syllabus details - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Compare the relative electronegativity values of two or more elements based on their positions in the periodic table. ...
... Compare the relative electronegativity values of two or more elements based on their positions in the periodic table. ...
unit-3-atoms-and-nuclear - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... For example, when fission of uranium=235 occurs, the 2 or 3 neutrons given off cause the fission of other uranium-235 nuclei. Continues until all atoms are split or neutrons fail to hit uranium-235 nuclei. (mass hits a certain level. The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons ...
... For example, when fission of uranium=235 occurs, the 2 or 3 neutrons given off cause the fission of other uranium-235 nuclei. Continues until all atoms are split or neutrons fail to hit uranium-235 nuclei. (mass hits a certain level. The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons ...
Chapter 5 notes
... held together by chemical bonds A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements combined in a specific ratio and held together by chemical bonds. A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. A ...
... held together by chemical bonds A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements combined in a specific ratio and held together by chemical bonds. A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. A ...
AP Chemistry
... 66. The purpose of weighing the cup and its contents again at CaCl2(s) Ca2+ + 2 Clthe end of the experiment was to For the process of solid calcium chloride dissolving in water, (A) determine the mass of solute that was added. represented above, the entropy change might be expected to (B) determi ...
... 66. The purpose of weighing the cup and its contents again at CaCl2(s) Ca2+ + 2 Clthe end of the experiment was to For the process of solid calcium chloride dissolving in water, (A) determine the mass of solute that was added. represented above, the entropy change might be expected to (B) determi ...
Chemistry - Bourbon County Schools
... Explain how ionic and covalent compounds differ Describe the unique features of bonding in carbon compounds Compare the different types of intermolecular forces (e.g., van der Waals, dispersion) Explain and provide examples for dipole moments, bond polarity, and hydrogen bonding Describe the unique ...
... Explain how ionic and covalent compounds differ Describe the unique features of bonding in carbon compounds Compare the different types of intermolecular forces (e.g., van der Waals, dispersion) Explain and provide examples for dipole moments, bond polarity, and hydrogen bonding Describe the unique ...
Chemistry 400
... 8) Choose the transition (in a hydrogen atom) below that represents the absorption of the shortest wavelength photon. A) n = 1 to n = 2 B) n = 2 to n = 3 C) n = 4 to n = 5 D) n = 6 to n = 3 E) n = 3 to n = 1 9) Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) We can sometimes know the exact location an ...
... 8) Choose the transition (in a hydrogen atom) below that represents the absorption of the shortest wavelength photon. A) n = 1 to n = 2 B) n = 2 to n = 3 C) n = 4 to n = 5 D) n = 6 to n = 3 E) n = 3 to n = 1 9) Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) We can sometimes know the exact location an ...
downloaded
... produced by transitions between levels lying close together in energy. Examples of this in atomic ions are transitions between highly excited states in, e.g., Rydberg series, and unexpected or forbidden transitions within ground configurations. Both of these are a challenge for experiment and need a ...
... produced by transitions between levels lying close together in energy. Examples of this in atomic ions are transitions between highly excited states in, e.g., Rydberg series, and unexpected or forbidden transitions within ground configurations. Both of these are a challenge for experiment and need a ...
Lecture 1 - Алтайский государственный технический
... Chemists make their observations in the macroscopic world and seek to understand the fundamental properties of matter at the level of the microscopic world (i.e. molecules and atoms). The reason why certain chemicals react the way they do is a direct consequence of their atomic structure. 2.1 The At ...
... Chemists make their observations in the macroscopic world and seek to understand the fundamental properties of matter at the level of the microscopic world (i.e. molecules and atoms). The reason why certain chemicals react the way they do is a direct consequence of their atomic structure. 2.1 The At ...
Summaries of Review Topics for AP Chemistry
... Metals Semimetals Nonmetals Network Covalent Molecular Covalent (1) Element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means; it contains only one kind of atom. Elements are represented by the chemical symbols. The symbols for most elements consist o ...
... Metals Semimetals Nonmetals Network Covalent Molecular Covalent (1) Element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means; it contains only one kind of atom. Elements are represented by the chemical symbols. The symbols for most elements consist o ...
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... after the name of the cation). 5. If the compound contains a polyatomic ion, simply name the ion. ...
... after the name of the cation). 5. If the compound contains a polyatomic ion, simply name the ion. ...
Florida`s - Wavefunction, Inc.
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeati ...
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeati ...
The Complete Notes - Joliet Junior College
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don’t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don’t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
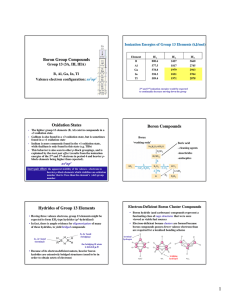
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... +3 oxidation state. Gallium is also found in a +3 oxidation state, but is sometimes found in a +1 oxidation state Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by ...
... +3 oxidation state. Gallium is also found in a +3 oxidation state, but is sometimes found in a +1 oxidation state Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by ...
Chemistry 101: The Complete Notes
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don‟t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don‟t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... 8. The -H and OH ends that were removed can also fit together with each other to form a molecule. This new molecule (H and OH) has a molecular formula of ___________ and is more familiarly known as 9. Write the molecular formula for sucrose. (Hint: you can either count all of the atoms like you di ...
... 8. The -H and OH ends that were removed can also fit together with each other to form a molecule. This new molecule (H and OH) has a molecular formula of ___________ and is more familiarly known as 9. Write the molecular formula for sucrose. (Hint: you can either count all of the atoms like you di ...
Key - GCC
... All samples of a given substance will have the same ratio of atoms by mass (e.g., carbon dioxide is always CO2). c. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 4 postulates: all matter is made of atoms (once thought to be indivisible); all atoms of a given elements are identical (atoms of different elements are differen ...
... All samples of a given substance will have the same ratio of atoms by mass (e.g., carbon dioxide is always CO2). c. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 4 postulates: all matter is made of atoms (once thought to be indivisible); all atoms of a given elements are identical (atoms of different elements are differen ...
Chemistry - Set as Home Page
... 24. Molecular formula of CHCl3 and its Empirical formula is __________. 25. Molecular formula of benzene is C6H6 and its empirical formula is __________. 26. 58.5 is the __________ of NaCl. 27. 4.5 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. 28. 28 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. ...
... 24. Molecular formula of CHCl3 and its Empirical formula is __________. 25. Molecular formula of benzene is C6H6 and its empirical formula is __________. 26. 58.5 is the __________ of NaCl. 27. 4.5 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. 28. 28 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. ...
1 • Introduction The Scientific Method (1 of 20) 1
... • metals often are written with the ° symbol to emphasize that the metal is in the neutral elemental state, not an ion. • some compounds have common names that you should just know... water, H 2 O; ammonia, NH3 ; methane, CH4 • remember the seven diatomic elements so they can be written as diatomic ...
... • metals often are written with the ° symbol to emphasize that the metal is in the neutral elemental state, not an ion. • some compounds have common names that you should just know... water, H 2 O; ammonia, NH3 ; methane, CH4 • remember the seven diatomic elements so they can be written as diatomic ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus - Tuloso
... Knowledge of specific facts of chemistry is essential for an understanding of principles and concepts. These descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course t ...
... Knowledge of specific facts of chemistry is essential for an understanding of principles and concepts. These descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course t ...
Chemistry - School District of Springfield Township
... • The Periodic Table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways to compare and organize the elements. o Elements with similar properties have been placed into groups. o The physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular pattern when they are arranged in order o ...
... • The Periodic Table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways to compare and organize the elements. o Elements with similar properties have been placed into groups. o The physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular pattern when they are arranged in order o ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.