Carbene Singlets, Triplets, and the Physics that
... (molecular, in the likely event of two molecules interacting) orbitals, resulting in a mixing of pure orbitals. This mixing can either yield a bonding or an anti-bonding orbital, as seen in the interaction diagram (see figure 3). Orbital mixing diagrams like these are often qualitative, and while kn ...
... (molecular, in the likely event of two molecules interacting) orbitals, resulting in a mixing of pure orbitals. This mixing can either yield a bonding or an anti-bonding orbital, as seen in the interaction diagram (see figure 3). Orbital mixing diagrams like these are often qualitative, and while kn ...
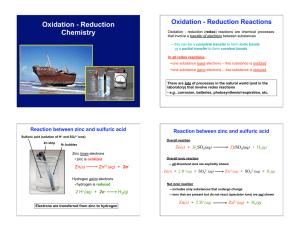
Oxidation - Reduction Chemistry
... 1. All elements in their free state (uncombined with other elements) have an oxidation number of zero (e.g., Na, Cu, Mg, H2, O2, Cl2, etc.) 2. H is +1, except in metal hydrides, where it is -1 (e.g., NaH, CaH2) 3. O is -2, except in peroxides, where it is -1, and in OF2, where it is +2 4. The metall ...
... 1. All elements in their free state (uncombined with other elements) have an oxidation number of zero (e.g., Na, Cu, Mg, H2, O2, Cl2, etc.) 2. H is +1, except in metal hydrides, where it is -1 (e.g., NaH, CaH2) 3. O is -2, except in peroxides, where it is -1, and in OF2, where it is +2 4. The metall ...
oxidation–reduction reaction
... compound is the number of electrons lost or gained by the atom when it forms ions. • Oxidation numbers are tools that scientists use in written chemical equations to help them keep track of the movement of electrons in a redox reaction. ...
... compound is the number of electrons lost or gained by the atom when it forms ions. • Oxidation numbers are tools that scientists use in written chemical equations to help them keep track of the movement of electrons in a redox reaction. ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Pure substances have constant composition. Salt water samples from different seas or lakes have different amounts of salt ...
... Pure substances have constant composition. Salt water samples from different seas or lakes have different amounts of salt ...
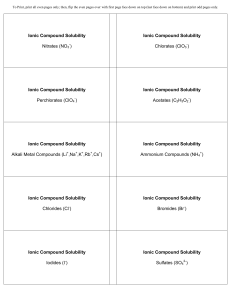
Ionic Compound Solubility Nitrates (NO3 ) Ionic Compound
... Definition A substance that is able to donate a H+ ion (a proton) and, hence, increases the concentration of H+(aq) when it dissolves in water. ...
... Definition A substance that is able to donate a H+ ion (a proton) and, hence, increases the concentration of H+(aq) when it dissolves in water. ...
General Chemistry Discretes Test
... For question 3, the correct choice is A . One is asked in this question to determine which of the choices contains a false description of the gas. Under conditions of high pressure and low temperature, the gas is not behaving ideally and corrections must be made for the volume of the gas molecules a ...
... For question 3, the correct choice is A . One is asked in this question to determine which of the choices contains a false description of the gas. Under conditions of high pressure and low temperature, the gas is not behaving ideally and corrections must be made for the volume of the gas molecules a ...
physical chemistry - University Science Books
... to permit this type of investigation in all cases, and we sometimes have to settle for a good, semiquantitative understanding. It is useful to keep in mind the scope and limitations of a given approach. The principles of physical chemistry can be applied to the study of any chemical system. For exam ...
... to permit this type of investigation in all cases, and we sometimes have to settle for a good, semiquantitative understanding. It is useful to keep in mind the scope and limitations of a given approach. The principles of physical chemistry can be applied to the study of any chemical system. For exam ...
O - Free Exam Papers
... • Many elements form ions with some definite charge (E.g. Na+, Mg2+ and O2-). It is often possible to work out the charge using the Periodic Table. • If we know the charges on the ions that make up the compound then we can work out its formula. • This topic is covered in more detail in the Topic on ...
... • Many elements form ions with some definite charge (E.g. Na+, Mg2+ and O2-). It is often possible to work out the charge using the Periodic Table. • If we know the charges on the ions that make up the compound then we can work out its formula. • This topic is covered in more detail in the Topic on ...
Gr. 11 Chemistry Student Workbook (Spring 2016)
... The most basic piece of personal protective equipment is a pair of goggles, and these will always be made available to students. Like a calculator for mathematics, and running shoes for physical education goggles are personal pieces of equipment best owned by students. When students own their own go ...
... The most basic piece of personal protective equipment is a pair of goggles, and these will always be made available to students. Like a calculator for mathematics, and running shoes for physical education goggles are personal pieces of equipment best owned by students. When students own their own go ...
Copy of Acids, bases, salts answer key
... Limitations of Arrhenius theory : Arhhenius’ theory became quite popular and was widely accepted yet it had the following limitations: This theory was applicable only to aqueous solutions. Substances like Ammonia (NH3) do not contain hydroxide (OH) ion, even then its aqueous solution acts as a ...
... Limitations of Arrhenius theory : Arhhenius’ theory became quite popular and was widely accepted yet it had the following limitations: This theory was applicable only to aqueous solutions. Substances like Ammonia (NH3) do not contain hydroxide (OH) ion, even then its aqueous solution acts as a ...
CNT Sensors for Detecting Gases with Low Adsorption Energy by Ionization
... the initial breakdown voltage was defined as the voltage necessary for 0.1mA current. On the left side of the curve indicating the lower concentration, the initial breakdown voltage was fast increased with the reduction of the concentration because the dark discharge current depends on the amount of ...
... the initial breakdown voltage was defined as the voltage necessary for 0.1mA current. On the left side of the curve indicating the lower concentration, the initial breakdown voltage was fast increased with the reduction of the concentration because the dark discharge current depends on the amount of ...
SAMPLE PAPER -2 Time Allowed: 3 Hrs
... (iii) The amino acids which our body system cannot produce and are necessary to be supplied through the diet are known as Essential Amino Acids. The amino acids which our body can synthesize are known as Non Essential Amino Acids. Essential Amino Acid Histidine ...
... (iii) The amino acids which our body system cannot produce and are necessary to be supplied through the diet are known as Essential Amino Acids. The amino acids which our body can synthesize are known as Non Essential Amino Acids. Essential Amino Acid Histidine ...
RxnTypesPrednotesIIAP
... and [AgCl2] are two important complexes that form. The diammine silver complex results when a solution containing the silver ion is reacted with an aqueous ammonium hydroxide solution. The dichloroargentate complex only forms when there is a strong excess of the chloride ion. For example, if 6 M hyd ...
... and [AgCl2] are two important complexes that form. The diammine silver complex results when a solution containing the silver ion is reacted with an aqueous ammonium hydroxide solution. The dichloroargentate complex only forms when there is a strong excess of the chloride ion. For example, if 6 M hyd ...
summer fun - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... The lists presented above may seem rather extensive, but they contain practically all the ions you are likely to encounter in AP Chemistry. (You may get a few more in September, but this will give you a good start!) Naming an ionic compound is simple. Write down the name of the cation (positive ion) ...
... The lists presented above may seem rather extensive, but they contain practically all the ions you are likely to encounter in AP Chemistry. (You may get a few more in September, but this will give you a good start!) Naming an ionic compound is simple. Write down the name of the cation (positive ion) ...
The EMF technique
... • Samples need to be dense, and seals need to be gas-tight • Impurities in gas mixtures must be avoided • The gas mixture in each chamber should be uniform, that is, partial pressures at the sample surface should be the same as the known ...
... • Samples need to be dense, and seals need to be gas-tight • Impurities in gas mixtures must be avoided • The gas mixture in each chamber should be uniform, that is, partial pressures at the sample surface should be the same as the known ...
Unit 10
... Determine the types of reactants involved and the products formed in the reaction. Write down the correct formulae of reactants on the left hand side of the arrow. Write down the correct formulae of products on the right hand side of the arrow. Balance the equation with simple whole numbers such tha ...
... Determine the types of reactants involved and the products formed in the reaction. Write down the correct formulae of reactants on the left hand side of the arrow. Write down the correct formulae of products on the right hand side of the arrow. Balance the equation with simple whole numbers such tha ...
Defects in ceramic structure 2
... the number of atoms or ions has to maintain that ratio, but only the number of sites. ...
... the number of atoms or ions has to maintain that ratio, but only the number of sites. ...
Electron Induced Fluorescence Spectra of Methane
... particle in any excited state, Y is a molecular fragment, [M-Y] molecule stripped of this fragment, and hv energy of a photon emitted during deexcitation. The processes mentioned above can be studied also in discharges. There are two great advantages of the presented method in comparison to discharg ...
... particle in any excited state, Y is a molecular fragment, [M-Y] molecule stripped of this fragment, and hv energy of a photon emitted during deexcitation. The processes mentioned above can be studied also in discharges. There are two great advantages of the presented method in comparison to discharg ...
TOPIC 12. THE ELEMENTS
... An irreplaceable gas with vital applications in magnetic resonance imaging machines is used and lost - filling party balloons! An object made from some metals retains a memory of its initial shape and if distorted, it will return to the original shape when heated. Origin of the elements. As discusse ...
... An irreplaceable gas with vital applications in magnetic resonance imaging machines is used and lost - filling party balloons! An object made from some metals retains a memory of its initial shape and if distorted, it will return to the original shape when heated. Origin of the elements. As discusse ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... 8 Which type of bonding is present in a sample of an element that is malleable? (1) ionic (3) nonpolar covalent (2) metallic (4) polar covalent 9 Which atom has the greatest attraction for the electrons in a chemical bond? (1) hydrogen (3) silicon (2) oxygen (4) sulfur ...
... 8 Which type of bonding is present in a sample of an element that is malleable? (1) ionic (3) nonpolar covalent (2) metallic (4) polar covalent 9 Which atom has the greatest attraction for the electrons in a chemical bond? (1) hydrogen (3) silicon (2) oxygen (4) sulfur ...
lecture1426861925
... which is generally attributed to partial reflection of electrons at the surface of the metal. The emission obtained from different faces of a metal is also found to vary and the vary and the value of A for polycrystalline materials is quite low. The number of material available for use as cathodes i ...
... which is generally attributed to partial reflection of electrons at the surface of the metal. The emission obtained from different faces of a metal is also found to vary and the vary and the value of A for polycrystalline materials is quite low. The number of material available for use as cathodes i ...
Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
... simplified by using an equation derived from the Ka expression called the HendersonHasselbalch Equation • The equation calculates the pH of a buffer from the Ka and initial concentrations of the weak acid and salt of the conjugate base – as long as the “x is small” approximation is valid ...
... simplified by using an equation derived from the Ka expression called the HendersonHasselbalch Equation • The equation calculates the pH of a buffer from the Ka and initial concentrations of the weak acid and salt of the conjugate base – as long as the “x is small” approximation is valid ...
Paramagnetic organometallic compounds – The example chromium
... one (n + 1)s, and three (n + 1)p), and a completely filled valence shell with eighteen electrons (i.e. the electron configuration of a noble gas) presages stability. The loss of a ligand (e.g. a CO molecule from Cr(CO)6) then leaves the metal with only 16 electrons, i.e. ‘coordinatively unsaturated’ ...
... one (n + 1)s, and three (n + 1)p), and a completely filled valence shell with eighteen electrons (i.e. the electron configuration of a noble gas) presages stability. The loss of a ligand (e.g. a CO molecule from Cr(CO)6) then leaves the metal with only 16 electrons, i.e. ‘coordinatively unsaturated’ ...
- Deans Community High School
... 10. a) Using the ionisation energies in the data booklet calculate the energy required For; ...
... 10. a) Using the ionisation energies in the data booklet calculate the energy required For; ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... • The higher elements in the group are metallic and lose electrons to form cations. • Oxides change from acidic to amphoteric to basic as you move down the group. • All Group 5A(15) elements form gaseous hydrides with the formula EH3. – All except NH3 are extremely reactive and toxic. ...
... • The higher elements in the group are metallic and lose electrons to form cations. • Oxides change from acidic to amphoteric to basic as you move down the group. • All Group 5A(15) elements form gaseous hydrides with the formula EH3. – All except NH3 are extremely reactive and toxic. ...