1 MATTER: Anything which occupies space , has volume and can
... a. An irregular shape or no regular arrangement of particles. b. A short range order i.e. regular arrangement of particle in small space. c. Do not have definite heat of fusion. Gradually soften/ melt/ fuses over a range of temperature. (not fixed) d. Isotropic in nature i.e. their physical properti ...
... a. An irregular shape or no regular arrangement of particles. b. A short range order i.e. regular arrangement of particle in small space. c. Do not have definite heat of fusion. Gradually soften/ melt/ fuses over a range of temperature. (not fixed) d. Isotropic in nature i.e. their physical properti ...
76 kJ/mole
... atomic orbitals (AO) having specific 1) shape and 2) spatial orientation. B. Most importantly, AOs can interact, combine and overlap to give more complex wave having new shape and spatial orientation. C. These new wave functions are called linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAOs) D. AOs, LCAOs ...
... atomic orbitals (AO) having specific 1) shape and 2) spatial orientation. B. Most importantly, AOs can interact, combine and overlap to give more complex wave having new shape and spatial orientation. C. These new wave functions are called linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAOs) D. AOs, LCAOs ...
Chemical bonding
... Chemical bonding • You should already know: – how to determine valence electrons – what kind of elements make up covalent and ionic bonds – which type of bond are electrons shared and which type of bond are electrons transferred – which elements gain electrons and which lose electrons ...
... Chemical bonding • You should already know: – how to determine valence electrons – what kind of elements make up covalent and ionic bonds – which type of bond are electrons shared and which type of bond are electrons transferred – which elements gain electrons and which lose electrons ...
Setting the stage
... five atoms, 15 with six atoms, 9 with seven atoms, 10 with eight atoms, 9 with nine atoms, 15 with ten or more atoms and 17 deuterated molecules. 204 different molecules altogether who‘s ingredients include H, C, N, O, F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, K, Ti, Fe, I. ...
... five atoms, 15 with six atoms, 9 with seven atoms, 10 with eight atoms, 9 with nine atoms, 15 with ten or more atoms and 17 deuterated molecules. 204 different molecules altogether who‘s ingredients include H, C, N, O, F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, K, Ti, Fe, I. ...
physical setting chemistry
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
Polarity of Molecules
... Valence bond (VB) model Combines the notion of electron-pair bonding (Lewis valence) with the idea of atomic orbitals Review atomic orbitals from Ch 6! ...
... Valence bond (VB) model Combines the notion of electron-pair bonding (Lewis valence) with the idea of atomic orbitals Review atomic orbitals from Ch 6! ...
1. Formulae, equations and amounts of substance
... Gas syringes can be used for a variety of experiments where the volume of a gas is measured, possibly to work out moles of gas or to follow reaction rates. The volume of a gas depends on pressure and temperature so when recording volume it is important to note down the temperature and pressure of th ...
... Gas syringes can be used for a variety of experiments where the volume of a gas is measured, possibly to work out moles of gas or to follow reaction rates. The volume of a gas depends on pressure and temperature so when recording volume it is important to note down the temperature and pressure of th ...
11 myp covalent bonding
... – As metals have 3 or less electrons in their valence shell, it’s easier to lose 1 or 2 or 3 electrons than gain 7 or 6 or 5 electrons. – Similarly, since most non-metals have 5 or more electrons in their valence shell, when they react with metals, it’s easier for them to gain 3 or 2 or 1 electrons ...
... – As metals have 3 or less electrons in their valence shell, it’s easier to lose 1 or 2 or 3 electrons than gain 7 or 6 or 5 electrons. – Similarly, since most non-metals have 5 or more electrons in their valence shell, when they react with metals, it’s easier for them to gain 3 or 2 or 1 electrons ...
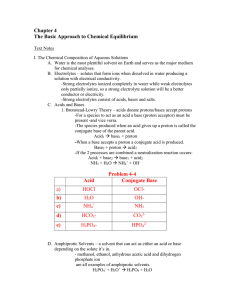
Chapter 4
... I. The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solutions A. Water is the most plentiful solvent on Earth and serves as the major medium for chemical analyses. B. Electrolytes – solutes that form ions when dissolved in water producing a solution with electrical conductivity. -Strong electrolytes ionized comp ...
... I. The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solutions A. Water is the most plentiful solvent on Earth and serves as the major medium for chemical analyses. B. Electrolytes – solutes that form ions when dissolved in water producing a solution with electrical conductivity. -Strong electrolytes ionized comp ...
Basics of Magnetism - Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced
... 3d transition element ions Details: If E is towards a fixed nucleus, classically all LX, LY, LZ are constants (fixed plane for a central force). In QM LZ & L2 are constants of motion but in a non-central field (as in a crystal) the orbital plane is not fixed & the components of L are not constants ...
... 3d transition element ions Details: If E is towards a fixed nucleus, classically all LX, LY, LZ are constants (fixed plane for a central force). In QM LZ & L2 are constants of motion but in a non-central field (as in a crystal) the orbital plane is not fixed & the components of L are not constants ...
1 Mole
... That’s right – open your book to page 323 and copy that table into your notes… go on… do it! This spot had better not be blank when I check your notebook! ...
... That’s right – open your book to page 323 and copy that table into your notes… go on… do it! This spot had better not be blank when I check your notebook! ...
Key Words Electronic Homework Problems Questions and Problems
... ular H2 is ionized first to H1 2 and then to H2 . 10.50 The formation of H2 from two H atoms is an energetically favorable process. Yet statistically there is less than a 100 percent chance that any two H atoms will undergo the reaction. Apart from energy considerations, how would you account for th ...
... ular H2 is ionized first to H1 2 and then to H2 . 10.50 The formation of H2 from two H atoms is an energetically favorable process. Yet statistically there is less than a 100 percent chance that any two H atoms will undergo the reaction. Apart from energy considerations, how would you account for th ...
Energetics of adsorption of neutral and charged molecules at the air
... groups are required to balance solvation of the charged group. Figure 4 shows the surface SH signal for a series ofpn-alkyl phenolate and anilinium ions at a fixed bulk concentration. In both cases, it can be seen that when the alkyl chain has five or more carbons, hydrophobicity overcomes solvation ...
... groups are required to balance solvation of the charged group. Figure 4 shows the surface SH signal for a series ofpn-alkyl phenolate and anilinium ions at a fixed bulk concentration. In both cases, it can be seen that when the alkyl chain has five or more carbons, hydrophobicity overcomes solvation ...
No Slide Title
... • Values of k0 reported in the literature for electrochemical reactions vary from about 10 cm/s for redox of aromatic hydrocarbons such as anthracene to about 109 cm/s for reduction of proton to molecular hydrogen • So electrochemistry deals with a range of more than 10 orders of magnitude in kinet ...
... • Values of k0 reported in the literature for electrochemical reactions vary from about 10 cm/s for redox of aromatic hydrocarbons such as anthracene to about 109 cm/s for reduction of proton to molecular hydrogen • So electrochemistry deals with a range of more than 10 orders of magnitude in kinet ...
Topic 9 Oxidation and Reduction Answers - slider-dpchemistry-11
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
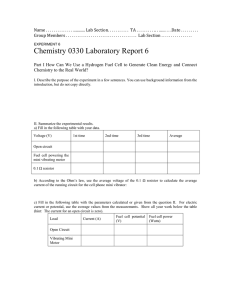
experiment 7 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... 4. Calculate the maximum electric work (in kJ/mol of H2) using an experimentally measured open circuit cell potential from the previous table assuming that only the reversible electrical work is performed at constant temperature and pressure. Compare this with the Wel max calculated under standard c ...
... 4. Calculate the maximum electric work (in kJ/mol of H2) using an experimentally measured open circuit cell potential from the previous table assuming that only the reversible electrical work is performed at constant temperature and pressure. Compare this with the Wel max calculated under standard c ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structure
... rod. The plastic pen held above the electroscope carries a static charge, which is transferred to the metals via inductance. Both metal surfaces pick up the same charge (both become either positively or negatively charged), so they repel and the gold sheet moves away from the fixed metal plate. Both ...
... rod. The plastic pen held above the electroscope carries a static charge, which is transferred to the metals via inductance. Both metal surfaces pick up the same charge (both become either positively or negatively charged), so they repel and the gold sheet moves away from the fixed metal plate. Both ...
UNIT 7 Lecture Notes
... • KCl(s) K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) • A chemical change is when chemical bonds are broken, atoms are rearranged, and new bonds are formed to create entirely new molecules or compounds • This is different than a nuclear change, which is when the atoms that make up the molecules change. • This is also differe ...
... • KCl(s) K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) • A chemical change is when chemical bonds are broken, atoms are rearranged, and new bonds are formed to create entirely new molecules or compounds • This is different than a nuclear change, which is when the atoms that make up the molecules change. • This is also differe ...
Lewis Acids and Bases Hard and Soft Acid/Base Theory
... Hard and Soft Acid/Base Theory Definitions of Lewis Acid-Base Theory. Lewis acid/base theory (sometimes called donor-acceptor theory) is a broad, widely applicable approach to the classification of chemical substances and the analysis of chemical reactions. According to this theory, a base is define ...
... Hard and Soft Acid/Base Theory Definitions of Lewis Acid-Base Theory. Lewis acid/base theory (sometimes called donor-acceptor theory) is a broad, widely applicable approach to the classification of chemical substances and the analysis of chemical reactions. According to this theory, a base is define ...
міністерство освіти і науки україни
... arrangement within the solid of a small representative group of atoms or molecules, called the ‘unit cell.’ By multiplying identical unit cells in three directions, the location of all the particles in the crystal is determined. In nature, 14 different types of crystal structures or lattices are fou ...
... arrangement within the solid of a small representative group of atoms or molecules, called the ‘unit cell.’ By multiplying identical unit cells in three directions, the location of all the particles in the crystal is determined. In nature, 14 different types of crystal structures or lattices are fou ...
Option A Materials - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... Because aluminium is more reactive than carbon, aluminium oxide cannot be reduced to aluminium by heating with carbon and electrolysis must be used. Alumina (aluminium oxide) is an ionic solid made up of Al3+ and O2− ions. In order to conduct electricity, the ions must be free to move. This requires ...
... Because aluminium is more reactive than carbon, aluminium oxide cannot be reduced to aluminium by heating with carbon and electrolysis must be used. Alumina (aluminium oxide) is an ionic solid made up of Al3+ and O2− ions. In order to conduct electricity, the ions must be free to move. This requires ...
No Slide Title
... (b) This is a combination reaction (two reactants form a single product). The oxidation number of Li changes from 0 to +1 while that of N changes from 0 to −3. (c) This is a metal displacement reaction. The Ni metal replaces (reduces) the Pb2+ ion. The oxidation number of Ni increases from 0 to +2 w ...
... (b) This is a combination reaction (two reactants form a single product). The oxidation number of Li changes from 0 to +1 while that of N changes from 0 to −3. (c) This is a metal displacement reaction. The Ni metal replaces (reduces) the Pb2+ ion. The oxidation number of Ni increases from 0 to +2 w ...