Chemistry Final Study Guide
... 43. The three major categories of elements on the periodic table are the __________, __________, and __________. 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer ...
... 43. The three major categories of elements on the periodic table are the __________, __________, and __________. 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer ...
... these reactions to be reversible and the intermediates to be stable. We describe here the electrolytic and chemical preparation of cation radicals of various porphyrins and of ethyl chlorophyllide a as well as the formation of the dication of magnesium octaethylporphyrin. Electrolysis 3 of magnesium ...
200 ways to pass the regents
... 47. The masses of the reactants in a chemical equation is always equal to the masses of the products. “Law of Conservation of Mass.” 48. The gram formula mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all of the atoms in it. ...
... 47. The masses of the reactants in a chemical equation is always equal to the masses of the products. “Law of Conservation of Mass.” 48. The gram formula mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all of the atoms in it. ...
Lecture 8
... refers to formation from its elements, all in standard states. By definition,it is zero for any element in its stable(standard ) state. enthalpy change ΔHΘ in any reaction to be calculated from ...
... refers to formation from its elements, all in standard states. By definition,it is zero for any element in its stable(standard ) state. enthalpy change ΔHΘ in any reaction to be calculated from ...
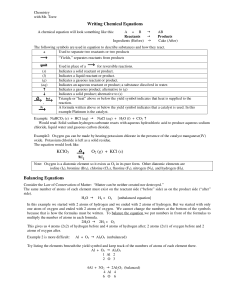
Writing Chemical Equations KClO3 O2 (g) + KCl (s) Balancing
... Indicates a solid reactant or product. Indicates a liquid reactant or product. Indicates a gaseous reactant or product. Indicates an aqueous reactant or product; a substance dissolved in water. Indicates a gaseous product; alternative to (g) Indicates a solid product; alternative to (s) Triangle or ...
... Indicates a solid reactant or product. Indicates a liquid reactant or product. Indicates a gaseous reactant or product. Indicates an aqueous reactant or product; a substance dissolved in water. Indicates a gaseous product; alternative to (g) Indicates a solid product; alternative to (s) Triangle or ...
Chemistry Nomenclature Notes
... -They become negatively charged and are called anions. -The size of the negative charge is determined by the number of electrons gained. -The number of electrons gained is determined by the proximity of Noble gas. -Named by dropping the ending and adding an ‘ide’ ending Ex: Chlorine is a group 7 ele ...
... -They become negatively charged and are called anions. -The size of the negative charge is determined by the number of electrons gained. -The number of electrons gained is determined by the proximity of Noble gas. -Named by dropping the ending and adding an ‘ide’ ending Ex: Chlorine is a group 7 ele ...
Tips for Learning General Chemistry Rules, Trends and Exceptions
... One of the most famous oxidation reduction reactions occurs when you throw a metal, M, in water, H2 O. The following reaction happens: M + H2 O ‡ M2+ + OH- + H2 The metal is oxidized (dissolves) and reduced bydrogen (H2 that explodes) and a strong base (OH) are formed. When you watch me throw sodium ...
... One of the most famous oxidation reduction reactions occurs when you throw a metal, M, in water, H2 O. The following reaction happens: M + H2 O ‡ M2+ + OH- + H2 The metal is oxidized (dissolves) and reduced bydrogen (H2 that explodes) and a strong base (OH) are formed. When you watch me throw sodium ...
Sodium hydroxide
... • Copper is less reactive than carbon, so it can be extracted from its ores by heating it with carbon. For example, copper is formed if copper oxide is heated strongly with charcoal, which is mostly carbon: copper(II) oxide + carbon → copper + carbon dioxide 2CuO + C → 2Cu + CO2 • Removing O2 from a ...
... • Copper is less reactive than carbon, so it can be extracted from its ores by heating it with carbon. For example, copper is formed if copper oxide is heated strongly with charcoal, which is mostly carbon: copper(II) oxide + carbon → copper + carbon dioxide 2CuO + C → 2Cu + CO2 • Removing O2 from a ...
CHEMICAL REACTION
... • Color change These easily observed changes indicate that a chemical reaction may have taken place. Absolute proof is provided by chemical analysis of the products. ...
... • Color change These easily observed changes indicate that a chemical reaction may have taken place. Absolute proof is provided by chemical analysis of the products. ...
Classifying Chemical Reactions 9-3
... Ways to Express a Chemical Reaction The way atoms are joined is changed in a chemical reaction. Can be described several ways: 1. In a sentence ...
... Ways to Express a Chemical Reaction The way atoms are joined is changed in a chemical reaction. Can be described several ways: 1. In a sentence ...
Reactions (The Basics)
... Generally take place between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution Generally 3 things happen: ...
... Generally take place between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution Generally 3 things happen: ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... Draw Carbon Nitrogen atomic number: 7 atomic mass: 14 Carbon atomic number 6 atomic mass: 12 ...
... Draw Carbon Nitrogen atomic number: 7 atomic mass: 14 Carbon atomic number 6 atomic mass: 12 ...
S4 Standard Grade Revision Booklet
... 4. Give (i) word equations and (ii) equations using the chemical formulae (not necessarily balanced) for the reactions between: a) potassium and oxygen b) lithium and water c) magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. 5. Calculate the percentage by mass of: a) Sodium in sodium chloride (NaCl) b) Lead ...
... 4. Give (i) word equations and (ii) equations using the chemical formulae (not necessarily balanced) for the reactions between: a) potassium and oxygen b) lithium and water c) magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. 5. Calculate the percentage by mass of: a) Sodium in sodium chloride (NaCl) b) Lead ...
Slajd 1 - Uniwersytet Warszawski
... Verification of the hypothesis was done in two ways 1) using the quantum chemical method by which thermodynamic functions, enthalpy, and free enthalpy were calculated, 2) using MS method applying ‘soft’ ionization techniques APCI and ESI, which allow samples to be analysed in a liquid mobile phase, ...
... Verification of the hypothesis was done in two ways 1) using the quantum chemical method by which thermodynamic functions, enthalpy, and free enthalpy were calculated, 2) using MS method applying ‘soft’ ionization techniques APCI and ESI, which allow samples to be analysed in a liquid mobile phase, ...
3a-General Reactions 2010
... Chemical equations describe the change(s) in Reactant(s) to Product(s) including physical state(s). Notations: (g), (l), (s), (aq) 2 Na (s) + Cl2(g) --> 2 NaCl (s) Others: arrows for gas ( ) and solid ( ) for heat, for reversibility (equilibrium) © Copyright 1995-2010 R.J. Rusay ...
... Chemical equations describe the change(s) in Reactant(s) to Product(s) including physical state(s). Notations: (g), (l), (s), (aq) 2 Na (s) + Cl2(g) --> 2 NaCl (s) Others: arrows for gas ( ) and solid ( ) for heat, for reversibility (equilibrium) © Copyright 1995-2010 R.J. Rusay ...
Chemistry 30 Notes - Heat of Formation February 2nd
... We know from the question that 297 kJ of energy is released for 1 mole of SO2 — the definition of heat of formation. Determine how much energy will be released for 0.390 mol of SO2: kJ released = (0.39 mol)(-297 kJ/mol) = - 116 kJ Heat of Formation Turn now to a special type of chemical reaction, on ...
... We know from the question that 297 kJ of energy is released for 1 mole of SO2 — the definition of heat of formation. Determine how much energy will be released for 0.390 mol of SO2: kJ released = (0.39 mol)(-297 kJ/mol) = - 116 kJ Heat of Formation Turn now to a special type of chemical reaction, on ...
AP Chemistry Jeopardy
... HSO4- is acidic because it can further produce H+ ions in solution (but it also has amphoteric properties). ...
... HSO4- is acidic because it can further produce H+ ions in solution (but it also has amphoteric properties). ...
chemistry - cloudfront.net
... Write the complete electron structure for a neutral sodium atom. According to its electron structure, what period of the periodic table should sodium be in? How many valence electrons does it have? What ion will sodium tend to form? What is meant by a noble gas electron configuration? Why are th ...
... Write the complete electron structure for a neutral sodium atom. According to its electron structure, what period of the periodic table should sodium be in? How many valence electrons does it have? What ion will sodium tend to form? What is meant by a noble gas electron configuration? Why are th ...
Test 4
... A process that will occur without input of energy from a external source. Second law of thermodynamics In any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe always increases. Positional disorder Randomness that comes from the number of different arrangements of a system. Molar entropy of fusion The ...
... A process that will occur without input of energy from a external source. Second law of thermodynamics In any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe always increases. Positional disorder Randomness that comes from the number of different arrangements of a system. Molar entropy of fusion The ...
Types of Reactions and Solution Chemistry
... Acids and bases are important compounds. We have talked about how to name acids specifically the binary halogen acids (HF, HCl, HBr, and HI as being names hydrofluoric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, and hydroiodic acid) and the oxoacids (H2SO4, H2CO3, HNO3, and HNO2 for example: sulfuri ...
... Acids and bases are important compounds. We have talked about how to name acids specifically the binary halogen acids (HF, HCl, HBr, and HI as being names hydrofluoric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, and hydroiodic acid) and the oxoacids (H2SO4, H2CO3, HNO3, and HNO2 for example: sulfuri ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.