Cellular Respiration - Mayfield City Schools
... 4. Summary of products: 2 acetyl CoA 2 ATP + 4 CO2 + 2 FADH2 + 6 NADH VI. Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis 1. Third major pathway that occurs along the inner mitochondrial MEMBRANE (CRISTAE). 2. Produces most of the ATP in cellular respiration; yields 32 to 34 ATP molecules a. Only 4 ATP ...
... 4. Summary of products: 2 acetyl CoA 2 ATP + 4 CO2 + 2 FADH2 + 6 NADH VI. Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis 1. Third major pathway that occurs along the inner mitochondrial MEMBRANE (CRISTAE). 2. Produces most of the ATP in cellular respiration; yields 32 to 34 ATP molecules a. Only 4 ATP ...
Cellular Biology I
... Two linked together form a disaccharide Polysaccharides are long chains consisting of 8 or more monomers – usually glucose A. starch – energy storage in plants B. glycogen – energy storage in ...
... Two linked together form a disaccharide Polysaccharides are long chains consisting of 8 or more monomers – usually glucose A. starch – energy storage in plants B. glycogen – energy storage in ...
Cellular Respiration
... Oxidation-reduction reaction starts the ETC. High energy electrons enter the chain, low energy electrons leave. There is a series of carriers that transport the electrons, first reduced when it accepts the electrons, then oxidized when it releases them. ...
... Oxidation-reduction reaction starts the ETC. High energy electrons enter the chain, low energy electrons leave. There is a series of carriers that transport the electrons, first reduced when it accepts the electrons, then oxidized when it releases them. ...
2) Where
... 3 Steps of Cellular Respira1on (each produces some ATP) 1) Glycolysis -‐ spli[ng of glucose (2 ATP) (anaerobic -‐ no O2 needed) 2) Citric Acid (Kreb’s) cycle (2 ATP) (aerobic -‐ ...
... 3 Steps of Cellular Respira1on (each produces some ATP) 1) Glycolysis -‐ spli[ng of glucose (2 ATP) (anaerobic -‐ no O2 needed) 2) Citric Acid (Kreb’s) cycle (2 ATP) (aerobic -‐ ...
Cellular Respiration - Mrs. Brenner`s Biology
... process that plants use to make food, but plants and animals need a way to change food into smaller packets of usable energy. ...
... process that plants use to make food, but plants and animals need a way to change food into smaller packets of usable energy. ...
CH 7 Reading Guide 2014
... 34. At this point, you should be able to account for the total number of ATPs that could be formed from a glucose molecule. To accomplish this, we have to add the ATPs formed by substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to the ATPs formed by chemiosmosis. Each NADH can ...
... 34. At this point, you should be able to account for the total number of ATPs that could be formed from a glucose molecule. To accomplish this, we have to add the ATPs formed by substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to the ATPs formed by chemiosmosis. Each NADH can ...
6O2 + C6H12O6 ------------------------
... I. What is Cell Respiration? a. The breakdown of _______________ (chemical energy from food) to form ________ for energy use in cells. b. ________________ is the type of energy used by cells to drive reactions in the body. c. The equation: **MEMORIZE THIS! ...
... I. What is Cell Respiration? a. The breakdown of _______________ (chemical energy from food) to form ________ for energy use in cells. b. ________________ is the type of energy used by cells to drive reactions in the body. c. The equation: **MEMORIZE THIS! ...
Calvin Cycle Answers
... 2. Because inorganic CO2 is put into a biological molecule eventually used to make organic glucose. 3. Because it needs to happen 3 times to fix enough carbon for 1 PGA/G3P. 4. Because it catalyzes 2 reactions – reduction of RuBP and regeneration of RuBP so CO2 and O2 are competing for the ...
... 2. Because inorganic CO2 is put into a biological molecule eventually used to make organic glucose. 3. Because it needs to happen 3 times to fix enough carbon for 1 PGA/G3P. 4. Because it catalyzes 2 reactions – reduction of RuBP and regeneration of RuBP so CO2 and O2 are competing for the ...
synthetic photosynthesis
... University of Sydney’s molecular electronics group. They have done it by combining synthetic porphyrins with C60 buckyball molecules and coating the mixture onto a tin dioxide monolayer itself deposited on an optically transparent electrode (see Figure 1). The synthetic porphyrins capture energy fro ...
... University of Sydney’s molecular electronics group. They have done it by combining synthetic porphyrins with C60 buckyball molecules and coating the mixture onto a tin dioxide monolayer itself deposited on an optically transparent electrode (see Figure 1). The synthetic porphyrins capture energy fro ...
Quiz 7 Name: 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell
... 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell membrane in an animal cell, where do the “used-up” ADP and Pi go? A) ADP and Pi accumulate in the cytosol and don’t form ATP again B) ADP and Pi are regenerated to ATP by the Na+/K+ pump running in reverse C) ADP and Pi are regenerated to ATP in the chl ...
... 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell membrane in an animal cell, where do the “used-up” ADP and Pi go? A) ADP and Pi accumulate in the cytosol and don’t form ATP again B) ADP and Pi are regenerated to ATP by the Na+/K+ pump running in reverse C) ADP and Pi are regenerated to ATP in the chl ...
CHAPTER 3: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... carriers that pass electrons from one to the other, resulting in energy that is stored as a hydrogen ion gradient. Organization of Cristae The electron transport chain is located within the cristae of the mitochondria. The complexes in the chain establish a hydrogen ion gradient between the matrix ...
... carriers that pass electrons from one to the other, resulting in energy that is stored as a hydrogen ion gradient. Organization of Cristae The electron transport chain is located within the cristae of the mitochondria. The complexes in the chain establish a hydrogen ion gradient between the matrix ...
Photosynthesis & Respiration
... Occurs in Chloroplasts Photosynthetic Membrane in clusters of pigments cells called a Photosystem Photosystems: capture E in sunlight in Pigments such as chlorophyll e- transport occurs in photosystems, ...
... Occurs in Chloroplasts Photosynthetic Membrane in clusters of pigments cells called a Photosystem Photosystems: capture E in sunlight in Pigments such as chlorophyll e- transport occurs in photosystems, ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 7. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. ...
... 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 7. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. ...
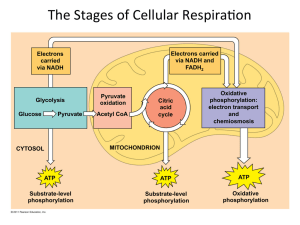
The Stages of Cellular RespiraWon
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
Energy Review - MrsAllisonMagee
... Why is oxygen needed in cell resp? • To act as the final electron acceptor of the ETS ...
... Why is oxygen needed in cell resp? • To act as the final electron acceptor of the ETS ...
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes - Science Learning Center
... electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation to convert the stored energy into ATP. O2 is the final electron acceptor for the electron transport chain, if no O2 then the no electron transport. (Since all the NADH and FADH2 from Krebs must be processed by the electron transport system the cell au ...
... electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation to convert the stored energy into ATP. O2 is the final electron acceptor for the electron transport chain, if no O2 then the no electron transport. (Since all the NADH and FADH2 from Krebs must be processed by the electron transport system the cell au ...
chapter7_Sections 5
... lost by the electrons as they flow through the chains is used to move H+ across the membrane. ...
... lost by the electrons as they flow through the chains is used to move H+ across the membrane. ...
Chapter 5 - Ellis Benjamin
... • ATP produced through phosphorylation – donor molecule transfers P to ADP • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Net gain of 2 ATPs • Results in 2 pyruvate and 2 NADH molecules per glucose that goes through glycolysis ...
... • ATP produced through phosphorylation – donor molecule transfers P to ADP • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Net gain of 2 ATPs • Results in 2 pyruvate and 2 NADH molecules per glucose that goes through glycolysis ...
Photosynthesis PPT
... accessory pigments with different structures absorb light of different wavelengths chlorophyll b, carotenoids, xanthophylls ...
... accessory pigments with different structures absorb light of different wavelengths chlorophyll b, carotenoids, xanthophylls ...
File
... 7. When describing the cell’s membrane potential, the cell interior is : a. More positively charged than the exterior b. More negatively charged than the exterior c. Electrically neutral d. Continuously reversing its electrical charge e. Positively charged whenever the sodium-potassium pump is acti ...
... 7. When describing the cell’s membrane potential, the cell interior is : a. More positively charged than the exterior b. More negatively charged than the exterior c. Electrically neutral d. Continuously reversing its electrical charge e. Positively charged whenever the sodium-potassium pump is acti ...
Unit 4 Photosynthesis
... This whole process has a specific name: Movement of protons within the thylakoid space due to the redox reactions that move electrons down the Electron Transport Chain H+ Gradient develops ...
... This whole process has a specific name: Movement of protons within the thylakoid space due to the redox reactions that move electrons down the Electron Transport Chain H+ Gradient develops ...
Cell Respiration Take Home Test 1. When cells break down food
... c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic cellular respiration a. is performed only by organisms that are incapable of photosynthesis. b. breaks down sugar molecules to release ...
... c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic cellular respiration a. is performed only by organisms that are incapable of photosynthesis. b. breaks down sugar molecules to release ...
18_Energy metabolism. Biological oxidation. Chemiosmotic theory
... Complex II (succinate-ubiquinon oxidoreductase) Transfers electrons from succinate to Co Q. Form 1 consist of: - enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (FAD – prosthetic group) - iron-sulfur clusters. Succinate reduces FAD to FADH2. Then electrons pass to Fe-S proteins which reduce Q to QH2 Form 2 and 3 co ...
... Complex II (succinate-ubiquinon oxidoreductase) Transfers electrons from succinate to Co Q. Form 1 consist of: - enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (FAD – prosthetic group) - iron-sulfur clusters. Succinate reduces FAD to FADH2. Then electrons pass to Fe-S proteins which reduce Q to QH2 Form 2 and 3 co ...