Practice Exam 4
... Ne and Ar are both atoms so they should have less entropy than a molecular substance, which has more complexity. Ar will have a higher entropy than Ne because it has a larger mass and more fundamental particles. The correct order is H2 O(ℓ) < Ne(g) < Ar(g) < CO2 (g). 017 10.0 points Consider the fol ...
... Ne and Ar are both atoms so they should have less entropy than a molecular substance, which has more complexity. Ar will have a higher entropy than Ne because it has a larger mass and more fundamental particles. The correct order is H2 O(ℓ) < Ne(g) < Ar(g) < CO2 (g). 017 10.0 points Consider the fol ...
CHEMISTRY OF p-ELEMENTS - Львівський національний
... Hans Christian Oersted, a Danish chemist, was the first who isolated aluminum in 1825, using a chemical process involving potassium amalgam. Between 1827 and 1845, Friedrich Wohler, a German chemist, improved Oersted's process by using metallic potassium. He was the first to measure the specific gr ...
... Hans Christian Oersted, a Danish chemist, was the first who isolated aluminum in 1825, using a chemical process involving potassium amalgam. Between 1827 and 1845, Friedrich Wohler, a German chemist, improved Oersted's process by using metallic potassium. He was the first to measure the specific gr ...
Mnemonic Devices - Free WonderKids-e
... • Cu & Ag may react with conc. Nitric Acid to produce nitrogen oxides but not hydrogen; • Au may react with a mixture, called aqua regia, of three parts conc. HCl and one part conc. HNO 3 . ...
... • Cu & Ag may react with conc. Nitric Acid to produce nitrogen oxides but not hydrogen; • Au may react with a mixture, called aqua regia, of three parts conc. HCl and one part conc. HNO 3 . ...
Gas Laws
... Hydrogen is the only element that has an exposed proton when an electron is lost. The exposure of the proton and the fact that the other element that the hydrogen in bonded to has a very high electron affinity, the compound ends up having a very strong dipole moment called hydrogen bonding. 7. What ...
... Hydrogen is the only element that has an exposed proton when an electron is lost. The exposure of the proton and the fact that the other element that the hydrogen in bonded to has a very high electron affinity, the compound ends up having a very strong dipole moment called hydrogen bonding. 7. What ...
The integration of flow reactors into synthetic organic chemistry
... laboratory practices have also become standardized to make the best use of these tools and associated pieces of equipment. A standard sequence for a reaction today and over a century ago would still be easily recognizable to both bench chemists (Figure 1). From a simple analysis of the individual pr ...
... laboratory practices have also become standardized to make the best use of these tools and associated pieces of equipment. A standard sequence for a reaction today and over a century ago would still be easily recognizable to both bench chemists (Figure 1). From a simple analysis of the individual pr ...
Unit 12: Electrochemistry
... 1. Alternating Current (AC): The current produced by power plants; the polarity (positive to negative current) shifts (alternates) at a household rate of 60 cycles per second (Hz). 2. Anode: The electrode at which oxidation occurs. 3. Cathode: The electrode at which reduction occurs. 4. Converter: A ...
... 1. Alternating Current (AC): The current produced by power plants; the polarity (positive to negative current) shifts (alternates) at a household rate of 60 cycles per second (Hz). 2. Anode: The electrode at which oxidation occurs. 3. Cathode: The electrode at which reduction occurs. 4. Converter: A ...
258-261
... n the last section we saw how to use the balanced equation for a reaction to calculate the numbers of moles of reactants and products for a particular case. However, moles represent numbers of molecules, and we cannot count molecules directly. In chemistry we count by weighing. Therefore, in this se ...
... n the last section we saw how to use the balanced equation for a reaction to calculate the numbers of moles of reactants and products for a particular case. However, moles represent numbers of molecules, and we cannot count molecules directly. In chemistry we count by weighing. Therefore, in this se ...
File - UTeach Dallas Project
... Knowledge with understanding The candidates should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding in relation to:(a) scientific phenomena, facts, concepts, theories and laws. (b) scientific terminology, use of symbols, quantities and units. (c) scientific apparatus and instruments and their safe ...
... Knowledge with understanding The candidates should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding in relation to:(a) scientific phenomena, facts, concepts, theories and laws. (b) scientific terminology, use of symbols, quantities and units. (c) scientific apparatus and instruments and their safe ...
Worked out problems
... Analyze: We are given an incomplete, unbalanced (skeleton) equation for a redox reaction occurring in acidic solution and asked to complete and balance it. Plan: We use the half-reaction procedure we just learned. Solve: Step 1: We divide the equation into two halfreactions: Step 2:We balance each h ...
... Analyze: We are given an incomplete, unbalanced (skeleton) equation for a redox reaction occurring in acidic solution and asked to complete and balance it. Plan: We use the half-reaction procedure we just learned. Solve: Step 1: We divide the equation into two halfreactions: Step 2:We balance each h ...
Topic 9 Oxidation and Reduction Answers - slider-dpchemistry-11
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
Removal of Chlorine Removal of Chlorine
... decreases proportional with increase in chlorine Bridging –OH not affected by chlorine gas exposure ...
... decreases proportional with increase in chlorine Bridging –OH not affected by chlorine gas exposure ...
Chemistry Higher Level Chapter 5 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... during respiration, when glucose reacts with oxygen. Modern lifestyles are dependent on the transfer of energy that occurs when fuels burn. As we explore the source of these energy changes, we will deepen our understanding of why bonds are broken and formed during a chemical reaction, and why electr ...
... during respiration, when glucose reacts with oxygen. Modern lifestyles are dependent on the transfer of energy that occurs when fuels burn. As we explore the source of these energy changes, we will deepen our understanding of why bonds are broken and formed during a chemical reaction, and why electr ...
5 Energetics - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... during respiration, when glucose reacts with oxygen. Modern lifestyles are dependent on the transfer of energy that occurs when fuels burn. As we explore the source of these energy changes, we will deepen our understanding of why bonds are broken and formed during a chemical reaction, and why electr ...
... during respiration, when glucose reacts with oxygen. Modern lifestyles are dependent on the transfer of energy that occurs when fuels burn. As we explore the source of these energy changes, we will deepen our understanding of why bonds are broken and formed during a chemical reaction, and why electr ...
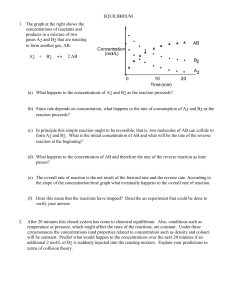
Problem 1-2
... If you use the equations for these equilibrium constants you have to fill in the numbers representing the pressures/concentrations dimensionless i.e. you have to divide the given pressures/concentrations by the standard pressure (p° = 1,000 bar)/standard concentration (c° = 1 mol/L). The double cont ...
... If you use the equations for these equilibrium constants you have to fill in the numbers representing the pressures/concentrations dimensionless i.e. you have to divide the given pressures/concentrations by the standard pressure (p° = 1,000 bar)/standard concentration (c° = 1 mol/L). The double cont ...
1.6 Energy changes in chemical reactions
... The traditional division of chemistry into physical, inorganic, and organic is an arbitrary one and the majority of chemists work across these divides. Most real problems also require chemists to interact with scientists in other disciplines. For example, chemists, physicists, mathematicians, and me ...
... The traditional division of chemistry into physical, inorganic, and organic is an arbitrary one and the majority of chemists work across these divides. Most real problems also require chemists to interact with scientists in other disciplines. For example, chemists, physicists, mathematicians, and me ...
Acid-Base Equilibria - Riverside Local Schools
... acids and bases by their characteristic properties. Acids have a sour taste (for example, citric acid in lemon juice) and cause certain dyes to change color (for example, litmus turns red on contact with acids). Indeed, the word acid comes from the Latin word acidus, meaning sour or tart. Bases, in ...
... acids and bases by their characteristic properties. Acids have a sour taste (for example, citric acid in lemon juice) and cause certain dyes to change color (for example, litmus turns red on contact with acids). Indeed, the word acid comes from the Latin word acidus, meaning sour or tart. Bases, in ...
7.1 CHEMICAL SYSTEMS IN EQUILIBRIUM: Dynamic Equilibrium in
... That is the proportion demanded by the equation. In some reactions you might choose to use an excess of one of the reactants. You would do this if it is particularly important to use up as much as possible of the other reactant - if, for example, it was much more expensive. That doesn't apply in thi ...
... That is the proportion demanded by the equation. In some reactions you might choose to use an excess of one of the reactants. You would do this if it is particularly important to use up as much as possible of the other reactant - if, for example, it was much more expensive. That doesn't apply in thi ...
x - SharpSchool
... equilibrium theories and principles apply to a variety of phenomena in our world eg) ...
... equilibrium theories and principles apply to a variety of phenomena in our world eg) ...
Chapter 23 + Practice Problems - Bloomsburg Area School District
... body (after water) and make up about 10% to 20% of the mass of a cell. Made up of specific sequences of amino acids, proteins have molecular masses that range from 6000 to more than 9 million atomic mass units. About 9000 different protein molecules are found in cells in the human body. Nitrogen acc ...
... body (after water) and make up about 10% to 20% of the mass of a cell. Made up of specific sequences of amino acids, proteins have molecular masses that range from 6000 to more than 9 million atomic mass units. About 9000 different protein molecules are found in cells in the human body. Nitrogen acc ...
Molecules, Moles and Chemical Equations File
... from physics that power is defined as energy per unit time. So as the time required for the explosion to occur becomes shorter, the power of the explosion will increase. Modern explosives are generally solids. But that was not always true; liquid nitroglycerin was one of the first widely used explos ...
... from physics that power is defined as energy per unit time. So as the time required for the explosion to occur becomes shorter, the power of the explosion will increase. Modern explosives are generally solids. But that was not always true; liquid nitroglycerin was one of the first widely used explos ...
teaching and learning materials - UNESDOC
... experiences and low-cost equipment designs, has some limitations. In chemistry, for example, major areas of the subject have been ignored. One of these is organic chemistry. In several countries, the welcome accorded to the basic ideas, has been coupled with questions about these important missing a ...
... experiences and low-cost equipment designs, has some limitations. In chemistry, for example, major areas of the subject have been ignored. One of these is organic chemistry. In several countries, the welcome accorded to the basic ideas, has been coupled with questions about these important missing a ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.