MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
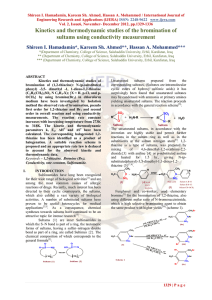
... The power law model correlates reaction with two basic parameters: the reaction rate constant and the order (participating species) The general expression for the power law model for an elementary reaction AB is written as: -rA = kCAn (where n is 1 ) This expression can be applicable to complex rea ...
... The power law model correlates reaction with two basic parameters: the reaction rate constant and the order (participating species) The general expression for the power law model for an elementary reaction AB is written as: -rA = kCAn (where n is 1 ) This expression can be applicable to complex rea ...
GQ2613291336
... Where Lt: conductivity of the dissolved HBr gas at any time (t). L∞: conductivity of the dissolved HBr gas at infinite time (t∞). t: time in sec. k: rate constant of reaction in sec-1. (L∞-Lt): concentration of product at any time. The value of k for each temperature was evaluated from the slope of ...
... Where Lt: conductivity of the dissolved HBr gas at any time (t). L∞: conductivity of the dissolved HBr gas at infinite time (t∞). t: time in sec. k: rate constant of reaction in sec-1. (L∞-Lt): concentration of product at any time. The value of k for each temperature was evaluated from the slope of ...
physical setting chemistry
... Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is one gas produced when fossil fuels are burned. When this gas reacts with water in the atmosphere, an acid is produced forming acid rain. The pH of the water in a lake changes when acid rain collects in the lake. Two samples of the same rainwater are tested using two indicator ...
... Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is one gas produced when fossil fuels are burned. When this gas reacts with water in the atmosphere, an acid is produced forming acid rain. The pH of the water in a lake changes when acid rain collects in the lake. Two samples of the same rainwater are tested using two indicator ...
Fundamentals
... Joseph Gay-Lussac made two key observations involving gas-phase reactions that would ultimately lead to combining ratios: 1. Twovolumes of hydrogen react with one volume of oxygen to yield two volumes of water. 2. One volume of hydrogen reacts with one volume of chlorine to yield two volumes of hydr ...
... Joseph Gay-Lussac made two key observations involving gas-phase reactions that would ultimately lead to combining ratios: 1. Twovolumes of hydrogen react with one volume of oxygen to yield two volumes of water. 2. One volume of hydrogen reacts with one volume of chlorine to yield two volumes of hydr ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... the quantum mechanical model, we can only define the probability of finding an electron at a given location. When electrons drop from higher energy levels to lower ones, they give off energy in the form of light. The color of light emitted depends on the energy difference between the levels. The gre ...
... the quantum mechanical model, we can only define the probability of finding an electron at a given location. When electrons drop from higher energy levels to lower ones, they give off energy in the form of light. The color of light emitted depends on the energy difference between the levels. The gre ...
Energetics - WordPress.com
... Ba(OH)2.8H2O(s) + 2NH4Cl(s) → BaCl2.2H2O(s) + 2NH3(g/aq) + 8H2O(l) ...
... Ba(OH)2.8H2O(s) + 2NH4Cl(s) → BaCl2.2H2O(s) + 2NH3(g/aq) + 8H2O(l) ...
mc_ch08 - MrBrownsChem1LCHS
... Significance of a Chemical Equation • Some of the quantitative information revealed by a chemical equation includes 1. The coefficients of a chemical reaction indicate relative, not absolute, amounts of reactants and ...
... Significance of a Chemical Equation • Some of the quantitative information revealed by a chemical equation includes 1. The coefficients of a chemical reaction indicate relative, not absolute, amounts of reactants and ...
C:\SUBJECTS\SUBJECTS\Chemistry
... E. A hydrocarbon. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A. copper (11) ion can be reduced to copper (1) ion by hydrochloric acid and zinc. B. Sodium metal dissolves in water giving oxygen C. Nitrogen is insoluble in water D. Carbondioxide is soluble in water E. Lead has a higher atomic weight ...
... E. A hydrocarbon. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A. copper (11) ion can be reduced to copper (1) ion by hydrochloric acid and zinc. B. Sodium metal dissolves in water giving oxygen C. Nitrogen is insoluble in water D. Carbondioxide is soluble in water E. Lead has a higher atomic weight ...
Enthalpy Change of Hydrogen Bond Formation between
... digital multimeter, was passed through the resistor for a measured period of time. The total area under a recorded curve was then measured with a K & E compensating polar planimeter. The millicalories of heat evolved were then calculated for a series of current inputs. A bucket-type three-tube assem ...
... digital multimeter, was passed through the resistor for a measured period of time. The total area under a recorded curve was then measured with a K & E compensating polar planimeter. The millicalories of heat evolved were then calculated for a series of current inputs. A bucket-type three-tube assem ...
Fundamental Knowledge for Analysis of Chemical Reactor
... What is a chemical reaction? A chemical species is composed of atoms The chemical identity of a chemical species: kind, number,structure and configuration example: water, methane and ethylene Identity response for the chemical and physical properties: nicotine fits Difference between structure and c ...
... What is a chemical reaction? A chemical species is composed of atoms The chemical identity of a chemical species: kind, number,structure and configuration example: water, methane and ethylene Identity response for the chemical and physical properties: nicotine fits Difference between structure and c ...
20.2 Oxidation Numbers
... Many parts of your car’s body are made of steel, an iron alloy. The salt can cause the metal to corrode, or rust, faster than it would otherwise because when mixed with water, the salt creates a conductive solution that allows electrons to transfer more easily. ...
... Many parts of your car’s body are made of steel, an iron alloy. The salt can cause the metal to corrode, or rust, faster than it would otherwise because when mixed with water, the salt creates a conductive solution that allows electrons to transfer more easily. ...
TEKS 8 - UNT College of Education
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
Unfamiliar Oxidation States and Tkeir Stabilization
... almost entirely devoid of chemical significance. With metals, on the other hand, where constancy of covalence is relatively uncommon, the oxidation-state concept ordinarily possesses a true chemical meaning in the sense that conversion to well-defined lower or higher oxidation states involves reacti ...
... almost entirely devoid of chemical significance. With metals, on the other hand, where constancy of covalence is relatively uncommon, the oxidation-state concept ordinarily possesses a true chemical meaning in the sense that conversion to well-defined lower or higher oxidation states involves reacti ...
Electricity Unit
... Recall that the charged parts of atoms are electrons and protons. When two protons come close together, they push one another apart. In other words, the protons repel each other. But if a proton and an electron come close together, they attract one another. Why do protons repel protons but attract e ...
... Recall that the charged parts of atoms are electrons and protons. When two protons come close together, they push one another apart. In other words, the protons repel each other. But if a proton and an electron come close together, they attract one another. Why do protons repel protons but attract e ...
Section 5
... Soft-soft interaction creates bonding MO that is significantly more stable (lower energy) than MO of base (HOMO) or acid (LUMO) ...
... Soft-soft interaction creates bonding MO that is significantly more stable (lower energy) than MO of base (HOMO) or acid (LUMO) ...
STUDY OF ELECTRODE KINETICS AND THERMODYNAMIC PARAMETERS OF Research Article
... This reaction needs about 0.5 V less negative than that required for the reduction of isonicotinic acid i.e. the potential that is very close to the reduction potential of isoniazid. Because of this reason, reaction 1 & 3 gives a single wave and reaction 2 give a separate wave. In basic medium (pH 8 ...
... This reaction needs about 0.5 V less negative than that required for the reduction of isonicotinic acid i.e. the potential that is very close to the reduction potential of isoniazid. Because of this reason, reaction 1 & 3 gives a single wave and reaction 2 give a separate wave. In basic medium (pH 8 ...
Revised Syllabus - M. Sc. First Year - Chemistry
... Student can get requisite credits from the concerned school where he is mutually permitted on terms mutually agreed to complete the same and be eligible to appear for term end examination. ...
... Student can get requisite credits from the concerned school where he is mutually permitted on terms mutually agreed to complete the same and be eligible to appear for term end examination. ...
«Классы и номенклатура неорганических соединений»
... particles, which 1 mole of substance consist B. 6,02 ∙ 1022 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist C. 6,02 ∙ 1020 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist D. 6,02 ∙ 1019 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 kg of substanc ...
... particles, which 1 mole of substance consist B. 6,02 ∙ 1022 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist C. 6,02 ∙ 1020 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist D. 6,02 ∙ 1019 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 kg of substanc ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.