More Reaction Information
... • For reactions that are not metal + nonmetal, or do not involve O2, we need a method for determining how the electrons are transferred. • Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an oxidation state that allows them to determine the electron flow in the reaction. – Even though t ...
... • For reactions that are not metal + nonmetal, or do not involve O2, we need a method for determining how the electrons are transferred. • Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an oxidation state that allows them to determine the electron flow in the reaction. – Even though t ...
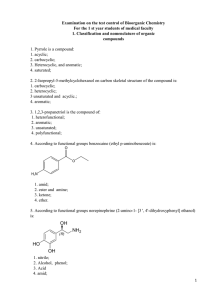
2. 2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol on carbon skeletal
... 1. OH- group consisting of carboxylic acid functional groups; 2. hydroxyl group with sp 3-hybrid oxygen; 3. N-H acidic center; 4. OH group bonded directly to the heterocycle; 39. The most strong acidic properties of the compound shown in: 1. acetic acid; 2. propanoic acid; 3. 2-methylpropanoic acid; ...
... 1. OH- group consisting of carboxylic acid functional groups; 2. hydroxyl group with sp 3-hybrid oxygen; 3. N-H acidic center; 4. OH group bonded directly to the heterocycle; 39. The most strong acidic properties of the compound shown in: 1. acetic acid; 2. propanoic acid; 3. 2-methylpropanoic acid; ...
8 SHS Ch 8 Lecture shs_ch_8_lecture_2012
... 1. Combustion Reactions Combustion reactions occur when a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen gas. This is also called burning!!! In order to burn something you need the 3 things in the “fire ...
... 1. Combustion Reactions Combustion reactions occur when a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen gas. This is also called burning!!! In order to burn something you need the 3 things in the “fire ...
Lesson 9 Review Teacher`s Copy
... 3.2.j. An electrochemical cell can be either voltaic or electrolytic. In an electrochemical cell, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode. (3) 3.2.k. A voltaic cell spontaneously converts chemical energy to electrical energy. (5) 3.2.h. A half-reaction can be written to represent ...
... 3.2.j. An electrochemical cell can be either voltaic or electrolytic. In an electrochemical cell, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode. (3) 3.2.k. A voltaic cell spontaneously converts chemical energy to electrical energy. (5) 3.2.h. A half-reaction can be written to represent ...
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... + Cl2 2NaCl Metals react with hydrogen to form metal hydride This reaction takes place only for most reactive metals. 2Na(s) + H2(g) 2NaH(s) ...
... + Cl2 2NaCl Metals react with hydrogen to form metal hydride This reaction takes place only for most reactive metals. 2Na(s) + H2(g) 2NaH(s) ...
29.2 Chemical Bonds
... A chemical bond forms when atoms exchange or share electrons. Most of the properties of substances come from how they form chemical bonds with other substances. ...
... A chemical bond forms when atoms exchange or share electrons. Most of the properties of substances come from how they form chemical bonds with other substances. ...
Document
... A chemical bond forms when atoms exchange or share electrons. Most of the properties of substances come from how they form chemical bonds with other substances. ...
... A chemical bond forms when atoms exchange or share electrons. Most of the properties of substances come from how they form chemical bonds with other substances. ...
Spring 2013 Semester Exam Study Guide (Bonding, Nomenclature
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
Lecture 7
... as base: BeO(s) + 2H3O+(aq) → Be2+(aq) + 3H2O(l) as acid: BeO(s) + 2OH-(aq) + H2O(l) → Be(OH)4-(aq) 2. Beryllium chloride forms a layer lattice rather than an ionic one. In this way it is like aluminium chloride. Beryllium and aluminium are diagonal neighbors in the periodic table and this is an exa ...
... as base: BeO(s) + 2H3O+(aq) → Be2+(aq) + 3H2O(l) as acid: BeO(s) + 2OH-(aq) + H2O(l) → Be(OH)4-(aq) 2. Beryllium chloride forms a layer lattice rather than an ionic one. In this way it is like aluminium chloride. Beryllium and aluminium are diagonal neighbors in the periodic table and this is an exa ...
chm 434f/1206f solid state materials chemistry
... SHAPE, SIZE AND DEFECTS ARE EVERYTHING! • Form or morphology and physical size of product controls synthesis method of choice and potential utility • Single crystal, phase pure, defect free solids - do not exist and if they did not likely of much interest! • Single crystal (SC) that has been defect ...
... SHAPE, SIZE AND DEFECTS ARE EVERYTHING! • Form or morphology and physical size of product controls synthesis method of choice and potential utility • Single crystal, phase pure, defect free solids - do not exist and if they did not likely of much interest! • Single crystal (SC) that has been defect ...
AP Chem
... If this reaction occurs at STP, approximately how many liters of O2 is required to produce 70g of FeO? A. 22 B. 33 C. 44 D. 55 E. 66 19. A beaker containing 150ml of .2M Pb(NO3)2 is added to a beaker containing 50ml of .2M MgCl2. What is the final concentration of Pb2+ ions in the solution? A. .2M B ...
... If this reaction occurs at STP, approximately how many liters of O2 is required to produce 70g of FeO? A. 22 B. 33 C. 44 D. 55 E. 66 19. A beaker containing 150ml of .2M Pb(NO3)2 is added to a beaker containing 50ml of .2M MgCl2. What is the final concentration of Pb2+ ions in the solution? A. .2M B ...
Stage 2 Chemistry Intended Student Learning 2014
... chemistry of the environment. The elemental chemistry component of the topic focuses on the periodic table and the concept of electronegativity; together these underlie most of the other topics in this subject outline. The environmental chemistry component focuses on a small number of inorganic mole ...
... chemistry of the environment. The elemental chemistry component of the topic focuses on the periodic table and the concept of electronegativity; together these underlie most of the other topics in this subject outline. The environmental chemistry component focuses on a small number of inorganic mole ...
Students know
... a. Students know the rate of reaction is the decrease in concentration of reactants or the increase in concentration of products with time. b. Students know how reaction rates depend on such factors as concentration, temperature, and pressure. c. Students know the role a catalyst plays in increasing ...
... a. Students know the rate of reaction is the decrease in concentration of reactants or the increase in concentration of products with time. b. Students know how reaction rates depend on such factors as concentration, temperature, and pressure. c. Students know the role a catalyst plays in increasing ...
final review cp2 1213 by chapter
... 1.Which of the following explains why methane (CH4) has a boiling point of – 161 °C and octane (C8H18) has a boiling point of 125.6 °C. A.the London dispersion forces are stronger in methane B.the hydrogen bonds are stronger in octane C.octane can hydrogen bond and methane cannot D.the hydrogen bond ...
... 1.Which of the following explains why methane (CH4) has a boiling point of – 161 °C and octane (C8H18) has a boiling point of 125.6 °C. A.the London dispersion forces are stronger in methane B.the hydrogen bonds are stronger in octane C.octane can hydrogen bond and methane cannot D.the hydrogen bond ...
Types of Changes in Matter
... If an element appears more than once per side, balance it last. Balance polyatomic ions as single units. “1 SO4” instead of “1 S” and “4 O” ...
... If an element appears more than once per side, balance it last. Balance polyatomic ions as single units. “1 SO4” instead of “1 S” and “4 O” ...
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
... standard state at T is formed from the corresponding separated elements at T, each element being in its reference form. - The reference form (or reference phase) of an element at T is usually taken as the form of the element that is most stable at T and 1-bar pressure. ...
... standard state at T is formed from the corresponding separated elements at T, each element being in its reference form. - The reference form (or reference phase) of an element at T is usually taken as the form of the element that is most stable at T and 1-bar pressure. ...
1A - The changing atom History of the atom • The model of the atom
... Oxidation and reduction must occur simultaneously as all reactions involve a movement of electrons. These reactions are given the shorthand term of REDOX reactions. As they involve REDuction and OXidation Redox reactions can now be applied to reaction that do not involve oxygen or hydrogen: ...
... Oxidation and reduction must occur simultaneously as all reactions involve a movement of electrons. These reactions are given the shorthand term of REDOX reactions. As they involve REDuction and OXidation Redox reactions can now be applied to reaction that do not involve oxygen or hydrogen: ...
What is Thermodynamics?
... measure of how much energy is dispersed, per unit temperature, in any process. This energy is not available to do work. In a reversible process ...
... measure of how much energy is dispersed, per unit temperature, in any process. This energy is not available to do work. In a reversible process ...
A NOVEL BIOCHEMICAL METHOD FOR PRODUCTION OF AN ANTIBACTERIAL DRUG
... gallic acid produces 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid which is then reduced to aldehyde. This process is common for both conventional and novel processes. Conventionally the compound 3,4,5 trimethoxybenzaldehyde is produced by chemical methods like reduction of 3,4,5triethoxybenzoilchloride by modified ...
... gallic acid produces 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid which is then reduced to aldehyde. This process is common for both conventional and novel processes. Conventionally the compound 3,4,5 trimethoxybenzaldehyde is produced by chemical methods like reduction of 3,4,5triethoxybenzoilchloride by modified ...
Document
... The study of chemical reactions and physical behavior that may occur to the reaction of benzophenone with isopropyl alcohol and catalysis amount of glacial acetic acid under the influence of photochemical effects of visible sun light, IR light, laser irradiation or mixing of IR and sun light using f ...
... The study of chemical reactions and physical behavior that may occur to the reaction of benzophenone with isopropyl alcohol and catalysis amount of glacial acetic acid under the influence of photochemical effects of visible sun light, IR light, laser irradiation or mixing of IR and sun light using f ...
Topic 3: Periodicity
... increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove a third electron). In the higher oxidation states the elements usually not exist as a free metal ions, but covalently bonded or as a oxyanions (MnO4-). ...
... increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove a third electron). In the higher oxidation states the elements usually not exist as a free metal ions, but covalently bonded or as a oxyanions (MnO4-). ...
summer fun - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... b) The leading subscript (lower left) is the atomic number or proton number. c) The trailing superscript (upper right) is the charge or the number of protons (atomic number) minus the number of electrons. The sign (+ or -) always must be included. The number is zero for a neutral atom, but the zero ...
... b) The leading subscript (lower left) is the atomic number or proton number. c) The trailing superscript (upper right) is the charge or the number of protons (atomic number) minus the number of electrons. The sign (+ or -) always must be included. The number is zero for a neutral atom, but the zero ...
Mole Equation Homework Hint: Start equations with the numbers
... 3. Iron (III) oxide is formed when iron combines with oxygen. How many grams of Fe2O3 are formed when 16.7 g of Fe reacts completely with oxygen? 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) --> 2Fe2 O3(s) ...
... 3. Iron (III) oxide is formed when iron combines with oxygen. How many grams of Fe2O3 are formed when 16.7 g of Fe reacts completely with oxygen? 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) --> 2Fe2 O3(s) ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.