Period 4 - cloudfront.net
... In a glass of water, the molecules of water are kept in the glass and held to another by: Intramolecular forces, shared electrons, intermolecular forces, or ionic bonds? ...
... In a glass of water, the molecules of water are kept in the glass and held to another by: Intramolecular forces, shared electrons, intermolecular forces, or ionic bonds? ...
Solubility and Solubility Equilibrium
... Now, equilibrium is this idea of reversibility in chemical reactions. It might seem kind of oxymoronic to talk about equilibrium for insoluble species, but we can talk about equilibrium of insoluble molecules because, to some small extent, all insoluble products dissolve in solution and reach an equ ...
... Now, equilibrium is this idea of reversibility in chemical reactions. It might seem kind of oxymoronic to talk about equilibrium for insoluble species, but we can talk about equilibrium of insoluble molecules because, to some small extent, all insoluble products dissolve in solution and reach an equ ...
Chapter 8
... • The four regions of high electron density surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen ...
... • The four regions of high electron density surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... a. K1939 b. 2311Na. c. 20882Pb d. 3315P 21. White gold is an alloy that typically contains 45.0% by mass gold and the remainder is platinum. If 154 g of gold are available, how many grams of platinum are required to combine with the gold to form this alloy? 22. What is the empirical formula of a com ...
... a. K1939 b. 2311Na. c. 20882Pb d. 3315P 21. White gold is an alloy that typically contains 45.0% by mass gold and the remainder is platinum. If 154 g of gold are available, how many grams of platinum are required to combine with the gold to form this alloy? 22. What is the empirical formula of a com ...
Exam 2
... A. be harder and have a smaller atomic radius. B. have a higher melting temperature and a larger atomic radius. ...
... A. be harder and have a smaller atomic radius. B. have a higher melting temperature and a larger atomic radius. ...
Chapter 8
... • The four regions of high electron density surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen ...
... • The four regions of high electron density surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen ...
Electrochemistry - Menihek Home Page
... The oxidation number of hydrogen in its compounds is always +1 except in metal hydrides, where it is -1 (the oxidation number of H in CH4 is +1, but in CaH2, it is -1) ...
... The oxidation number of hydrogen in its compounds is always +1 except in metal hydrides, where it is -1 (the oxidation number of H in CH4 is +1, but in CaH2, it is -1) ...
12 U Chem Review
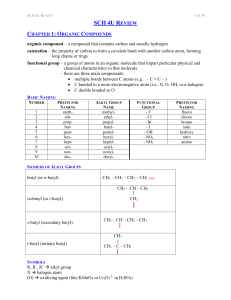
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
sch4ureview
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
Chapter 14 Acids and Bases
... • Dissociation refers to a reaction where a molecule or substance breaks apart into smaller units. • The units are not necessarily ions, although this is often the case. • Ionization generally refers to a reaction which forms ions from an uncharged species. ...
... • Dissociation refers to a reaction where a molecule or substance breaks apart into smaller units. • The units are not necessarily ions, although this is often the case. • Ionization generally refers to a reaction which forms ions from an uncharged species. ...
No Slide Title
... because the water molecules have a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom (-) and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms (+), where “” indicates a small positive or negative charge. The reason these partial charges exist will be discussed later in the semester. Because cations and ani ...
... because the water molecules have a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom (-) and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms (+), where “” indicates a small positive or negative charge. The reason these partial charges exist will be discussed later in the semester. Because cations and ani ...
ch19 MSJ jlm
... (This is also called electromotive force (emf) Why is this reaction spontaneous? Why is the voltage 0.46 volt? ...
... (This is also called electromotive force (emf) Why is this reaction spontaneous? Why is the voltage 0.46 volt? ...
CHE 128 Autumn 2011 Specific Objectives – Exam 1 A periodic
... Calculate volume given the three spatial dimensions (length, width, height) of a substance Calculate density of a substance based on its mass and volume Compare densities to determine which substance will float on top or sink to the bottom Convert units raised to a power Identify an example of matte ...
... Calculate volume given the three spatial dimensions (length, width, height) of a substance Calculate density of a substance based on its mass and volume Compare densities to determine which substance will float on top or sink to the bottom Convert units raised to a power Identify an example of matte ...
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... Imagine 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 balloons tied together: ...
... Imagine 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 balloons tied together: ...
Chemistry with Physics Structure for Quiz
... is easily compressed, and mixes with any other gases. ...
... is easily compressed, and mixes with any other gases. ...
physical setting chemistry
... 47 Which ionic equation represents a spontaneous reaction that can occur in a voltaic cell? (1) Cu(s) ⫹ Zn(s) → Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) (2) Cu(s) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) → Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn(s) (3) Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn(s) → Cu(s) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) (4) Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) → Cu(s) ⫹ Zn(s) ...
... 47 Which ionic equation represents a spontaneous reaction that can occur in a voltaic cell? (1) Cu(s) ⫹ Zn(s) → Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) (2) Cu(s) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) → Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn(s) (3) Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn(s) → Cu(s) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) (4) Cu2⫹(aq) ⫹ Zn2⫹(aq) → Cu(s) ⫹ Zn(s) ...
Chapter 18.2
... and oxidizing/reducing agents, as covered in Chemistry 1010, which is found in section 4.9 of the Tro text). ...
... and oxidizing/reducing agents, as covered in Chemistry 1010, which is found in section 4.9 of the Tro text). ...
Group 1: The Alkali Metals
... Properties and Facts about Alkali Metals Alkali metals are known for being some of the most reactive metals. This is due in part to their larger atomic radii and low ionization energies. They tend to donate their electrons in reactions and often have an oxidation state of +1. These metals are charac ...
... Properties and Facts about Alkali Metals Alkali metals are known for being some of the most reactive metals. This is due in part to their larger atomic radii and low ionization energies. They tend to donate their electrons in reactions and often have an oxidation state of +1. These metals are charac ...
lecture slides file
... Physical changes are reversible changes (in size, shape, state of matter, density) when no new substances are formed. Heating of Pt wire changes its appearance from silvery metallic to glowing yellowred. Upon cooling, original appearance is restored and no new compounds are formed. Shattered glass l ...
... Physical changes are reversible changes (in size, shape, state of matter, density) when no new substances are formed. Heating of Pt wire changes its appearance from silvery metallic to glowing yellowred. Upon cooling, original appearance is restored and no new compounds are formed. Shattered glass l ...
chapter4-bur.2917051..
... because the water molecules have a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom (-) and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms (+), where “” indicates a small positive or negative charge. The reason these partial charges exist will be discussed later in the semester. Because cations and ani ...
... because the water molecules have a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom (-) and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms (+), where “” indicates a small positive or negative charge. The reason these partial charges exist will be discussed later in the semester. Because cations and ani ...
THE s -BLOCK ELEMENTS OCK ELEMENTS THE s
... 49. The stability of peroxide and superoxide of alkali metals increase as we go down the group. Explain giving reason. 50. When water is added to compound (A) of calcium, solution of compound (B) is formed. When carbon dioxide is passed into the solution, it turns milky due to the formation of compo ...
... 49. The stability of peroxide and superoxide of alkali metals increase as we go down the group. Explain giving reason. 50. When water is added to compound (A) of calcium, solution of compound (B) is formed. When carbon dioxide is passed into the solution, it turns milky due to the formation of compo ...
Part One: Ions in Aqueous Solution A. Electrolytes and Non
... Formula unit equation: CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) Net ionic equation: Cu2+ (aq) + Zn(s) → Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) Displacement reaction: the more active metal, zinc, displaces ions of less active metal, ...
... Formula unit equation: CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) Net ionic equation: Cu2+ (aq) + Zn(s) → Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) Displacement reaction: the more active metal, zinc, displaces ions of less active metal, ...
Inorganic Chemistry 412 / 512
... (b) Is Pb4+ a stronger oxidant in acidic or basic solution, or is it oxidizing potential pH independent? Explain. [5] Stronger in acidic solution. See the downward slope of the Pb(IV)/Pb(II) equalibria in the above diagram. (c) Pb(IV) is a much stronger oxidant than Ge(IV). Explain. [6] The inert pa ...
... (b) Is Pb4+ a stronger oxidant in acidic or basic solution, or is it oxidizing potential pH independent? Explain. [5] Stronger in acidic solution. See the downward slope of the Pb(IV)/Pb(II) equalibria in the above diagram. (c) Pb(IV) is a much stronger oxidant than Ge(IV). Explain. [6] The inert pa ...