A comparison of carbon tetrachloride decomposition
... the two types of reactors are strongly related to the construction of the reactors. Barrier discharge reactor in the general case can be considered a cylindrical capacitor, whose capacity can be calculated by the equation: ...
... the two types of reactors are strongly related to the construction of the reactors. Barrier discharge reactor in the general case can be considered a cylindrical capacitor, whose capacity can be calculated by the equation: ...
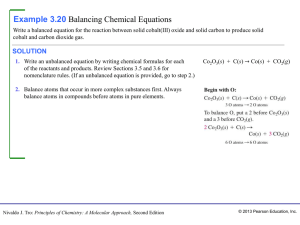
Section 6.3 Balancing Chemical Equations
... 1. Write the reactants as they actually exist before any reaction occurs. Remember that when a salt dissolves, its ions separate. 2. Consider the various solids that could form. To do this, simply exchange the anions of the added salts. 3. Use the solubility rules to decide whether a solid forms and ...
... 1. Write the reactants as they actually exist before any reaction occurs. Remember that when a salt dissolves, its ions separate. 2. Consider the various solids that could form. To do this, simply exchange the anions of the added salts. 3. Use the solubility rules to decide whether a solid forms and ...
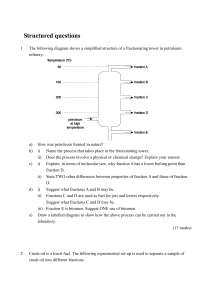
Structured questions
... After the experiment, the student found that there was a layer of oily liquid on the surface of the water in the beaker. Suggest what this oily liquid might be. One of the reactions involved in the cracking of octane gives two hydrocarbons, each containing the same number of carbon atoms. i) Write a ...
... After the experiment, the student found that there was a layer of oily liquid on the surface of the water in the beaker. Suggest what this oily liquid might be. One of the reactions involved in the cracking of octane gives two hydrocarbons, each containing the same number of carbon atoms. i) Write a ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... (E) The cooker forces the water to maintain constant density, allowing for hotter water. 11. A 50.0 mL aliquot of a sulfuric acid solution was treated with barium chloride and the resulting BaSO4 was isolated and weighed. If 0.667 g of BaSO 4 was obtained, what was the molarity of the H2SO4? (A) 0.0 ...
... (E) The cooker forces the water to maintain constant density, allowing for hotter water. 11. A 50.0 mL aliquot of a sulfuric acid solution was treated with barium chloride and the resulting BaSO4 was isolated and weighed. If 0.667 g of BaSO 4 was obtained, what was the molarity of the H2SO4? (A) 0.0 ...
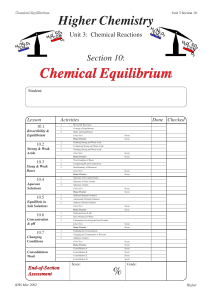
Chemical Equilibrium - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... The strong base will have dissociated completely meaning that all the OH—(aq) ions were available to react with the Fe3+(aq) ions . The weak base is only partially dissociated so less than 1% of the OH—(aq) ions are available at the beginning. However, as the OH—(aq) ions react with Fe3+(aq) they ...
... The strong base will have dissociated completely meaning that all the OH—(aq) ions were available to react with the Fe3+(aq) ions . The weak base is only partially dissociated so less than 1% of the OH—(aq) ions are available at the beginning. However, as the OH—(aq) ions react with Fe3+(aq) they ...
Advanced Chemistry
... (a) Determine the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant, Br2(g) and NO(g). In each case, explain your reasoning or provide calculations to justify your answer. Order of reaction for NO: look at experiments 3 + 4 (keep [Br2] constant). The initial [NO] in run 3 is 2x the initial [NO] of ...
... (a) Determine the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant, Br2(g) and NO(g). In each case, explain your reasoning or provide calculations to justify your answer. Order of reaction for NO: look at experiments 3 + 4 (keep [Br2] constant). The initial [NO] in run 3 is 2x the initial [NO] of ...
CHEM 250Q
... Sodium (Na) reacts with sulfur (S) to form a compound in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one sulfur atom. Element X also reacts with sodium in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one element X atom. Which is most likely the identity of element X? A. ...
... Sodium (Na) reacts with sulfur (S) to form a compound in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one sulfur atom. Element X also reacts with sodium in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one element X atom. Which is most likely the identity of element X? A. ...
Minimum Learning Competencies - Ministry of Education, Ethiopia
... the properties of substances; Explain dispersion forces & give examples of them; Define metallic bonding & explain the properties of metals related to the concept of bonding; Name two chemical bond theories; Explain the VBT & distinguish between the Lewis model ...
... the properties of substances; Explain dispersion forces & give examples of them; Define metallic bonding & explain the properties of metals related to the concept of bonding; Name two chemical bond theories; Explain the VBT & distinguish between the Lewis model ...
CH 17 Study Guide with answer Key
... The solubility of BaSO4 is 1.010–5 mol/L at 298 K. 7. a. This indicates that a precipitate will form. The precipitate will reduce the ion concentrations in the solution until the Ksp expression is ...
... The solubility of BaSO4 is 1.010–5 mol/L at 298 K. 7. a. This indicates that a precipitate will form. The precipitate will reduce the ion concentrations in the solution until the Ksp expression is ...
Document
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
Q1. This question is about the structure of atoms. (a) Choose words
... Complete the four spaces in the passage. The chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. This shows that there is one atom of .......................................... and three atoms of .................................. in each ......................................... of ammonia. These atoms are joined ...
... Complete the four spaces in the passage. The chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. This shows that there is one atom of .......................................... and three atoms of .................................. in each ......................................... of ammonia. These atoms are joined ...
Complexing properties of bivalent and trivalent iron in the system
... of eqn (4) expressing the dependence of redox potential on negative decadic logarithm of the relative concentration of acid. For low pH values and relatively low concentrations of citric acid, some sections parallel to the axis of abscissas appear on the plots, which indicates that an unambiguous bo ...
... of eqn (4) expressing the dependence of redox potential on negative decadic logarithm of the relative concentration of acid. For low pH values and relatively low concentrations of citric acid, some sections parallel to the axis of abscissas appear on the plots, which indicates that an unambiguous bo ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... The first electron affinity of an element is the enthalpy change that occurs when one electron is gained by each atom in a mole of gaseous atoms of the element to give one mole of ions, each with a single negative charge in standard conditions; most common first enthalpies are negative. See table ...
... The first electron affinity of an element is the enthalpy change that occurs when one electron is gained by each atom in a mole of gaseous atoms of the element to give one mole of ions, each with a single negative charge in standard conditions; most common first enthalpies are negative. See table ...
LaBrake, Fundamentals Diagnostic Questions
... 19. All of the following statements are true regarding the nuclear model of the atom, except: a) The positive charge is densely found in the center of the atom, while the negatively charged electrons exist in a diffuse cloud outside the nucleus. b) Most of the space of an atom is empty space. c) The ...
... 19. All of the following statements are true regarding the nuclear model of the atom, except: a) The positive charge is densely found in the center of the atom, while the negatively charged electrons exist in a diffuse cloud outside the nucleus. b) Most of the space of an atom is empty space. c) The ...
1994 Released Exam
... Cu’+ electrolyte was CuS04. (C) The Zn” solutionwas more concentratedthan the Cu” solution. (D) The solutionsin the half-cells had different volumes. (E) The salt bridge containedKC1 as the electrolyte. 37. A sampleof 3.30 gramsof an ideal gas at 15O.O”C and 1.25 atmospherespressurehas a volume of 2 ...
... Cu’+ electrolyte was CuS04. (C) The Zn” solutionwas more concentratedthan the Cu” solution. (D) The solutionsin the half-cells had different volumes. (E) The salt bridge containedKC1 as the electrolyte. 37. A sampleof 3.30 gramsof an ideal gas at 15O.O”C and 1.25 atmospherespressurehas a volume of 2 ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.