Concepts and relevance of genome
... more statistical power to show a genetic effect, but the case–control study design can also be effective in identifying multiple genes associated with the phenotype. We can see examples of each in the literature8 – 10 The statistical analysis of genome-wide association can begin once samples have be ...
... more statistical power to show a genetic effect, but the case–control study design can also be effective in identifying multiple genes associated with the phenotype. We can see examples of each in the literature8 – 10 The statistical analysis of genome-wide association can begin once samples have be ...
Table S1.
... Only genes are taken into account that overlap by at least one base pair with window. Attributes are then calculated at exon level for each exon that fulfils the patch overlap definition (overlap >25% of exon length or >10% of window size): _elen = total length of exonic DNA with window, standardize ...
... Only genes are taken into account that overlap by at least one base pair with window. Attributes are then calculated at exon level for each exon that fulfils the patch overlap definition (overlap >25% of exon length or >10% of window size): _elen = total length of exonic DNA with window, standardize ...
Additional file 5
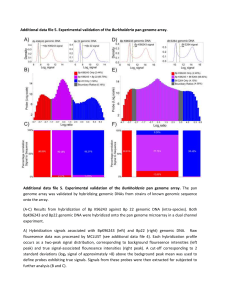
... D) Hybridization signals associated with BpK96243 (left) and BtE264 (right) genomic DNA. See panel A) for details. E) Probe distributions of common and strain-specific probes. Red probes correspond to probes showing true signals only in the BpK96243 hybridization, purple probes to those common to bo ...
... D) Hybridization signals associated with BpK96243 (left) and BtE264 (right) genomic DNA. See panel A) for details. E) Probe distributions of common and strain-specific probes. Red probes correspond to probes showing true signals only in the BpK96243 hybridization, purple probes to those common to bo ...
- Biological Sciences
... share conserved sequence positions with other vertebrate tRNA genes. Thus, the platypus genome exhibits neither the unusual structure of the tRNALys gene (Janke et al. 1994) nor the unconventional anticodon of the tRNAAsp gene (Janke and Pääbo 1993) seen in the marsupial Didelphis virginiana. Furt ...
... share conserved sequence positions with other vertebrate tRNA genes. Thus, the platypus genome exhibits neither the unusual structure of the tRNALys gene (Janke et al. 1994) nor the unconventional anticodon of the tRNAAsp gene (Janke and Pääbo 1993) seen in the marsupial Didelphis virginiana. Furt ...
Distribution in percentage Inter-environmental
... Want to know the diversity of a microbial community? FlowCan for physiology (limited to a few parameters) Pigments analysis (differentiate phylum only–takes years ) Sequencing a biomarker of diversity (e.g., 16S/18S) Very sensitive: detect thousands of lowly abundant taxa Want to know t ...
... Want to know the diversity of a microbial community? FlowCan for physiology (limited to a few parameters) Pigments analysis (differentiate phylum only–takes years ) Sequencing a biomarker of diversity (e.g., 16S/18S) Very sensitive: detect thousands of lowly abundant taxa Want to know t ...
The California Institute for Telecommunications and
... Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Jacobs School of Engineering, UCSD ...
... Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Jacobs School of Engineering, UCSD ...
2610//16 1 Allele-specific expression, ASE [1] Defini8on of allele
... Allele-specific expression, defini=on ...
... Allele-specific expression, defini=on ...
Geographic Distribution And Adaptive Significance
... expected that each sequence exists in 2 copies across the genome. However, recent studies have shown that a large portion of the genome actually deviates from 2 copies, caused by different genetic mechanisms, such as transposition, simple repeat expansions and segmental duplications (Conrad et al. 2 ...
... expected that each sequence exists in 2 copies across the genome. However, recent studies have shown that a large portion of the genome actually deviates from 2 copies, caused by different genetic mechanisms, such as transposition, simple repeat expansions and segmental duplications (Conrad et al. 2 ...
Molecular analysis of putative genetic factors affecting BSE
... the laboratory. Some of the samples were 6 years old and in very limited supply when used so the purity could not be improved. Given this variability between samples the study was continued by analysing individual samples, rather than pools. This was considerably more labour intensive, but increased ...
... the laboratory. Some of the samples were 6 years old and in very limited supply when used so the purity could not be improved. Given this variability between samples the study was continued by analysing individual samples, rather than pools. This was considerably more labour intensive, but increased ...
Microbial Ecology: Where are we now?
... diversity and the need to generate clone libraries due to inaccessibility of sequences (Egert and Friedrich 2003). Typing of Bacterial Pathogens. The need to characterize and differentiate bacterial pathogens has resulted in various identification schemes to understand their ecology and epidemiology ...
... diversity and the need to generate clone libraries due to inaccessibility of sequences (Egert and Friedrich 2003). Typing of Bacterial Pathogens. The need to characterize and differentiate bacterial pathogens has resulted in various identification schemes to understand their ecology and epidemiology ...
1 Single molecule sequencing of THCA synthase reveals
... Multiple primer pairs were designed to amplify THCAS, and the amplicons were sequenced using Pacific Bioscience’s circular consensus sequencing (CCS) method and a size-‐selected Illumina paired-‐250bp read system ...
... Multiple primer pairs were designed to amplify THCAS, and the amplicons were sequenced using Pacific Bioscience’s circular consensus sequencing (CCS) method and a size-‐selected Illumina paired-‐250bp read system ...
Documentation - Broad Institute
... dominant call or a variant seen frequently enough). This file is required as an input for v-profiler. b)
... dominant call or a variant seen frequently enough). This file is required as an input for v-profiler. b)
Background and Overview of Comparative Genomics
... These genes have functions in basic metabolism or in determining specialized characteristics of the thousands of different cell types that make up the human body. The protein product of a gene may act as an enzyme (or an enzyme subunit), a transport molecule, a structural protein, a hormone, or a re ...
... These genes have functions in basic metabolism or in determining specialized characteristics of the thousands of different cell types that make up the human body. The protein product of a gene may act as an enzyme (or an enzyme subunit), a transport molecule, a structural protein, a hormone, or a re ...
From essential to persistent genes
... take into account gene–environment interactions. Others have centered on comparative genomics, and this allowed scientists to compare genomes from closely or distantly related microorganisms. But as an ever-increasing number of genome projects were completed, the outcome of the comparisons did not i ...
... take into account gene–environment interactions. Others have centered on comparative genomics, and this allowed scientists to compare genomes from closely or distantly related microorganisms. But as an ever-increasing number of genome projects were completed, the outcome of the comparisons did not i ...
Query Results
... Download Sequence: If the tag matches an ORF (as it is in this example), the transcript sequence is given. The 5’ and 3’ UTRs, the start and stop codons, and the tag sequence are all highlighted. If the tag matches an intergenic region, the 500 flanking nucleotides upstream and downstrem the tag ar ...
... Download Sequence: If the tag matches an ORF (as it is in this example), the transcript sequence is given. The 5’ and 3’ UTRs, the start and stop codons, and the tag sequence are all highlighted. If the tag matches an intergenic region, the 500 flanking nucleotides upstream and downstrem the tag ar ...
Primer on Molecular Genetics
... heredity. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotide bases, whose sequences carry the information required for constructing proteins, which provide the structural components of cells and tissues as well as enzymes for essential biochemical reactions. The human genome is estimated to comprise at lea ...
... heredity. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotide bases, whose sequences carry the information required for constructing proteins, which provide the structural components of cells and tissues as well as enzymes for essential biochemical reactions. The human genome is estimated to comprise at lea ...
Human Heredity - Lyndhurst School
... produce red hair. An individual with red hair usually has two of these recessive alleles, inheriting a copy from each parent. Dominant alleles for the MC1R gene help produce darker hair colors. Another trait that displays simple dominance is the Rhesus, or Rh blood group. The allele for Rh factor co ...
... produce red hair. An individual with red hair usually has two of these recessive alleles, inheriting a copy from each parent. Dominant alleles for the MC1R gene help produce darker hair colors. Another trait that displays simple dominance is the Rhesus, or Rh blood group. The allele for Rh factor co ...
The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome XVI.
... some seems to be typical of the large yeast chromosomes, and shows large duplications with other yeast chromosomes. Chromosome XVI contains 487 potential protein-encoding genes, 17 tRNA genes and two small nuclear RNA genes; 27% of the genes have significant similarities to human gene products, and ...
... some seems to be typical of the large yeast chromosomes, and shows large duplications with other yeast chromosomes. Chromosome XVI contains 487 potential protein-encoding genes, 17 tRNA genes and two small nuclear RNA genes; 27% of the genes have significant similarities to human gene products, and ...
Statistically Significant Patterns in DNA Sequences
... the genomic sequence is short, a random occurence of the motif is not expected the genomic sequence is long, random occurences of motifs are expected, however, functional sites occure clustered resulting in local overrepresenation of sites a sequence or set of sequences is expected to have similar/h ...
... the genomic sequence is short, a random occurence of the motif is not expected the genomic sequence is long, random occurences of motifs are expected, however, functional sites occure clustered resulting in local overrepresenation of sites a sequence or set of sequences is expected to have similar/h ...
How Can Transposons Accelerate Your Genomics
... 1. Mix EZ-Tn5 Transposome with electrocompetent cells of choice 2. Place in electroporator cuvette and electroporate 3. Transfer to SOC/LB medium, incubate with shaking for 1 hour ...
... 1. Mix EZ-Tn5 Transposome with electrocompetent cells of choice 2. Place in electroporator cuvette and electroporate 3. Transfer to SOC/LB medium, incubate with shaking for 1 hour ...
molecularevolution.rnaseq
... Summary • Several methods now exist to build strand sepecific RNA-Seq libraries. • Quantification methods support strand specific libraries. For example Scripture will compute expression on both strand if desired. ...
... Summary • Several methods now exist to build strand sepecific RNA-Seq libraries. • Quantification methods support strand specific libraries. For example Scripture will compute expression on both strand if desired. ...
The dog genome map and its use in mammalian comparative
... Knowledge of the genome organization of a species of interest is required for detailed genetic analyses, including the identification of genes causing hereditary diseases and comparative genomic studies. In the recent years extraordinary progress has been achieved in the dog genome mapping. Moreover ...
... Knowledge of the genome organization of a species of interest is required for detailed genetic analyses, including the identification of genes causing hereditary diseases and comparative genomic studies. In the recent years extraordinary progress has been achieved in the dog genome mapping. Moreover ...
Molecular markers closely linked to fusarium resistance genes in
... Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. ciceri races 4 and 5 was used to develop DNA amplification fingerprinting markers linked to both resistance loci. Bulked segregant analysis revealed 19 new markers on linkage group 2 of the genetic map on which the resistance genes are located. Closest linkage (2.0 cM) was o ...
... Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. ciceri races 4 and 5 was used to develop DNA amplification fingerprinting markers linked to both resistance loci. Bulked segregant analysis revealed 19 new markers on linkage group 2 of the genetic map on which the resistance genes are located. Closest linkage (2.0 cM) was o ...
Whole genome sequencing

Whole genome sequencing (also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing) is a laboratory process that determines the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast.Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA profiling, which only determines the likelihood that genetic material came from a particular individual or group, and does not contain additional information on genetic relationships, origin or susceptibility to specific diseases. Also unlike full genome sequencing, SNP genotyping covers less than 0.1% of the genome. Almost all truly complete genomes are of microbes; the term ""full genome"" is thus sometimes used loosely to mean ""greater than 95%"". The remainder of this article focuses on nearly complete human genomes.High-throughput genome sequencing technologies have largely been used as a research tool and are currently being introduced in the clinics. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data will be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of gene sequencing at SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response.





![2610//16 1 Allele-specific expression, ASE [1] Defini8on of allele](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006248723_1-82195dc62ecf1cc4d0499f4ecaf3249f-300x300.png)