Comparing Free Energies
... (5.6), together with the condition DGrxn < 0, makes explicit the competition between energetic (DHrxn) and entropic factors (DSrxn) in determining how thermodynamically favorable a process is at a given temperature. Based on Eq. (5.6) we can predict that processes for which DHrxn< 0 and DSrxn > 0 wi ...
... (5.6), together with the condition DGrxn < 0, makes explicit the competition between energetic (DHrxn) and entropic factors (DSrxn) in determining how thermodynamically favorable a process is at a given temperature. Based on Eq. (5.6) we can predict that processes for which DHrxn< 0 and DSrxn > 0 wi ...
NC PowerPoints - Taylor High School
... pentyl ethanoate is used in nail varnish for example. Ethyl ethanoate is one of a number of solvents used to extract caffeine from coffee and tea. De-caffeinated products produced with ethyl ethanoate are often described on the packaging as "naturally decaffeinated" because ethyl ethanoate is a chem ...
... pentyl ethanoate is used in nail varnish for example. Ethyl ethanoate is one of a number of solvents used to extract caffeine from coffee and tea. De-caffeinated products produced with ethyl ethanoate are often described on the packaging as "naturally decaffeinated" because ethyl ethanoate is a chem ...
Group II Elements - Innovative Education.org
... The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions such as this, small and highly charged, have a high charge density and the charge density of the Be2+ ion is very high indeed. As a consequence of this the properties of beryllium and its compounds ar ...
... The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions such as this, small and highly charged, have a high charge density and the charge density of the Be2+ ion is very high indeed. As a consequence of this the properties of beryllium and its compounds ar ...
C:\Documents and Settings\mrh70950\My Documents
... C. Hybrid atomic orbitals and rehybridization–reconciling VSEPR and MO’s 1. sp3 orbitals a. Linear, head-on overlap of two atomic orbitals generates a σ bond b. sp3-hybridization of tetrahedral C atoms in molecules c. Orbital overlap diagrams of molecules 2. sp2 orbitals a. Linear, head-on overlap o ...
... C. Hybrid atomic orbitals and rehybridization–reconciling VSEPR and MO’s 1. sp3 orbitals a. Linear, head-on overlap of two atomic orbitals generates a σ bond b. sp3-hybridization of tetrahedral C atoms in molecules c. Orbital overlap diagrams of molecules 2. sp2 orbitals a. Linear, head-on overlap o ...
Chemistry Standard Course of Study -- Detailed - UNCG GK-12
... Explain how metallic bonding determines the characteristics of metals: high MP, high BP, high conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster. Students should be able to: ...
... Explain how metallic bonding determines the characteristics of metals: high MP, high BP, high conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster. Students should be able to: ...
Enzymes
... mechanical model for the coupling of oxidation-reduction reactions. [Note: Figure illustrates normal direction of electron ...
... mechanical model for the coupling of oxidation-reduction reactions. [Note: Figure illustrates normal direction of electron ...
Chapter 8 - profpaz.com
... Stoichiometry is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation. Stoichiometry allows chemists to predict how much of a reactant is necessary to form a given amount of product or how much of a reactant is required to completely react with another rea ...
... Stoichiometry is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation. Stoichiometry allows chemists to predict how much of a reactant is necessary to form a given amount of product or how much of a reactant is required to completely react with another rea ...
Chapter 4 Quantities of Reactants and Products 4.1 Chemical
... 4.7 Percent Composition and Empirical Formulas (p. 150) In a combustion analysis of a compound containing carbon and hydrogen, the compound reacts with oxygen and all of the carbon in the compound is converted to carbon dioxide and the hydrogen in the compound is converted to water. 2 C4H10(g) + 13 ...
... 4.7 Percent Composition and Empirical Formulas (p. 150) In a combustion analysis of a compound containing carbon and hydrogen, the compound reacts with oxygen and all of the carbon in the compound is converted to carbon dioxide and the hydrogen in the compound is converted to water. 2 C4H10(g) + 13 ...
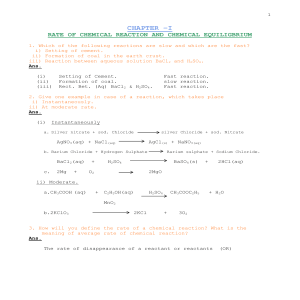
Complete the following equations
... The reaction between nitrogen and chlorine gas produces nitrogen trichloride, NCl3, as the sole product. However, reactions between phosphorus, Arsenic, and antimony with chlorine gas will produce both trichloride, MCl3, and pentachloride compounds (MCl5). Explain why nitrogen (a member of Group 5A ...
... The reaction between nitrogen and chlorine gas produces nitrogen trichloride, NCl3, as the sole product. However, reactions between phosphorus, Arsenic, and antimony with chlorine gas will produce both trichloride, MCl3, and pentachloride compounds (MCl5). Explain why nitrogen (a member of Group 5A ...
Saturday Study Session 1 1st Class Reactions
... 2003B Answer the following questions that relate to chemical reactions. (a) Iron(III) oxide can be reduced with carbon monoxide according to the following equation. Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g) A 16.2 L sample of CO(g) at 1.50 atm and 200.°C is combined with 15.39 g of Fe2O3(s). (i) How m ...
... 2003B Answer the following questions that relate to chemical reactions. (a) Iron(III) oxide can be reduced with carbon monoxide according to the following equation. Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g) A 16.2 L sample of CO(g) at 1.50 atm and 200.°C is combined with 15.39 g of Fe2O3(s). (i) How m ...
Chemical Reactions
... the reactants with the energy of the products. Enthalpy is a measure of internal energy. So, when you calculate the difference between the enthalpy of the products and the enthalpy of the reactants, you find the enthalpy change (∆H), which can be represented mathematically as: ΔH = energy used in re ...
... the reactants with the energy of the products. Enthalpy is a measure of internal energy. So, when you calculate the difference between the enthalpy of the products and the enthalpy of the reactants, you find the enthalpy change (∆H), which can be represented mathematically as: ΔH = energy used in re ...
19a - The BOD
... “Dissolved oxygen” is there. It is a measure of how much oxygen is dissolved in a water sample. It is a measure of oxygen content. BOD is the amount of oxygen that would be consumed to completely decompose the organic matter in a water sample. It is not an indication of oxygen content. It is an indi ...
... “Dissolved oxygen” is there. It is a measure of how much oxygen is dissolved in a water sample. It is a measure of oxygen content. BOD is the amount of oxygen that would be consumed to completely decompose the organic matter in a water sample. It is not an indication of oxygen content. It is an indi ...
Starter S-30
... How many moles of NH3 would be produced? For every 1 mole of N2, 2 moles of NH3 ...
... How many moles of NH3 would be produced? For every 1 mole of N2, 2 moles of NH3 ...
View PDF
... ____ 23. An active metal and a halogen react to form a(n) a. salt. c. acid. b. hydroxide. d. oxide. ____ 24. In the equation 2Al(s) + 3Fe(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) → 3Fe(s) + 2Al(NO 3 ) 3 (aq), iron has been replaced by a. nitrate. c. aluminum. b. water. d. nitrogen. ____ 25. If a certain metal is placed in an ...
... ____ 23. An active metal and a halogen react to form a(n) a. salt. c. acid. b. hydroxide. d. oxide. ____ 24. In the equation 2Al(s) + 3Fe(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) → 3Fe(s) + 2Al(NO 3 ) 3 (aq), iron has been replaced by a. nitrate. c. aluminum. b. water. d. nitrogen. ____ 25. If a certain metal is placed in an ...
Subject Materials for Chemistry
... 27. How is steel manufactured by Bessemer process? Ans: For fig ref.page number 22 fig.number2.6. Steel is manufactured from pig iron in a Bessemer converter, which is a pear shaped furnace lined inside with silicon. Molten pig iron is taken in Bessemer converter is heated with a hot blast of air. O ...
... 27. How is steel manufactured by Bessemer process? Ans: For fig ref.page number 22 fig.number2.6. Steel is manufactured from pig iron in a Bessemer converter, which is a pear shaped furnace lined inside with silicon. Molten pig iron is taken in Bessemer converter is heated with a hot blast of air. O ...
Exam No. 1
... This element will combine with the phosphate ion (PO43-) to form a compound with the formula: **(a) XPO4 (c) X2PO4 ...
... This element will combine with the phosphate ion (PO43-) to form a compound with the formula: **(a) XPO4 (c) X2PO4 ...
Chapter 18 review
... a. It is exothermic. b. It takes place at a rapid rate. c. It results in increased disorder of the system. d. It releases free energy. ____ 19. Which of the following is true about the combustion of carbon? a. The reaction is spontaneous. b. The reaction is endothermic. c. Enthalpy remains constant. ...
... a. It is exothermic. b. It takes place at a rapid rate. c. It results in increased disorder of the system. d. It releases free energy. ____ 19. Which of the following is true about the combustion of carbon? a. The reaction is spontaneous. b. The reaction is endothermic. c. Enthalpy remains constant. ...
Free response review
... c. The radius of an oxide ion is larger than the radius of an oxygen atom. d. The first ionization energy of aluminum is smaller than the first ionization energy of magnesium e. The third ionization energy of an element is always larger than its second ionization energy 2. Write the formulas to show ...
... c. The radius of an oxide ion is larger than the radius of an oxygen atom. d. The first ionization energy of aluminum is smaller than the first ionization energy of magnesium e. The third ionization energy of an element is always larger than its second ionization energy 2. Write the formulas to show ...
Name__________________________ Honors Chemistry Final
... Label the B-L acid (A), base (B), conjugate acid (CA), and conjugate base (CB) in each of the following reactions. 1. H2SO4(aq) + NH3(aq) HSO4-(aq) + NH4+(aq) 2. HC2H3O2(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) 3. NaHCO3(aq) + HCl(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2CO3(aq) 4. HPO4-2(aq) + H2O(l) H2PO4-(aq) + OH-(a ...
... Label the B-L acid (A), base (B), conjugate acid (CA), and conjugate base (CB) in each of the following reactions. 1. H2SO4(aq) + NH3(aq) HSO4-(aq) + NH4+(aq) 2. HC2H3O2(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) 3. NaHCO3(aq) + HCl(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2CO3(aq) 4. HPO4-2(aq) + H2O(l) H2PO4-(aq) + OH-(a ...
1 Intro / Review : Chemical Kinetics
... Also, the orientations of the reactant molecules during the collision must allow for the rearrangement of reactant bonds to form product bonds. Essential knowledge 4.B.3: A successful collision can be viewed as following a reaction path with an associated energy profile. Enduring understanding 4.D: ...
... Also, the orientations of the reactant molecules during the collision must allow for the rearrangement of reactant bonds to form product bonds. Essential knowledge 4.B.3: A successful collision can be viewed as following a reaction path with an associated energy profile. Enduring understanding 4.D: ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.