TDA8953 2 × 210 W class-D power amplifier
... switch on every 100 ms. The average power dissipation will be low in this situation because the duty cycle is short. Switching the amplifier on and off in this way will generate unwanted ‘audio holes’. This can be avoided by increasing the value of CPROT (up to 220 pF) to delay amplifier switch-off. ...
... switch on every 100 ms. The average power dissipation will be low in this situation because the duty cycle is short. Switching the amplifier on and off in this way will generate unwanted ‘audio holes’. This can be avoided by increasing the value of CPROT (up to 220 pF) to delay amplifier switch-off. ...
Modeling a Supercapacitor using PLECS
... [1]. The large surface area and extremely small separation distance results in a very large capacitance value. However, the small separation distance between the electrodes results in a low breakdown voltage of approximately 3V. Therefore, in practical applications, multiple supercapacitors are conn ...
... [1]. The large surface area and extremely small separation distance results in a very large capacitance value. However, the small separation distance between the electrodes results in a low breakdown voltage of approximately 3V. Therefore, in practical applications, multiple supercapacitors are conn ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon ICB1FL03G Smart Ballast Control IC for
... active L-level during UVLO (undervoltage lockout) and a limitation of the max. H-level at 11V during normal operation. Turning on the MOSFET softly (with reduced diDRAIN/dt), the Gate drive voltage rises within 220ns from L-level to H-level. The fall time of the Gate drive voltage is less than 50ns ...
... active L-level during UVLO (undervoltage lockout) and a limitation of the max. H-level at 11V during normal operation. Turning on the MOSFET softly (with reduced diDRAIN/dt), the Gate drive voltage rises within 220ns from L-level to H-level. The fall time of the Gate drive voltage is less than 50ns ...
Lecture 11: Symmetrical faults
... Two phases of a line may touch, or flashover may occur between two phases – a line-to-line fault. When two lines touch each other and also touch the ground, the fault is called a double line-to-ground fault. Lighting strokes cause most faults on high-voltage transmission lines producing a very high ...
... Two phases of a line may touch, or flashover may occur between two phases – a line-to-line fault. When two lines touch each other and also touch the ground, the fault is called a double line-to-ground fault. Lighting strokes cause most faults on high-voltage transmission lines producing a very high ...
ADM1175 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Current Sense Input Pin. A sense resistor between the VCC pin and the SENSE pin sets the analog current limit. The hot swap operation of the ADM1175 controls the external FET gate to maintain the (VCC − VSENSE) voltage at or below 100 mV. Undervoltage or Overvoltage Input Pin. This pin is active hig ...
... Current Sense Input Pin. A sense resistor between the VCC pin and the SENSE pin sets the analog current limit. The hot swap operation of the ADM1175 controls the external FET gate to maintain the (VCC − VSENSE) voltage at or below 100 mV. Undervoltage or Overvoltage Input Pin. This pin is active hig ...
LT5526 - High Linearity, Low Power Downconverting Mixer.
... external DC blocking capacitors). The LT5526 is characterized and production tested using single-ended LO drive. Low side or high side LO injection can be used. ...
... external DC blocking capacitors). The LT5526 is characterized and production tested using single-ended LO drive. Low side or high side LO injection can be used. ...
Series Circuit - Spring Branch ISD
... i. Does the equivalent resistance increase or decrease? [Increase to 6 Ω] ii. Does the current increase or decrease? [ Decrease to 1.67A] iii. What happens to the voltage drop across each resistor? [ Drops 3.33 V, 5V and 1.66V] 2. I have two bulbs of [ 2 Ω and 3Ω] in Parallel connected to a battery ...
... i. Does the equivalent resistance increase or decrease? [Increase to 6 Ω] ii. Does the current increase or decrease? [ Decrease to 1.67A] iii. What happens to the voltage drop across each resistor? [ Drops 3.33 V, 5V and 1.66V] 2. I have two bulbs of [ 2 Ω and 3Ω] in Parallel connected to a battery ...
Battery Powered Crossover for In-Ear Monitors Arttu Valtteri Nurmi
... There are a number of drawbacks with this method. First order filters have a very slow roll off into the stopband, which often causes overlap between two drivers; they both reproduce some of the same frequencies near the crossover region causing a hump in the response curve. Also the impedance of ba ...
... There are a number of drawbacks with this method. First order filters have a very slow roll off into the stopband, which often causes overlap between two drivers; they both reproduce some of the same frequencies near the crossover region causing a hump in the response curve. Also the impedance of ba ...
Solar PV Standard Plan - Simplified Central/String Inverter Systems
... SCOPE: Use this plan ONLY for utility-interactive central/string inverter systems not exceeding a system AC inverter output rating of 10kW on the roof of a one- or two-family dwelling or accessory structure. The photovoltaic system must interconnect to the load side of a single-phase AC service pane ...
... SCOPE: Use this plan ONLY for utility-interactive central/string inverter systems not exceeding a system AC inverter output rating of 10kW on the roof of a one- or two-family dwelling or accessory structure. The photovoltaic system must interconnect to the load side of a single-phase AC service pane ...
MAX8660/MAX8660A/MAX8660B/MAX8661 High-Efficiency, Low-I , PMICs with Dynamic Voltage Management for Mobile Applications
... and an 8th always-on LDO are integrated with powermanagement functions. Two dynamically controlled DCDC outputs power the processor core and internal memory. Two other DC-DC converters power I/O, memory, and other peripherals. Additional functions include on/off control for outputs, low-battery dete ...
... and an 8th always-on LDO are integrated with powermanagement functions. Two dynamically controlled DCDC outputs power the processor core and internal memory. Two other DC-DC converters power I/O, memory, and other peripherals. Additional functions include on/off control for outputs, low-battery dete ...
CHAPTER 5 MOS FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS (MOSFETs)
... p‐channel enhanced‐type MOSFETs are fabricated on n‐type substrate with p+ source and p+ drain Normally, source is connected to high voltage and drain is connected to low voltage As a negative voltage applies to the gate, the resulting field pushes electrons in n‐type substrate away from the sur ...
... p‐channel enhanced‐type MOSFETs are fabricated on n‐type substrate with p+ source and p+ drain Normally, source is connected to high voltage and drain is connected to low voltage As a negative voltage applies to the gate, the resulting field pushes electrons in n‐type substrate away from the sur ...
project reports
... The main motivation for this circuit design is to achive redundance in a three-phase power supply for a motor used subsea. The subsea application requires a power supply that can tolerate faults in some of the components without a drop in the output voltage. The circuit is made up of independent cel ...
... The main motivation for this circuit design is to achive redundance in a three-phase power supply for a motor used subsea. The subsea application requires a power supply that can tolerate faults in some of the components without a drop in the output voltage. The circuit is made up of independent cel ...
EE6503-Power Electronics
... 2. List the advantages of GTO over SCR 3. Examine the current commutation of SCR 4. Name the limitation of high frequency operation of a power electronic device 5. List the use of snubber circuit 6. Tabulate the various forced commutation techniques used to turn off SCR 7. Distinguish between SCR an ...
... 2. List the advantages of GTO over SCR 3. Examine the current commutation of SCR 4. Name the limitation of high frequency operation of a power electronic device 5. List the use of snubber circuit 6. Tabulate the various forced commutation techniques used to turn off SCR 7. Distinguish between SCR an ...
Lecture 4
... The complete circuit is fabricated on a single crystal of silicon and thus constitutes an integrated circuit. We simply note the relatively large number of active semiconductor devices — transistors — and the relatively small number of resistors and one capacitor. Such a distribution of components ...
... The complete circuit is fabricated on a single crystal of silicon and thus constitutes an integrated circuit. We simply note the relatively large number of active semiconductor devices — transistors — and the relatively small number of resistors and one capacitor. Such a distribution of components ...
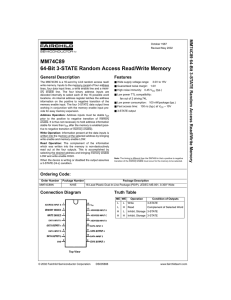
MM74C89 64-Bit 3-STATE Random Access Read/Write Memory
... prior to the positive to negative transition of memory enable. It is thus not necessary to hold address information stable for more than tHA after the memory is enabled (positive to negative transition of memory enable). Write Operation: Information present at the data inputs is written into the mem ...
... prior to the positive to negative transition of memory enable. It is thus not necessary to hold address information stable for more than tHA after the memory is enabled (positive to negative transition of memory enable). Write Operation: Information present at the data inputs is written into the mem ...
MAX6791–MAX6796 High-Voltage, Micropower, Single/Dual Linear Regulators with Supervisory Functions General Description
... (ENABLE1 and ENABLE2) that control each regulator independently. The single-output MAX6795/MAX6796 feature one enable input (ENABLE). All devices include a hold input (HOLD) that aids the implementation of a self-holding circuit without requiring external components. Once the regulator is enabled, s ...
... (ENABLE1 and ENABLE2) that control each regulator independently. The single-output MAX6795/MAX6796 feature one enable input (ENABLE). All devices include a hold input (HOLD) that aids the implementation of a self-holding circuit without requiring external components. Once the regulator is enabled, s ...
Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes
... Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky ...
... Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.