PRE AP CHEMISTRY REVIEW PROBLEMS NON COLLEGE
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
Chapters 12 – 20 Practice Problems
... If [A] is doubled, the reaction rate will increase by a factor of 4. The reaction is second order overall. ...
... If [A] is doubled, the reaction rate will increase by a factor of 4. The reaction is second order overall. ...
Belarus, National Final, 2001 (PDF 149K).
... c) Explain why compounds A and B predominantly yield C and D, respectively. d) What type of isomerism is exhibited by compound C at low temperatures? Why are these isomers not observed at ordinary temperatures? e) Draw the structures of the two low-temperature isomers of C in a way that clearly show ...
... c) Explain why compounds A and B predominantly yield C and D, respectively. d) What type of isomerism is exhibited by compound C at low temperatures? Why are these isomers not observed at ordinary temperatures? e) Draw the structures of the two low-temperature isomers of C in a way that clearly show ...
104 Homework Packet - Rogue Community College
... equilibrium to the __________, adding products (or removing reactants) drives the equilibrium to the __________, increasing temperature favors the ___________________ reaction, decreasing temperature favors the ____________________ reaction, increasing pressure shifts the reaction toward ___________ ...
... equilibrium to the __________, adding products (or removing reactants) drives the equilibrium to the __________, increasing temperature favors the ___________________ reaction, decreasing temperature favors the ____________________ reaction, increasing pressure shifts the reaction toward ___________ ...
acids - WordPress.com
... 6. The solution is left to cool to complete the crystallisation. 7. The residual liquid can be filtered away and the crystals can be carefully collected and rinsed & dried between 2 pieces of filter paper. ...
... 6. The solution is left to cool to complete the crystallisation. 7. The residual liquid can be filtered away and the crystals can be carefully collected and rinsed & dried between 2 pieces of filter paper. ...
Review on N acylation reaction
... Usually hydrochloride acceptor should be a base which is stronger than the base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number of solvents. In some cases the selectivity of acyla ...
... Usually hydrochloride acceptor should be a base which is stronger than the base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number of solvents. In some cases the selectivity of acyla ...
Section 7.1 Describing Reactions
... you expect to learn. After reading, state what you learned about each item you listed. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook at the end of your textbook. What I Expect to Learn ...
... you expect to learn. After reading, state what you learned about each item you listed. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook at the end of your textbook. What I Expect to Learn ...
AP Chemistry
... 1213. Although structural isomers C3H7OH and C2H5OCH3 exhibit different properties, which of the following would be expected to be the same for both compounds? (A) Heats of fusion (D) Molecular masses (B) Melting points (E) Heats of vaporization (C) Solubility constants 1250. Which of the following ...
... 1213. Although structural isomers C3H7OH and C2H5OCH3 exhibit different properties, which of the following would be expected to be the same for both compounds? (A) Heats of fusion (D) Molecular masses (B) Melting points (E) Heats of vaporization (C) Solubility constants 1250. Which of the following ...
Introduction to Chemistry and the Metric System
... shared pair of electrons, unshared pair, single bond, double bond, triple bond VSEPR Theory, hybrid orbitals, shapes of molecules, sigma bonds, pi bonds, polarity Intermolecular Forces (in order from weakest to strongest): London Dispersion Forces, dipole-dipole interactions, H-bonding, ionic ...
... shared pair of electrons, unshared pair, single bond, double bond, triple bond VSEPR Theory, hybrid orbitals, shapes of molecules, sigma bonds, pi bonds, polarity Intermolecular Forces (in order from weakest to strongest): London Dispersion Forces, dipole-dipole interactions, H-bonding, ionic ...
Scientific Principles: Chemical Properties
... • Are pure substances consisting of one type of atom • Cannot be broken down or changed into another substance • Combine with other elements to form compounds ...
... • Are pure substances consisting of one type of atom • Cannot be broken down or changed into another substance • Combine with other elements to form compounds ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... If a reaction has an equilibrium constant (Keq) just greater than 1, how do we interpret that information? A catalyst works by ____. If sulfur dioxide and oxygen can be made into sulfur trioxide, what is the reverse reaction? What is the effect of adding more water to the following equilibrium react ...
... If a reaction has an equilibrium constant (Keq) just greater than 1, how do we interpret that information? A catalyst works by ____. If sulfur dioxide and oxygen can be made into sulfur trioxide, what is the reverse reaction? What is the effect of adding more water to the following equilibrium react ...
Chemistry - Edgbarrow School
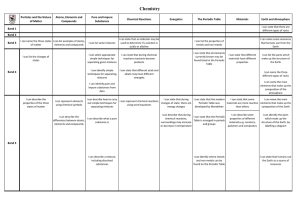
... I can describe how to carry I can state that during I can state that the modern I can state that some I can name the main I can represent chemical reactions out simple techniques for changes of state, there are Periodic Table was materials are more reactive elements that make up the using word equat ...
... I can describe how to carry I can state that during I can state that the modern I can state that some I can name the main I can represent chemical reactions out simple techniques for changes of state, there are Periodic Table was materials are more reactive elements that make up the using word equat ...
2008 local exam - American Chemical Society
... (A) The initial precipitate will contain CaF2 only. (B) The initial precipitate will contain MgF2 only. (C) The initial precipitate will contain both CaF2 and MgF2 with more CaF2. (D) The initial precipitate will contain both CaF2 and MgF2 with more MgF2. 37. Which range includes the average oxidati ...
... (A) The initial precipitate will contain CaF2 only. (B) The initial precipitate will contain MgF2 only. (C) The initial precipitate will contain both CaF2 and MgF2 with more CaF2. (D) The initial precipitate will contain both CaF2 and MgF2 with more MgF2. 37. Which range includes the average oxidati ...
File
... 47. The last step in the production of nitric acid is the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with water. 3NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2HNO3 (aq) + NO (g) How many grams of nitrogen dioxide must react with water to produce 5.00 x 1022 molecules of nitrogen monoxide? 48. How are mole ratios used in chemical calcula ...
... 47. The last step in the production of nitric acid is the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with water. 3NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2HNO3 (aq) + NO (g) How many grams of nitrogen dioxide must react with water to produce 5.00 x 1022 molecules of nitrogen monoxide? 48. How are mole ratios used in chemical calcula ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
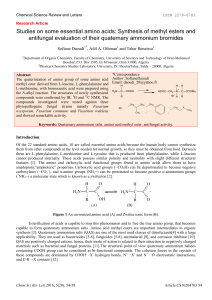
... All the chemicals and reagents were obtained from Sigma Aldrich and Biochem. Melting points were measured using BUCHI 540 apparatus and are uncorrected, IR spectra were recorded as potassium bromide pellets on a Shimadzu 8300 spectrophotometer (ῡ max in cm−1), The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorde ...
... All the chemicals and reagents were obtained from Sigma Aldrich and Biochem. Melting points were measured using BUCHI 540 apparatus and are uncorrected, IR spectra were recorded as potassium bromide pellets on a Shimadzu 8300 spectrophotometer (ῡ max in cm−1), The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorde ...
1 - Cathedral High School
... 3.2.1 Describe and explain the periodic trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed i ...
... 3.2.1 Describe and explain the periodic trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed i ...
Unit A Review Questions
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
About writing chemical equations ppt
... to take the place of one of the elements of that compound. A + BC B + AC Zn + 2HCl H2 + ZnCl2 Note: Activity series table helps to predict which substances (elements) will be able to replace various other substances. ...
... to take the place of one of the elements of that compound. A + BC B + AC Zn + 2HCl H2 + ZnCl2 Note: Activity series table helps to predict which substances (elements) will be able to replace various other substances. ...
Chemistry: Chemical Reactions Notes STOP
... 1. If you are given a word equation with only reactants finish the word equation by writing the chemical names of the products. Remember positive ions keep the same name as their neutral element ( ...
... 1. If you are given a word equation with only reactants finish the word equation by writing the chemical names of the products. Remember positive ions keep the same name as their neutral element ( ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... C is smaller than is Si. Therefore, C can form pi bonds to O; Si cannot form pi bonds to O. In both cases, the C or Si will form a total of four bonds. In the case of CO2, the pi bonds are strong enough that the entropic favorability of forming small molecules drives formation of the monomeric CO2 m ...
... C is smaller than is Si. Therefore, C can form pi bonds to O; Si cannot form pi bonds to O. In both cases, the C or Si will form a total of four bonds. In the case of CO2, the pi bonds are strong enough that the entropic favorability of forming small molecules drives formation of the monomeric CO2 m ...
Objective 3 Stations Student Sheet
... 1. How is the periodic table organized? 2. What family of elements has valence electrons at two energy levels? 3. What are the elements called that are between metals and nonmetals? 4. Which family of nonmetals has seven valence electrons? 5. What are some properties of noble gases? 6. What is anoth ...
... 1. How is the periodic table organized? 2. What family of elements has valence electrons at two energy levels? 3. What are the elements called that are between metals and nonmetals? 4. Which family of nonmetals has seven valence electrons? 5. What are some properties of noble gases? 6. What is anoth ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.