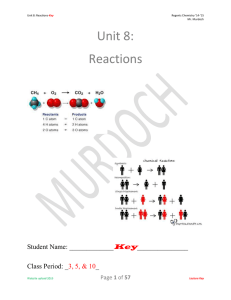
Calculations on the equations reaction
... QUESTIONS FOR INTERVIEW IN CHEMISTRY FOR ENTRANS IN KazNMU ...
... QUESTIONS FOR INTERVIEW IN CHEMISTRY FOR ENTRANS IN KazNMU ...
Questions
... These compounds can also be distinguished from one another by the use of concentrated sulphuric acid. (i) ...
... These compounds can also be distinguished from one another by the use of concentrated sulphuric acid. (i) ...
Unit 8: Reactions
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in society
... with the chemicals takes place. Part of this involves all chemicals being clearly labelled with an EU Hazard symbol (some of these are shown below). ...
... with the chemicals takes place. Part of this involves all chemicals being clearly labelled with an EU Hazard symbol (some of these are shown below). ...
CSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers.indd
... regular way, whereas those in liquid water have small spaces between them and are randomly arranged, and those in steam have large spaces between them and are randomly arranged. The particles in ice vibrate in their fixed positions, whereas those in liquid water move slowly past each other and those ...
... regular way, whereas those in liquid water have small spaces between them and are randomly arranged, and those in steam have large spaces between them and are randomly arranged. The particles in ice vibrate in their fixed positions, whereas those in liquid water move slowly past each other and those ...
Solutes
... • These are, by definition, strong electrolytes and exist totally as ions in aqueous solution. ...
... • These are, by definition, strong electrolytes and exist totally as ions in aqueous solution. ...
Final Exam Review Notes
... – eg. changing shape, changing physical state, dissolving – eg. boiling water, melting ice, hammering gold into foil chemical change or reaction: – a process that changes the chemical composition (and thus the chemical formula) of starting materials (reactants) — eg. oxidation of matter (burning or ...
... – eg. changing shape, changing physical state, dissolving – eg. boiling water, melting ice, hammering gold into foil chemical change or reaction: – a process that changes the chemical composition (and thus the chemical formula) of starting materials (reactants) — eg. oxidation of matter (burning or ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society
... with the chemicals takes place. Part of this involves all chemicals being clearly labelled with an EU Hazard symbol (some of these are shown below). ...
... with the chemicals takes place. Part of this involves all chemicals being clearly labelled with an EU Hazard symbol (some of these are shown below). ...
Document
... 8. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 9. What is the magnitude of the force on A if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 10. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QA = QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N QA = QB = +1 C 11. What is ...
... 8. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 9. What is the magnitude of the force on A if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 10. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QA = QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N QA = QB = +1 C 11. What is ...
GCE Getting Started - Edexcel
... Atoms of metallic elements in Groups 1,2 and 3 can form positive ions when they take part in reactions since they are readily able to lose electrons. Atoms of Group 1 metals lose one electron and form ions with a 1+ charge, e.g. Na+ Atoms of Group 2 metals lose two electrons and form ions with a 2+ ...
... Atoms of metallic elements in Groups 1,2 and 3 can form positive ions when they take part in reactions since they are readily able to lose electrons. Atoms of Group 1 metals lose one electron and form ions with a 1+ charge, e.g. Na+ Atoms of Group 2 metals lose two electrons and form ions with a 2+ ...
Dr. Spencer`s PPT
... Nonelectrolytes are not dissociated into ions in solution Extent of dissolution does not dictate strong or weak electrolyte solution (i.e., HC2H3O2 is very soluble but is a weak electrolyte while Ba(OH)2 is only slightly soluble is a strong electrolyte) ...
... Nonelectrolytes are not dissociated into ions in solution Extent of dissolution does not dictate strong or weak electrolyte solution (i.e., HC2H3O2 is very soluble but is a weak electrolyte while Ba(OH)2 is only slightly soluble is a strong electrolyte) ...
Lecture 1 - Алтайский государственный технический
... The diameters of atomic nuclei are about 10-4A. Thus, the nuclei are about 0.01% the diameter of the atom as a whole. If the nucleus had a diameter equal to that of a pinhead, then the atom itself would have a diameter of some 10 meters (about 39 and a half feet). The nucleus of an atom is therefor ...
... The diameters of atomic nuclei are about 10-4A. Thus, the nuclei are about 0.01% the diameter of the atom as a whole. If the nucleus had a diameter equal to that of a pinhead, then the atom itself would have a diameter of some 10 meters (about 39 and a half feet). The nucleus of an atom is therefor ...
Document
... c. attraction between protons and electrons holds matter together/apart explains Fs, Ff, Fn, etc. 2. conductors and insulators a. metals are conductors because valence electrons are loosely held by individual atoms and can travel from atom to atom (excess charge on a conductor spreads out on the o ...
... c. attraction between protons and electrons holds matter together/apart explains Fs, Ff, Fn, etc. 2. conductors and insulators a. metals are conductors because valence electrons are loosely held by individual atoms and can travel from atom to atom (excess charge on a conductor spreads out on the o ...
AP Chemistry Notes and Worksheets 2014
... electrons, which knock off some of the atom‟s electrons giving them positive charges, and then these positively charged atoms pass through an electric field. The atoms are deflected based on their size, and then detected on a computerized plate. Look at the image created for a sample of neon to th ...
... electrons, which knock off some of the atom‟s electrons giving them positive charges, and then these positively charged atoms pass through an electric field. The atoms are deflected based on their size, and then detected on a computerized plate. Look at the image created for a sample of neon to th ...
Chemistry Unit Outcomes
... List the names of the first persons to recognize that it would be convenient to represent chemical substances using symbols? 2. Outline what John Dalton, an English chemist, did in 1808. 3. Explain how Dalton represented element and why there was a problem with Dalton’s system. 4. Define the term ch ...
... List the names of the first persons to recognize that it would be convenient to represent chemical substances using symbols? 2. Outline what John Dalton, an English chemist, did in 1808. 3. Explain how Dalton represented element and why there was a problem with Dalton’s system. 4. Define the term ch ...
2 Chemical equilibrium occurs when a reaction and its reverse
... Questions: What are the equilibrium expressions for these equilibria? 1. SnO2 (s) + 2CO (g) ↔ Sn (s) + 2CO2 (g) 2. CaCO3 (s) ↔ CaO (s) + CO2 (g) 3. Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) ↔ Cu (s) + Zn2+ (aq) 4. 2O3 (g) ↔ 3O2 (g) 5. 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) ↔ 2NOCl (g) ...
... Questions: What are the equilibrium expressions for these equilibria? 1. SnO2 (s) + 2CO (g) ↔ Sn (s) + 2CO2 (g) 2. CaCO3 (s) ↔ CaO (s) + CO2 (g) 3. Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) ↔ Cu (s) + Zn2+ (aq) 4. 2O3 (g) ↔ 3O2 (g) 5. 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) ↔ 2NOCl (g) ...
Study material of Science for class X
... Conclusion-On exposing AgCl to sunlight decomposition reaction takes place and silver chloride breaks down to produce silver and chlorine gas is released. ...
... Conclusion-On exposing AgCl to sunlight decomposition reaction takes place and silver chloride breaks down to produce silver and chlorine gas is released. ...
study material(2014-15) class xii-chemistry
... Tips and Techniques for teaching/learning each chapter. Students‘ common errors, un-attempted questions and their remediation. Reviewed Support Materials of the previous year. In order to ensure that the participants come well-prepared for the Workshop, the topics/chapters were distributed among the ...
... Tips and Techniques for teaching/learning each chapter. Students‘ common errors, un-attempted questions and their remediation. Reviewed Support Materials of the previous year. In order to ensure that the participants come well-prepared for the Workshop, the topics/chapters were distributed among the ...
Photosynthesis in Hydrogen-Dominated Atmospheres
... to generate a list of nearly [54] all plausible carbon-based chemicals of a defined size. For this work, we chose molecules of up to 9 non-hydrogen atoms, made of C, N, O, S in oxidation states −2, 0, 2 or 4, and P in oxidation state +5. Rings of 4 or more atoms were allowed. This resulted in a set ...
... to generate a list of nearly [54] all plausible carbon-based chemicals of a defined size. For this work, we chose molecules of up to 9 non-hydrogen atoms, made of C, N, O, S in oxidation states −2, 0, 2 or 4, and P in oxidation state +5. Rings of 4 or more atoms were allowed. This resulted in a set ...
M for Moles - Shop
... are often encountered in chemistry. Readers are assumed to have only a basic science concept and with minimum knowledge in chemistry. This e-book will show you how to solve those tricky moles calculations with plenty of examples, showing in clear and concise ways by following through stepwise and si ...
... are often encountered in chemistry. Readers are assumed to have only a basic science concept and with minimum knowledge in chemistry. This e-book will show you how to solve those tricky moles calculations with plenty of examples, showing in clear and concise ways by following through stepwise and si ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.