Biology, 8e (Campbell)
... E) There are covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms. Answer: A Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 46) When two atoms are equally electronegative, they will interact to form A) equal numbers of isotopes. B) ions. C) polar covalent bonds. D) nonpolar covalent bonds. E) ionic bonds. ...
... E) There are covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms. Answer: A Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 46) When two atoms are equally electronegative, they will interact to form A) equal numbers of isotopes. B) ions. C) polar covalent bonds. D) nonpolar covalent bonds. E) ionic bonds. ...
LEGGETT--AP CHEMISTRY * MINIMAL FINAL REVIEW
... 16. Which of the descriptions below is the best representation of the energy change involved in the process of breaking bonds in a molecule? (ignore any subsequent bond formation that may occur) A. Always exothermic B. Always endothermic C. Net energy change is zero D. Exothermic or endothermic depe ...
... 16. Which of the descriptions below is the best representation of the energy change involved in the process of breaking bonds in a molecule? (ignore any subsequent bond formation that may occur) A. Always exothermic B. Always endothermic C. Net energy change is zero D. Exothermic or endothermic depe ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 141)
... D) The pressure at the triple point, normal boiling and normal melting point for substance B and for substance A are the same. E) The pressure at the triple point for substance B is higher than that of substance A, but the normal boiling and normal melting point for substance A are lower than those ...
... D) The pressure at the triple point, normal boiling and normal melting point for substance B and for substance A are the same. E) The pressure at the triple point for substance B is higher than that of substance A, but the normal boiling and normal melting point for substance A are lower than those ...
Methane Activation by Transition-Metal Oxides, MOx
... does not occur for the high oxidation state of MO3. To form the hydride or carbide products from the reactants, it is necessary to break a M-O π bond. Thus, the observation that D1 or D2 formation is most exothermic for MO3 is consistent with these oxides having the weakest π bonds. Also, the observ ...
... does not occur for the high oxidation state of MO3. To form the hydride or carbide products from the reactants, it is necessary to break a M-O π bond. Thus, the observation that D1 or D2 formation is most exothermic for MO3 is consistent with these oxides having the weakest π bonds. Also, the observ ...
Revision IB2 Topic 1
... bubbling / effervescence / dissolving of / gas given off CaCO3 (do not accept CO2 produced); more vigorous reaction with HCl / OWTTE; 2HCl(aq) + CaCO3(s) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(1); [1] for correct formulas, [1] for balanced, state symbols not essential. ...
... bubbling / effervescence / dissolving of / gas given off CaCO3 (do not accept CO2 produced); more vigorous reaction with HCl / OWTTE; 2HCl(aq) + CaCO3(s) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(1); [1] for correct formulas, [1] for balanced, state symbols not essential. ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
- TestbankU
... 48) Nitrogen (N) normally forms three covalent bonds with a valence of 5. However, ammonium has four covalent bonds, each to a different hydrogen (H) atom (H has a valence of 1). What do you predict to be the charge on ammonium? A) +1 B) -1 C) +2 D) -2 Answer: A Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysi ...
... 48) Nitrogen (N) normally forms three covalent bonds with a valence of 5. However, ammonium has four covalent bonds, each to a different hydrogen (H) atom (H has a valence of 1). What do you predict to be the charge on ammonium? A) +1 B) -1 C) +2 D) -2 Answer: A Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysi ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
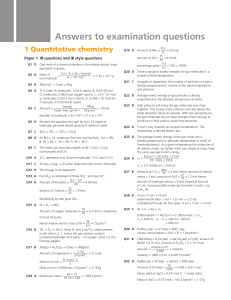
Answers to examination questions
... has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater than bonding pair repulsion. Q7 A Hydrogen bonding would only be expected to occur in CH2CH3COOH since it contains hydrogen bonded directly to oxygen. The −OH group is a ...
... has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater than bonding pair repulsion. Q7 A Hydrogen bonding would only be expected to occur in CH2CH3COOH since it contains hydrogen bonded directly to oxygen. The −OH group is a ...
10/18/11 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... -Sometimes empirical formulas and molecular formulas are the same. ex: H2O Empirical and molecular formula HNO3(nitric acid) Empirical and molecular formula Molecular formulas are often whole number ratios of the empirical formula. Molar Mass of a compound is equal to the molar mass of the empiric ...
... -Sometimes empirical formulas and molecular formulas are the same. ex: H2O Empirical and molecular formula HNO3(nitric acid) Empirical and molecular formula Molecular formulas are often whole number ratios of the empirical formula. Molar Mass of a compound is equal to the molar mass of the empiric ...
C:\Documents and Settings\mrh70950\My Documents
... B. LCAO-MO: how bonds form from atomic orbitals 1. Linear, head-on overlap of two atomic orbitals generates a σ bond (having a circular cross-section) and a σ* bond (usually empty) a. Electronic configuration diagrams C. Hybrid atomic orbitals and rehybridization–reconciling VSEPR and MO’s 1. sp3 o ...
... B. LCAO-MO: how bonds form from atomic orbitals 1. Linear, head-on overlap of two atomic orbitals generates a σ bond (having a circular cross-section) and a σ* bond (usually empty) a. Electronic configuration diagrams C. Hybrid atomic orbitals and rehybridization–reconciling VSEPR and MO’s 1. sp3 o ...
Ch 11 Review - mvhs
... C – Group IV has a nonmetal (C), metalloids (Si, Ge), and metals (Sn, Pb). Therefore, there are many types of bond that they make in different substances. D – BF3 is nonpolar, trigonal planar molecule since B is stable with an incomplete octet, while PF3 is a polar, trigonal bipyramidal molecule. 5. ...
... C – Group IV has a nonmetal (C), metalloids (Si, Ge), and metals (Sn, Pb). Therefore, there are many types of bond that they make in different substances. D – BF3 is nonpolar, trigonal planar molecule since B is stable with an incomplete octet, while PF3 is a polar, trigonal bipyramidal molecule. 5. ...
Module 9 Methods for Structure Determination Lecture 24 UV
... due to a similar fragmentation where one of the benzylic C-H is replaced by methyl group. Similarly, when an alkyl group attached to the benzene ring is a propyl group or larger, Mclafferty rearrangement occurs to give fragments. Using butyl benzene the effect of McLafferty rearrangement can be show ...
... due to a similar fragmentation where one of the benzylic C-H is replaced by methyl group. Similarly, when an alkyl group attached to the benzene ring is a propyl group or larger, Mclafferty rearrangement occurs to give fragments. Using butyl benzene the effect of McLafferty rearrangement can be show ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) a nonpolar covalent bond B) a polar covalent bond C) an ionic bond D) a hydrophobic interaction Answer: B Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 30) A covalent bond is likely to be polar when _____. A) one of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom ...
... A) a nonpolar covalent bond B) a polar covalent bond C) an ionic bond D) a hydrophobic interaction Answer: B Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 30) A covalent bond is likely to be polar when _____. A) one of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) a nonpolar covalent bond B) a polar covalent bond C) an ionic bond D) a hydrophobic interaction Answer: B Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 30) A covalent bond is likely to be polar when _____. A) one of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom ...
... A) a nonpolar covalent bond B) a polar covalent bond C) an ionic bond D) a hydrophobic interaction Answer: B Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 30) A covalent bond is likely to be polar when _____. A) one of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... Describe the covalent bond as the electrostatic attraction between a pair of electrons and positively charged nuclei. Describe how the covalent bond is formed as a result of electron sharing. Deduce the Lewis (electron dot) structures of molecules and ions for up to four electron pairs on each atom. ...
... Describe the covalent bond as the electrostatic attraction between a pair of electrons and positively charged nuclei. Describe how the covalent bond is formed as a result of electron sharing. Deduce the Lewis (electron dot) structures of molecules and ions for up to four electron pairs on each atom. ...
GHW - Louisiana Tech University
... The gram mole is the grams of any chemical substance using the value atomic mass obtained from the periodic table. E.g. for carbon gram mole is 12.01 grams of carbon since its atomic mass is 12.01 amu in the periodic table. if you take atomic mass in grams the number of atoms is simply 6.022 x 10 23 ...
... The gram mole is the grams of any chemical substance using the value atomic mass obtained from the periodic table. E.g. for carbon gram mole is 12.01 grams of carbon since its atomic mass is 12.01 amu in the periodic table. if you take atomic mass in grams the number of atoms is simply 6.022 x 10 23 ...
chemistry -- questions -
... __ 23. An atom's atomic number is best described as the number of a) protons it contains. b) neutrons it contains. c) electrons in the outermost shell. d) protons and neutrons it contains. e) protons and electrons it contains. __ 24. An atom's atomic mass is best described as the mass of a) the pro ...
... __ 23. An atom's atomic number is best described as the number of a) protons it contains. b) neutrons it contains. c) electrons in the outermost shell. d) protons and neutrons it contains. e) protons and electrons it contains. __ 24. An atom's atomic mass is best described as the mass of a) the pro ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.