Ch. 16 Study Guide
... 15. No matter how a reaction is set up, the value of the equilibrium will be the same if the temperature is kept constant. 16. The reaction quotient, Qc , is expressed as concentration of products over concentration of reactants, with each substance raised to its stoichiometric power. There is also ...
... 15. No matter how a reaction is set up, the value of the equilibrium will be the same if the temperature is kept constant. 16. The reaction quotient, Qc , is expressed as concentration of products over concentration of reactants, with each substance raised to its stoichiometric power. There is also ...
Environmental Chemistry
... atom bearing a partial positive charge in one molecule and an atom bearing a partial negative charge in a neighboring molecule The H atom must be bonded to an O, N, or F atom Hydrogen bonds typically are only about one-tenth as strong as the covalent bonds that connect atoms ...
... atom bearing a partial positive charge in one molecule and an atom bearing a partial negative charge in a neighboring molecule The H atom must be bonded to an O, N, or F atom Hydrogen bonds typically are only about one-tenth as strong as the covalent bonds that connect atoms ...
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
... Al2O3.xH2O from which the metal can be produced by electrolysis after dissolving in molten cryolite, Na3AlF6. The metal is mainly used in aluminium alloys. The organoaluminium compounds (e.g., Et3Al) are used in the catalysts involved in the polymerisation of ethene. Group 13 (IIIb) of the Periodic ...
... Al2O3.xH2O from which the metal can be produced by electrolysis after dissolving in molten cryolite, Na3AlF6. The metal is mainly used in aluminium alloys. The organoaluminium compounds (e.g., Et3Al) are used in the catalysts involved in the polymerisation of ethene. Group 13 (IIIb) of the Periodic ...
IIT-JEE - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Crystal defects: Point defects: When ions or atoms do not hold the theoretical position, this is called point defect. Point defects are of two types: Stoichiometric defects: Schottky defect: Due to missing of ions from lattice point in pairs. Frenkel defect: It is caused due to the creation of latti ...
... Crystal defects: Point defects: When ions or atoms do not hold the theoretical position, this is called point defect. Point defects are of two types: Stoichiometric defects: Schottky defect: Due to missing of ions from lattice point in pairs. Frenkel defect: It is caused due to the creation of latti ...
Chemistry Test Ch 11 Stoichiometry
... If 18.5 grams of Fe2(SO4)3 are actually made what is the percent yield? 5. Use the following equation answer these questions: C12H22O11 + 12O2 ---> 12CO2 + 11H2O A. If 3.45 g CO2 is produced how many water molecules are also produced? B. If there are 10.0 g of C12H22O11 and 10.0 g of oxygen reacting ...
... If 18.5 grams of Fe2(SO4)3 are actually made what is the percent yield? 5. Use the following equation answer these questions: C12H22O11 + 12O2 ---> 12CO2 + 11H2O A. If 3.45 g CO2 is produced how many water molecules are also produced? B. If there are 10.0 g of C12H22O11 and 10.0 g of oxygen reacting ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... Students should be able to draw an energy level diagram, show transitions between different energy levels and recognize that the lines in a line spectrum are directly related to these differences. An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible an ...
... Students should be able to draw an energy level diagram, show transitions between different energy levels and recognize that the lines in a line spectrum are directly related to these differences. An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible an ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... Students should be able to draw an energy level diagram, show transitions between different energy levels and recognize that the lines in a line spectrum are directly related to these differences. An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible an ...
... Students should be able to draw an energy level diagram, show transitions between different energy levels and recognize that the lines in a line spectrum are directly related to these differences. An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible an ...
Sulfuric Acid
... Acidic properties. Nitric acid is a strong monobasic acid and ionisation in aqueous solution. Oxidising properties. It acts as a powerful oxidising agent, due to the formation of nascent oxygen. Action on metals. Nitric acid reacts with almost all the metals, except noble metals, like Pt and A ...
... Acidic properties. Nitric acid is a strong monobasic acid and ionisation in aqueous solution. Oxidising properties. It acts as a powerful oxidising agent, due to the formation of nascent oxygen. Action on metals. Nitric acid reacts with almost all the metals, except noble metals, like Pt and A ...
1. Given the balanced equation
... For health reasons, the element chlorine is added to the drinking water because it will kill disease-causing organisms. Typically 0.50 ppm of chlorine is added to drinking water to make it safe. In 2.0 liters of drinking water (2000.g), how many grams of chlorine is present?[Show all work. Include i ...
... For health reasons, the element chlorine is added to the drinking water because it will kill disease-causing organisms. Typically 0.50 ppm of chlorine is added to drinking water to make it safe. In 2.0 liters of drinking water (2000.g), how many grams of chlorine is present?[Show all work. Include i ...
2015 Dr. Jay L. Wile, All rights reserved.
... e. Several grams of magnesium, which is one of the two simplest substances produced when magnesium oxide breaks down. f. The magnesium oxide from which the magnesium discussed above was produced. g. A strawberry h. A cup of tea with no leaves in it. 3. A student does a chemical reaction with two che ...
... e. Several grams of magnesium, which is one of the two simplest substances produced when magnesium oxide breaks down. f. The magnesium oxide from which the magnesium discussed above was produced. g. A strawberry h. A cup of tea with no leaves in it. 3. A student does a chemical reaction with two che ...
Atomic Structure
... The electronic configuration of an atom/ion can be defined by which the following (a) Aufbau principle (b) hund’s rule (c) Pauli exclusion principle (d) All the three, namely Aufbau, Pauli and Hund’s rule ...
... The electronic configuration of an atom/ion can be defined by which the following (a) Aufbau principle (b) hund’s rule (c) Pauli exclusion principle (d) All the three, namely Aufbau, Pauli and Hund’s rule ...
Spectroscopic Characterization of Mixed Fe−Ni
... a mixture composed of 5 g of deionized water and 5 g of ACS grade ethanol. Subsequently, metal nitrate precursor salts were dissolved into this mixture in the desired molar compositions for the final catalyst powder. This solution was then transferred to a ceramic boat and heated in air using a contr ...
... a mixture composed of 5 g of deionized water and 5 g of ACS grade ethanol. Subsequently, metal nitrate precursor salts were dissolved into this mixture in the desired molar compositions for the final catalyst powder. This solution was then transferred to a ceramic boat and heated in air using a contr ...
Surface chemistry and Catalysis
... layer adsorption. In BET it is assumed that the solid surface possesses uniform, localized sites and adsorption at one site does not affect adsorption at neighboring sites . It is further assumed that the molecule can be adsorbed in second, third…and nth layer, the surface area available for the nth ...
... layer adsorption. In BET it is assumed that the solid surface possesses uniform, localized sites and adsorption at one site does not affect adsorption at neighboring sites . It is further assumed that the molecule can be adsorbed in second, third…and nth layer, the surface area available for the nth ...
lecture1423183006
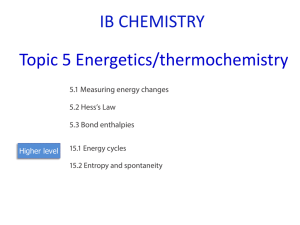
... 2.6.3 Heat of Combustion: Heat of combustion of a substance is the enthalpy change when one mole of the substance is completely burnt in oxygen. 2.6.4 Heat of Solution: When one substance dissolves in another there will be a change in enthalpy that is known as heat of solution & it depends on the co ...
... 2.6.3 Heat of Combustion: Heat of combustion of a substance is the enthalpy change when one mole of the substance is completely burnt in oxygen. 2.6.4 Heat of Solution: When one substance dissolves in another there will be a change in enthalpy that is known as heat of solution & it depends on the co ...
Efficient Homogeneous Catalysis in the Reduction of CO to CO
... resonance for 1 in the 11B NMR spectrum, a broad singlet at 41.7 ppm, is replaced by a singlet at 21.8 ppm, indicative of boron bound to three oxygen atoms.19 Single crystals of this new copper complex are grown by diffusion of hexane vapor into a concentrated toluene solution. The X-ray crystal str ...
... resonance for 1 in the 11B NMR spectrum, a broad singlet at 41.7 ppm, is replaced by a singlet at 21.8 ppm, indicative of boron bound to three oxygen atoms.19 Single crystals of this new copper complex are grown by diffusion of hexane vapor into a concentrated toluene solution. The X-ray crystal str ...
Activity C14: Rate of a Chemical Reaction 1
... S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) =========> SO2(g) + S (s) + H2O One way to determine the effect of concentration on the rate of the reaction is to use a Colorimeter to measure the formation of the solid sulfur generated. The solid sulfur will block the light in the Colorimeter and the amount of blockage is di ...
... S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) =========> SO2(g) + S (s) + H2O One way to determine the effect of concentration on the rate of the reaction is to use a Colorimeter to measure the formation of the solid sulfur generated. The solid sulfur will block the light in the Colorimeter and the amount of blockage is di ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.