CHAPTER 1 -Chemistry -Matter -Elements -Atoms
... A.speed. B. shape of the orbital it's in. C. Energy. D. Momentum. E. principle quantum number. 5. Wavelength and frequency are A. Directly related. B. proportional. C. Inversely related. D second cousins. E.the same 1. An electromagnetic wave has a wavelength of 656nm. How much energy is there in a ...
... A.speed. B. shape of the orbital it's in. C. Energy. D. Momentum. E. principle quantum number. 5. Wavelength and frequency are A. Directly related. B. proportional. C. Inversely related. D second cousins. E.the same 1. An electromagnetic wave has a wavelength of 656nm. How much energy is there in a ...
chapter_2_2007
... reactions in which electrons (and their energy) are transferred from one atom to another. ...
... reactions in which electrons (and their energy) are transferred from one atom to another. ...
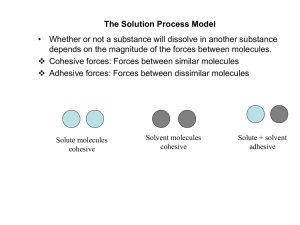
The Solution Process Model
... • Dissolution rate is a measure of how fast a solid drug dissolves in a liquid solvent. • Dissolution is defined as the process of dissolving a solute to form a homogeneous solution as described by Noyes Whitney equation. • When a particle of a drug is dissolved in water, the molecules at the very s ...
... • Dissolution rate is a measure of how fast a solid drug dissolves in a liquid solvent. • Dissolution is defined as the process of dissolving a solute to form a homogeneous solution as described by Noyes Whitney equation. • When a particle of a drug is dissolved in water, the molecules at the very s ...
Johnny Xie Period 5 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 6.1 The Nature of
... Work: force over a distance. There are two ways to transfer energy: through work or heat. ...
... Work: force over a distance. There are two ways to transfer energy: through work or heat. ...
FE Review Chemistry - UTSA College of Engineering
... Reactions • Oxidation and Reduction Reactions (Redox) – Involves transfer of e-; one compound gives up e- the other takes them up – Compound giving up e- is being oxidized, so reducing agent – Compound accepting e- is being reduced, oxidizing agent • Ex. Corrosion of Fe – Fe0 = Fe2+ +2e– 2H+ + 2e- ...
... Reactions • Oxidation and Reduction Reactions (Redox) – Involves transfer of e-; one compound gives up e- the other takes them up – Compound giving up e- is being oxidized, so reducing agent – Compound accepting e- is being reduced, oxidizing agent • Ex. Corrosion of Fe – Fe0 = Fe2+ +2e– 2H+ + 2e- ...
CHEM_1305_Practice_Exam_2
... 19) Which of the statements below best describes the following reaction? Na2CO3(s) Na2O(s) + CO2(g) A) Solid sodium carbonate decomposes to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to form sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium oxide combines with carbon d ...
... 19) Which of the statements below best describes the following reaction? Na2CO3(s) Na2O(s) + CO2(g) A) Solid sodium carbonate decomposes to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to form sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium oxide combines with carbon d ...
File
... 1. Name the type of reaction and draw structural diagrams to represent the following reactions: a) Reaction of propene to form an alcohol. b) Reaction of 3-methyl-2-pentanol with HBr. c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and ...
... 1. Name the type of reaction and draw structural diagrams to represent the following reactions: a) Reaction of propene to form an alcohol. b) Reaction of 3-methyl-2-pentanol with HBr. c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and ...
Chapter 8 Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Interpret notations in formula equations, such as those relating to states of matter or reaction conditions. Chemical Reaction • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances change into one or mor ...
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Interpret notations in formula equations, such as those relating to states of matter or reaction conditions. Chemical Reaction • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances change into one or mor ...
students - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
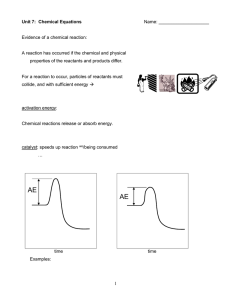
... A reaction has occurred if the chemical and physical properties of the reactants and products differ. ...
... A reaction has occurred if the chemical and physical properties of the reactants and products differ. ...
Chemistry 21 A - El Camino College
... 14. Consider all of the following compounds to be water soluble and write the formulas of the ions that would be formed if the compoundes were disolved in water. a) LiNO3 b) Na2HPO4 c) Ca(ClO3)2 d) KOH e) MgBr2 f) (NH4)2SO4 15. In aqueous solutions a) positive ions are called _______________________ ...
... 14. Consider all of the following compounds to be water soluble and write the formulas of the ions that would be formed if the compoundes were disolved in water. a) LiNO3 b) Na2HPO4 c) Ca(ClO3)2 d) KOH e) MgBr2 f) (NH4)2SO4 15. In aqueous solutions a) positive ions are called _______________________ ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 10 Periodic Trends Why? The
... Size increases down a group. The outermost electrons are in successively more extensive orbitals as n increases. Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one another very effectively from the increasing nuclear charge. This causes all orbitals (includin ...
... Size increases down a group. The outermost electrons are in successively more extensive orbitals as n increases. Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one another very effectively from the increasing nuclear charge. This causes all orbitals (includin ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... Addition – atoms of a compound are being attached to a double (triple) bond, which is accompanied by reduction in bond multiplicity Elimination – two atoms (groups) are removed from the molecule Rearrangement – an atom (group) migrates from one atom of a molecule to another atom, most often of the s ...
... Addition – atoms of a compound are being attached to a double (triple) bond, which is accompanied by reduction in bond multiplicity Elimination – two atoms (groups) are removed from the molecule Rearrangement – an atom (group) migrates from one atom of a molecule to another atom, most often of the s ...
Organic Reactions
... • Reactions occur between electrophiles and nucleophiles. • Just about any part of a molecule can be either electrophilic or nucleophilic depending one what you are comparing it to ...
... • Reactions occur between electrophiles and nucleophiles. • Just about any part of a molecule can be either electrophilic or nucleophilic depending one what you are comparing it to ...
types of reactions
... ex: 4 NH3 + 2 O2 4 NO3 + 6 H2O (all divisible by 2, so simplify) 2 NH3 + O2 2 NO3 + 3 H2O ...
... ex: 4 NH3 + 2 O2 4 NO3 + 6 H2O (all divisible by 2, so simplify) 2 NH3 + O2 2 NO3 + 3 H2O ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... 1. Using complete sentences, compare and contrast Reaction A and Reaction B in terms of the following parameters: a. Relative energy content of reactants and products b. amount of energy needed to make the reaction happen (Energy of activation) c. net amount of energy released or absorbed (exo or en ...
... 1. Using complete sentences, compare and contrast Reaction A and Reaction B in terms of the following parameters: a. Relative energy content of reactants and products b. amount of energy needed to make the reaction happen (Energy of activation) c. net amount of energy released or absorbed (exo or en ...