Chemical Reactions
... change chemical formulas. For example, if you have H2O on the left side of an equation but need two oxygens, you can add the coefficient “2” to read 2H2O. You cannot, however, get two oxygens by changing the formula to H2O2. The reactant is water, H2O, and not hydrogen peroxide, H2O2. For the equati ...
... change chemical formulas. For example, if you have H2O on the left side of an equation but need two oxygens, you can add the coefficient “2” to read 2H2O. You cannot, however, get two oxygens by changing the formula to H2O2. The reactant is water, H2O, and not hydrogen peroxide, H2O2. For the equati ...
chemistry paper 1
... Members of higher molecular mass are often used to make soap. The first few members are often used to make polymers. The members can commonly react with hydrogen halides to give halohydrocarbons. A. B. C. D. ...
... Members of higher molecular mass are often used to make soap. The first few members are often used to make polymers. The members can commonly react with hydrogen halides to give halohydrocarbons. A. B. C. D. ...
8.4 Weak Acids and Bases, Continued
... • Antacids are substances that neutralize excess stomach acid. Some antacids are bases that are not very soluble in water. • Aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide are examples of antacids that are not very soluble in water. They are used in combination to prevent unpleasant side effects. • Calc ...
... • Antacids are substances that neutralize excess stomach acid. Some antacids are bases that are not very soluble in water. • Aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide are examples of antacids that are not very soluble in water. They are used in combination to prevent unpleasant side effects. • Calc ...
Osmium(VIII) Catalyzed Oxidation of 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid
... which a known quantity of acrylonitrile (scavenger) had been added initially, was kept for 2 h in an inert atmosphere. On diluting the reaction mixture with methanol, a white precipitate was formed, indicating the intervention of free radicals in the reaction. The blank experiments of either DPC or ...
... which a known quantity of acrylonitrile (scavenger) had been added initially, was kept for 2 h in an inert atmosphere. On diluting the reaction mixture with methanol, a white precipitate was formed, indicating the intervention of free radicals in the reaction. The blank experiments of either DPC or ...
Determination of Cystein and Methionine by Oscillating Chemical
... Mechanisms for oscillatory chemical systems have been pursued almost as soon as chemists finally recognized the possibility of oscillation in a homogeneous medium [17–21]. Understanding why and how such complicated behavior arises in terms of chemical species and the interaction among them is a fasc ...
... Mechanisms for oscillatory chemical systems have been pursued almost as soon as chemists finally recognized the possibility of oscillation in a homogeneous medium [17–21]. Understanding why and how such complicated behavior arises in terms of chemical species and the interaction among them is a fasc ...
Chemical Equilibrium Equilibrium A state where the reactants and
... Knowing the equilibrium constant allows us to predict several important features of the reaction. 1) the tendency of the reaction to ___________ (but not the _______________) 2) whether a given set of concentrations represent an __________________ condition 3) the equilibrium position that will be ...
... Knowing the equilibrium constant allows us to predict several important features of the reaction. 1) the tendency of the reaction to ___________ (but not the _______________) 2) whether a given set of concentrations represent an __________________ condition 3) the equilibrium position that will be ...
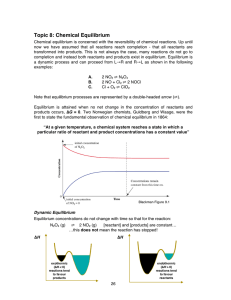
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... transformed into products. This is not always the case, many reactions do not go to completion and instead both reactants and products exist in equilibrium. Equilibrium is a dynamic process and can proceed from L→R and R→L as shown in the following examples: A. B. C. ...
... transformed into products. This is not always the case, many reactions do not go to completion and instead both reactants and products exist in equilibrium. Equilibrium is a dynamic process and can proceed from L→R and R→L as shown in the following examples: A. B. C. ...
13.0 Redox Reactions PowerPoint
... ▫ We will need to predict the redox equation that will occur, and then we will use the quantities provided to answer the question. The math is the same as Chem 20, we will just be using our knowledge of redox to start the question. ...
... ▫ We will need to predict the redox equation that will occur, and then we will use the quantities provided to answer the question. The math is the same as Chem 20, we will just be using our knowledge of redox to start the question. ...
Electrochemical Fundamentals
... Pt|H2|H+, Cl-|AgCl|Ag, E = 0.222 V Overall reaction H2 + 2AgCl 2Ag + 2Cl- + 2H+ may reverse the reaction upon the application of an outside voltage of 0.222 V ...
... Pt|H2|H+, Cl-|AgCl|Ag, E = 0.222 V Overall reaction H2 + 2AgCl 2Ag + 2Cl- + 2H+ may reverse the reaction upon the application of an outside voltage of 0.222 V ...
Rhenium- and molybdenum-catalyzed dehydration reactions
... sults in the choice of tungsten, molybdenum, or rhenium as catalyst for the dehydration reaction. In this thesis, rhenium- and molybdenum-based complexes are applied as catalysts for the dehydration reaction. Chapter 1 of this thesis provides an overview of the state of the art for the use of vario ...
... sults in the choice of tungsten, molybdenum, or rhenium as catalyst for the dehydration reaction. In this thesis, rhenium- and molybdenum-based complexes are applied as catalysts for the dehydration reaction. Chapter 1 of this thesis provides an overview of the state of the art for the use of vario ...
9.2 Oxidation Numbers
... Phosphates, like ammonium phosphate, are important components of fertilizers used to stimulate the growth of agricultural crops and to make our gardens green. Their commercial synthesis requires elemental phosphorus, which can be acquired by heating phosphate rock (containing calcium phosphate) with ...
... Phosphates, like ammonium phosphate, are important components of fertilizers used to stimulate the growth of agricultural crops and to make our gardens green. Their commercial synthesis requires elemental phosphorus, which can be acquired by heating phosphate rock (containing calcium phosphate) with ...
practice spring final exam
... (B) 0°C, 101.3 kPa (C) 0 K, 1 atm (D) 0 K, 760 atm 36. How much space do 5.7x1028 molecules of oxygen gas occupy? (A) 4227 L (B) 2.1x106 mL (C) 1.53x1051 L (D) 2.1x106 L 37. The mass of one mole of Ca(OH)2 is: (A) 29 g (B) 38 g (C) 57 g (D) 74 g 38. How many moles are in 100 g of O2 gas? (A) 1 mol ( ...
... (B) 0°C, 101.3 kPa (C) 0 K, 1 atm (D) 0 K, 760 atm 36. How much space do 5.7x1028 molecules of oxygen gas occupy? (A) 4227 L (B) 2.1x106 mL (C) 1.53x1051 L (D) 2.1x106 L 37. The mass of one mole of Ca(OH)2 is: (A) 29 g (B) 38 g (C) 57 g (D) 74 g 38. How many moles are in 100 g of O2 gas? (A) 1 mol ( ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Directions (51–57): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 On a field trip, Student X and Student Y collected two rock samples. Analysis revealed that both rocks contained lead a ...
... Directions (51–57): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 On a field trip, Student X and Student Y collected two rock samples. Analysis revealed that both rocks contained lead a ...
Analytical Chemistry
... 1. Electrolytes: Electrolytes are solutes which ionize in a solvent to produce an electrically conducting medium. Strong electrolytes ionize completely whereas weak electrolytes are only partially in the solvent. Table 1: Strong electrolytes 1.the inorganic acids HNO3,HClO4,H2SO4,HCl,HI, HBr,HClO3,H ...
... 1. Electrolytes: Electrolytes are solutes which ionize in a solvent to produce an electrically conducting medium. Strong electrolytes ionize completely whereas weak electrolytes are only partially in the solvent. Table 1: Strong electrolytes 1.the inorganic acids HNO3,HClO4,H2SO4,HCl,HI, HBr,HClO3,H ...
chapter 21 chemistry of the main-group elements i
... bond them together. To bond these four atoms into a chain requires three electron pairs. Since each electron pair in a bridging bond replaces two “normal” bonds, there must be at least two bridging bonds in the B4 H10 molecules. By analogy with B2 H 6 , we might write the structure below left. But t ...
... bond them together. To bond these four atoms into a chain requires three electron pairs. Since each electron pair in a bridging bond replaces two “normal” bonds, there must be at least two bridging bonds in the B4 H10 molecules. By analogy with B2 H 6 , we might write the structure below left. But t ...
Energy is the essence of chemistry It determines which reaction can
... ∆HB(C==C) < 2x∆HB(C—C) Thus replacing a multiple bond by more single bonds gives a more stable molecule. Example: CH2==CH2(g) + HCl(g) → CH3—CH2Cl(g) ∆H° = -72 kJ The product has a lower enthalpy than the reactants, i.e. more stable. Average bond enthalpies can be used to calculate reaction enthalpi ...
... ∆HB(C==C) < 2x∆HB(C—C) Thus replacing a multiple bond by more single bonds gives a more stable molecule. Example: CH2==CH2(g) + HCl(g) → CH3—CH2Cl(g) ∆H° = -72 kJ The product has a lower enthalpy than the reactants, i.e. more stable. Average bond enthalpies can be used to calculate reaction enthalpi ...
Thermodynamics
... because some of the heat may escape before it can be measured – we need ideally to measure the total heat energy evolved or absorbed, which can be done if all the heat is transferred to a liquid whose temperature we measure, however some heat is inevitably lost to the environment. For a reaction occ ...
... because some of the heat may escape before it can be measured – we need ideally to measure the total heat energy evolved or absorbed, which can be done if all the heat is transferred to a liquid whose temperature we measure, however some heat is inevitably lost to the environment. For a reaction occ ...
Topic 8 Acids and Bases File
... Ideally, the end point corresponds to the equivalence point in a titration. Lewis theory: An acid is defined as an electron pair acceptor (e.g. BF3) and a base is an electron donator (e.g. NH3). Monoprotic: Where one mole of the acid produces one mole of hydrogen ions, e.g. HCl. pH: Power of hydroge ...
... Ideally, the end point corresponds to the equivalence point in a titration. Lewis theory: An acid is defined as an electron pair acceptor (e.g. BF3) and a base is an electron donator (e.g. NH3). Monoprotic: Where one mole of the acid produces one mole of hydrogen ions, e.g. HCl. pH: Power of hydroge ...
Chemistry 11th
... Its chief property due to which it is widely used is that when it is mixed with one-third of its weight of water it sets with expansion into a hard mass of interlocking crystals of gypsum within 5-15 minutes. The setting is due to hydration of plaster of paris into gypsum. OR (a) B atom in BCl3 h ...
... Its chief property due to which it is widely used is that when it is mixed with one-third of its weight of water it sets with expansion into a hard mass of interlocking crystals of gypsum within 5-15 minutes. The setting is due to hydration of plaster of paris into gypsum. OR (a) B atom in BCl3 h ...
data table - Tenafly Public Schools
... the same? _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. How many characteristic properties of two substances must be different for the two substances to be the different? ___________________________ ...
... the same? _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. How many characteristic properties of two substances must be different for the two substances to be the different? ___________________________ ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.