- Kendriya Vidyalaya Jhunjhunu
... 1. The oxide of a metal M was water soluble. When a blue litmus strip was dipped in this solution, it did not undergo any change in colour. Predict the nature of the oxide. 2. Why does bee-sting cause pain and irritation? What relief can be given in such a case immediately? 3. Is the distilled water ...
... 1. The oxide of a metal M was water soluble. When a blue litmus strip was dipped in this solution, it did not undergo any change in colour. Predict the nature of the oxide. 2. Why does bee-sting cause pain and irritation? What relief can be given in such a case immediately? 3. Is the distilled water ...
SQA Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Principles of Chemical
... statement is most helpful? a) statement 1 b) statement 2 c) statement 3 ...
... statement is most helpful? a) statement 1 b) statement 2 c) statement 3 ...
(MDCAT) 2017 - University Of Health Sciences Lahore
... i) Describe metallic bonding in terms of positive ions surrounded by mobile electrons (sea of electrons). j) Describe, interpret and/or predict the effect of different types of bonding (ionic bonding; covalent bonding; hydrogen bonding; Van der Waal’s forces and metallic bonding) on the physical pro ...
... i) Describe metallic bonding in terms of positive ions surrounded by mobile electrons (sea of electrons). j) Describe, interpret and/or predict the effect of different types of bonding (ionic bonding; covalent bonding; hydrogen bonding; Van der Waal’s forces and metallic bonding) on the physical pro ...
Chemistry - Set as Home Page
... 10 ml of 3 M HCl was titrated with a standard solution of NaOH containing 80 grams per litre. The volume of the standard solution required to neutralize the acid would be _________ ml. ...
... 10 ml of 3 M HCl was titrated with a standard solution of NaOH containing 80 grams per litre. The volume of the standard solution required to neutralize the acid would be _________ ml. ...
Chapter 2: Mass Relations in Formulas, Chemical Reactions, and
... chemical reaction, atoms are neither destroyed nor created. To keep a chemical equation looking as simple as possible, we will generally ensure that stoichiometric coefficients are written using the smallest possible whole numbers (integers). Balancing a chemical equation consists in determining eac ...
... chemical reaction, atoms are neither destroyed nor created. To keep a chemical equation looking as simple as possible, we will generally ensure that stoichiometric coefficients are written using the smallest possible whole numbers (integers). Balancing a chemical equation consists in determining eac ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... If Keq is greater than 1 there is a higher concentration of products than reactants at equilibrium. (The higher value K = more products less reactants.) ...
... If Keq is greater than 1 there is a higher concentration of products than reactants at equilibrium. (The higher value K = more products less reactants.) ...
all practice examples
... A 0.0240 mol sample of N2O4(g) is allowed to come to equilibrium with NO2(g) in a 0.372 L flask at 25 C. Calculate the amount of N2O4(g) at equilibrium. N2O4(g) ⇌ 2 NO2(g) Kc = 4.61 x 10 -3 at 25 C ...
... A 0.0240 mol sample of N2O4(g) is allowed to come to equilibrium with NO2(g) in a 0.372 L flask at 25 C. Calculate the amount of N2O4(g) at equilibrium. N2O4(g) ⇌ 2 NO2(g) Kc = 4.61 x 10 -3 at 25 C ...
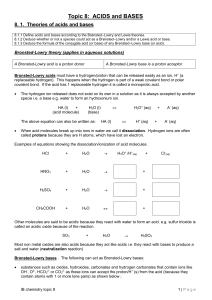
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... the acid is strong. For example, although a covalently bonded molecule and very polar, HF is a weak acid because the covalent bond is strong as a result of the small size of both the H and F atoms. HI is a stronger acid than HBr and HCl as its hydrogen-halogen bond is the weakest. ...
... the acid is strong. For example, although a covalently bonded molecule and very polar, HF is a weak acid because the covalent bond is strong as a result of the small size of both the H and F atoms. HI is a stronger acid than HBr and HCl as its hydrogen-halogen bond is the weakest. ...
Document
... The pressure of the system is assumed to be held constant, at normal pressure (1 atm). As you can see from the graph below, at normal pressure water freezes at 0ºC and boils at 100ºC. The plateaus on this diagram represent the points where water is being converted from one phase to another; at these ...
... The pressure of the system is assumed to be held constant, at normal pressure (1 atm). As you can see from the graph below, at normal pressure water freezes at 0ºC and boils at 100ºC. The plateaus on this diagram represent the points where water is being converted from one phase to another; at these ...
Effect of an industrial chemical waste on the uptake
... acids, as fractions of humic substances, are the most important HS components that, due to their high structural complexity, contribute to the overall fate of trace metal cations, such as Pb(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II), in environment. 5–7 They contain a variety of functional groups which may rea ...
... acids, as fractions of humic substances, are the most important HS components that, due to their high structural complexity, contribute to the overall fate of trace metal cations, such as Pb(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II), in environment. 5–7 They contain a variety of functional groups which may rea ...
East Meck Chemistry
... 3. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ________________ to form compounds 4. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No _______ atoms are created or destroyed. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ________________ to form compounds 4. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No _______ atoms are created or destroyed. ...
Lecture 2
... • acids form hydrogen ions H+ (hydronium, oxonium H3O+) in aqueous solut • bases form hydroxide ions OH- in aqueous solution • acid + base salt + water e.g. HNO3 + KOH KNO3 + H2O Brønsted-Lowry: • acids tend to lose H+ • bases tend to gain H+ • acid 1 + base 1 base 1 + acid 2 (conjugate pairs) ...
... • acids form hydrogen ions H+ (hydronium, oxonium H3O+) in aqueous solut • bases form hydroxide ions OH- in aqueous solution • acid + base salt + water e.g. HNO3 + KOH KNO3 + H2O Brønsted-Lowry: • acids tend to lose H+ • bases tend to gain H+ • acid 1 + base 1 base 1 + acid 2 (conjugate pairs) ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... 26. According to the rate law for the reaction, an increase in the concentration of hydronium ion has what effect on this reaction? (A) The rate of reaction increases. (B) The rate of reaction decreases. (C) The value of the equilibrium constant increases. (D) The value of the equilibrium constant d ...
... 26. According to the rate law for the reaction, an increase in the concentration of hydronium ion has what effect on this reaction? (A) The rate of reaction increases. (B) The rate of reaction decreases. (C) The value of the equilibrium constant increases. (D) The value of the equilibrium constant d ...
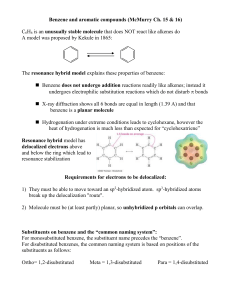
Ex: -F, -Cl, -Br
... Benzene does not undergo addition reactions readily like alkenes; instead it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions which do not disturb bonds X-ray diffraction shows all 6 bonds are equal in length (1.39 A) and that benzene is a planar molecule Hydrogenation under extreme conditions ...
... Benzene does not undergo addition reactions readily like alkenes; instead it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions which do not disturb bonds X-ray diffraction shows all 6 bonds are equal in length (1.39 A) and that benzene is a planar molecule Hydrogenation under extreme conditions ...
What`s in a Name? - Department of Chemistry | Washington
... ingredient of vinegar is acetic acid; glass is a super-cooled liquid silicate; our stomach contains 1 M hydrochloric acid. As you can see, it is important to be able to recognize a chemical by its name. In this tutorial, you will learn about the systematic naming of inorganic compounds. ...
... ingredient of vinegar is acetic acid; glass is a super-cooled liquid silicate; our stomach contains 1 M hydrochloric acid. As you can see, it is important to be able to recognize a chemical by its name. In this tutorial, you will learn about the systematic naming of inorganic compounds. ...
Chemistry Skills Practice Assignments
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...
4Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Earth’s average temperature would be about 60 °F colder than it is now. The temperature outside of my office today would be below 0 °F, and even the sunniest U.S. cities would most likely be covered with snow. However, if the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere were to increase, Eart ...
... Earth’s average temperature would be about 60 °F colder than it is now. The temperature outside of my office today would be below 0 °F, and even the sunniest U.S. cities would most likely be covered with snow. However, if the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere were to increase, Eart ...
A matter of Equilibrium
... Such reactions are called irreversible However many reactions can proceed in either direction: If we mix pure N2 and H2 we form ammonia: N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) But if we take pure ammonia we form N2 and H2: 2 NH3 (g) → N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) Such reactions are called reversible ...
... Such reactions are called irreversible However many reactions can proceed in either direction: If we mix pure N2 and H2 we form ammonia: N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) But if we take pure ammonia we form N2 and H2: 2 NH3 (g) → N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) Such reactions are called reversible ...
Solutes
... • These are, by definition, strong electrolytes and exist totally as ions in aqueous solution. ...
... • These are, by definition, strong electrolytes and exist totally as ions in aqueous solution. ...
ETPD: The Facts and The FAQs
... Schematic view of parallel currents j||, plasma motions, vperp, electric fields, and potential contours above auroral arc, sketched in green [Haerendel 1996] ...
... Schematic view of parallel currents j||, plasma motions, vperp, electric fields, and potential contours above auroral arc, sketched in green [Haerendel 1996] ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.