Chemistry Unit C2 Part 1
... Ammonia gas exists as molecules. A molecule is a particle made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. In ammonia, each molecule consists of one atom of nitrogen joined to three atoms of hydrogen. The atoms are held together by covalent bonds. A covalent bond is a shared pair of electron ...
... Ammonia gas exists as molecules. A molecule is a particle made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. In ammonia, each molecule consists of one atom of nitrogen joined to three atoms of hydrogen. The atoms are held together by covalent bonds. A covalent bond is a shared pair of electron ...
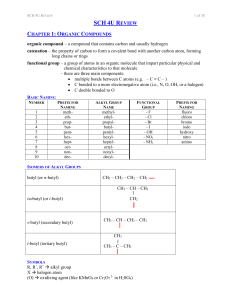
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
Supplemental Informaton
... •if there is mutually sharing, covalent compounds forms •if there is unequal sharing, polar covalent compounds forms. ii) electron transfer occurs, ionic compounds forms (next section). ...
... •if there is mutually sharing, covalent compounds forms •if there is unequal sharing, polar covalent compounds forms. ii) electron transfer occurs, ionic compounds forms (next section). ...
Day 13 Main Group Pt 1
... each group are more striking than the similarities. For example in Group IV, black, non-metallic carbon does not seem to have much in common with tin or lead. In Group V, it is not initially clear what gaseous nitrogen and metallic antimony (used to make pewter) have in common. These facts thwarted ...
... each group are more striking than the similarities. For example in Group IV, black, non-metallic carbon does not seem to have much in common with tin or lead. In Group V, it is not initially clear what gaseous nitrogen and metallic antimony (used to make pewter) have in common. These facts thwarted ...
Chemistry 20
... m) Copper metal and silver nitrate react to form silver metal and copper (II) nitrate. n) Sodium metal and chlorine react to make sodium chloride. o) Calcium phosphate and sulfuric acid make calcium sulfate and phosphoric acid. 13. Describe the difference between ionic and molecular compounds. You m ...
... m) Copper metal and silver nitrate react to form silver metal and copper (II) nitrate. n) Sodium metal and chlorine react to make sodium chloride. o) Calcium phosphate and sulfuric acid make calcium sulfate and phosphoric acid. 13. Describe the difference between ionic and molecular compounds. You m ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.