Electric Potential
... If the Higgs field did not exist... (A) we would have more mass (B) we would have less mass (C) we would have no mass (D) the top quark would become larger than the electron (E) nothing would change ...
... If the Higgs field did not exist... (A) we would have more mass (B) we would have less mass (C) we would have no mass (D) the top quark would become larger than the electron (E) nothing would change ...
Modeling the extraction of sputtered metal from Linköping University Post Print
... The hollow cathode discharge has two important features. First, being trapped inside the hollow cathode, ions participate in the sputtering process more efficiently than in the more open magnetron discharge geometry, which makes it possible to get a super saturated metal vapor in the hollow cathode ...
... The hollow cathode discharge has two important features. First, being trapped inside the hollow cathode, ions participate in the sputtering process more efficiently than in the more open magnetron discharge geometry, which makes it possible to get a super saturated metal vapor in the hollow cathode ...
Solution Preparation Final Goueth
... (D) The average velocity of the O2 molecules is one-half that of the CH4 molecules. 65. 168.00 J of energy are added to a sample of gallium initially at 25.0 °C, the temperature rises to 38.0 °C. What is the volume of the sample? Data for Gallium, Ga specific heat 0.372 J g¯1 °C¯1 ...
... (D) The average velocity of the O2 molecules is one-half that of the CH4 molecules. 65. 168.00 J of energy are added to a sample of gallium initially at 25.0 °C, the temperature rises to 38.0 °C. What is the volume of the sample? Data for Gallium, Ga specific heat 0.372 J g¯1 °C¯1 ...
Questions - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Propane is used as a fuel. How much energy will be produced when 1kg of propane is completely burnt? 1 ...
... Propane is used as a fuel. How much energy will be produced when 1kg of propane is completely burnt? 1 ...
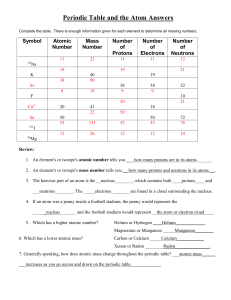
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... stoichiometry problems, I would highly suggest consulting this section of the site before answering these questions. When doing stoichiometry problems, people are frequently worried by statements such as “if you have an excess of (compound X)”. This statement shouldn’t worry you… what it really mean ...
... stoichiometry problems, I would highly suggest consulting this section of the site before answering these questions. When doing stoichiometry problems, people are frequently worried by statements such as “if you have an excess of (compound X)”. This statement shouldn’t worry you… what it really mean ...
Chemistry 1411 Practice Exam 1, Chapters 1
... Naturally-occurring copper is composed of 69.17% copper-63 with an atomic weight of 62.9396 amu, and 30.83% of another copper isotope. If the average (weighted average) atomic weight of copper is 63.546 amu, what is the atomic weight of the other copper isotope? (3 pts) ...
... Naturally-occurring copper is composed of 69.17% copper-63 with an atomic weight of 62.9396 amu, and 30.83% of another copper isotope. If the average (weighted average) atomic weight of copper is 63.546 amu, what is the atomic weight of the other copper isotope? (3 pts) ...
1411 Practice Exam 1
... Naturally-occurring copper is composed of 69.17% copper-63 with an atomic weight of 62.9396 amu, and 30.83% of another copper isotope. If the average (weighted average) atomic weight of copper is 63.546 amu, what is the atomic weight of the other copper isotope? (3 pts) ...
... Naturally-occurring copper is composed of 69.17% copper-63 with an atomic weight of 62.9396 amu, and 30.83% of another copper isotope. If the average (weighted average) atomic weight of copper is 63.546 amu, what is the atomic weight of the other copper isotope? (3 pts) ...
Chapter 14 Acids and Bases
... The difference between dissociation and ionisation • Dissociation refers to a reaction where a molecule or substance breaks apart into smaller units. • The units are not necessarily ions, although this is often the case. • Ionization generally refers to a reaction which forms ions from an uncharged ...
... The difference between dissociation and ionisation • Dissociation refers to a reaction where a molecule or substance breaks apart into smaller units. • The units are not necessarily ions, although this is often the case. • Ionization generally refers to a reaction which forms ions from an uncharged ...
Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Section 8.6 Molecular Polarity) Water is a neutral compound, but the electrons in the covale ...
... oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Section 8.6 Molecular Polarity) Water is a neutral compound, but the electrons in the covale ...
the Main-Group Metals - McQuarrie General Chemistry
... reacts violently with water. The other alkaline-earth metals react more rapidly with water, but the rates of these reactions are still much slower than those for the alkali metals. The alkaline-earth metals burn in oxygen to form MO(s) oxides, which are ionic solids. Magnesium is used as an incendia ...
... reacts violently with water. The other alkaline-earth metals react more rapidly with water, but the rates of these reactions are still much slower than those for the alkali metals. The alkaline-earth metals burn in oxygen to form MO(s) oxides, which are ionic solids. Magnesium is used as an incendia ...
A ---> B
... Rates and Stochiometry In the previous example (A---->B), we had 1:1 stoichiometry. Thus, at any ...
... Rates and Stochiometry In the previous example (A---->B), we had 1:1 stoichiometry. Thus, at any ...
Title Photochemical chlorination of methane Author(s) Tamura, Mikio
... As the reaction velocity is proportional to a power of the intensity of light approaching to 0.5, it is concluded that the reaction chains are terminated principally by the combination of chain carriers between themselves, rather than by such an inhibitor as oxygen or by the wall of the vessel. Now ...
... As the reaction velocity is proportional to a power of the intensity of light approaching to 0.5, it is concluded that the reaction chains are terminated principally by the combination of chain carriers between themselves, rather than by such an inhibitor as oxygen or by the wall of the vessel. Now ...
Heat
... Note we did not take into account the heat capacity of the calorimeter itself, but assumed it was small. For more precise work the heat capacity of the calorimeter would need to be included in the calculations. ...
... Note we did not take into account the heat capacity of the calorimeter itself, but assumed it was small. For more precise work the heat capacity of the calorimeter would need to be included in the calculations. ...
Chapter12
... c. Moles - The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation tells us the number of moles of reactants and products. The equation tells us that 1 mol of N2(g) reacts with 3mol of H2(g) to yield 2 mol of NH3(g). Using this information, we can calculate the amounts of reactants and products. Note: the ...
... c. Moles - The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation tells us the number of moles of reactants and products. The equation tells us that 1 mol of N2(g) reacts with 3mol of H2(g) to yield 2 mol of NH3(g). Using this information, we can calculate the amounts of reactants and products. Note: the ...
Chemistry 1B General Chemistry Laboratory
... you may not be allowed to work. Table of Contents: You must leave several pages blank at the beginning of your notebook for table of contents. That table will list each experiment that has been done and the page number for which it can be found. Experimental Notes and Content: • Title Page: Each exp ...
... you may not be allowed to work. Table of Contents: You must leave several pages blank at the beginning of your notebook for table of contents. That table will list each experiment that has been done and the page number for which it can be found. Experimental Notes and Content: • Title Page: Each exp ...
OCR Gateway Science
... (a) How does the volume of hydrogen produced depend on the mass of magnesium used? (b) Which reactant is limiting? Explain your answer. (Mg = 24) (c) Calculate the initial rate of reaction when 0.08 g of magnesium reacts with 20 cm3 of 2 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid. (d) 1 mole of gas occupies 24 dm3 a ...
... (a) How does the volume of hydrogen produced depend on the mass of magnesium used? (b) Which reactant is limiting? Explain your answer. (Mg = 24) (c) Calculate the initial rate of reaction when 0.08 g of magnesium reacts with 20 cm3 of 2 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid. (d) 1 mole of gas occupies 24 dm3 a ...
Topic 6 Kinetics File
... B. the energy of activation increases with temperature. C. the speed of molecules is dramatically increased with a 10 ºC increase in temperature. D. the fraction of high-energy molecules increases exponentially with temperature. 7. A catalyst will A. alter the mechanism (pathway) of a reaction. B. i ...
... B. the energy of activation increases with temperature. C. the speed of molecules is dramatically increased with a 10 ºC increase in temperature. D. the fraction of high-energy molecules increases exponentially with temperature. 7. A catalyst will A. alter the mechanism (pathway) of a reaction. B. i ...
File
... one system is equal to the energy that goes into the other system. The combined energy of the two systems remains fixed. Energy transfer can occur through either heat exchange or work. 5.B.3 Chemical systems undergo three main processes that change their energy: heating/cooling, phase transitions, ...
... one system is equal to the energy that goes into the other system. The combined energy of the two systems remains fixed. Energy transfer can occur through either heat exchange or work. 5.B.3 Chemical systems undergo three main processes that change their energy: heating/cooling, phase transitions, ...
Chemistry (SPA)
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reactions). ...
... They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reactions). ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.