HR2000 - Monolithic Power System
... and the sweeping frequency is controlled to limit the preheat current. The preheat time and ignition time can be smartly set up for types of lamps and applications. Sufficient protection functions are provided for different fault modes such as over voltage, over current, over temperature, capacitive ...
... and the sweeping frequency is controlled to limit the preheat current. The preheat time and ignition time can be smartly set up for types of lamps and applications. Sufficient protection functions are provided for different fault modes such as over voltage, over current, over temperature, capacitive ...
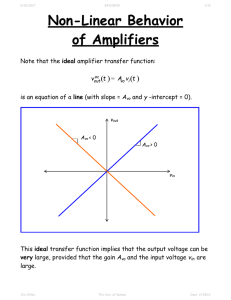
Non-Linear Behavior
... The derivative of the transfer curve for real amplifiers will not be a constant. We find that the gain of a amplifier will often be dependent on the input voltage! The main reason for this is amplifier saturation. Consider again the transfer function of an amplifier that saturates: ...
... The derivative of the transfer curve for real amplifiers will not be a constant. We find that the gain of a amplifier will often be dependent on the input voltage! The main reason for this is amplifier saturation. Consider again the transfer function of an amplifier that saturates: ...
Low Voltage circuit-breaker breaking techniques
... When the arcing current is low or drops, below 10 A for example, the heat energy exchanges may exceed internal arcing energy, causing the arc to «die» of cold. This results in an increase in arcing voltage (see fig. 4a). During this voltage rise, the arc may even suddenly be extinguished if it is "s ...
... When the arcing current is low or drops, below 10 A for example, the heat energy exchanges may exceed internal arcing energy, causing the arc to «die» of cold. This results in an increase in arcing voltage (see fig. 4a). During this voltage rise, the arc may even suddenly be extinguished if it is "s ...
Elect Machine Notes
... drops to the no-load current—which is nearly zero. This means the voltage drop across the resistive and reactive components of the transformer's primary side becomes very small. What's the net effect? In a noload situation, the voltage on the primary is almost equal to the supply voltage, and the se ...
... drops to the no-load current—which is nearly zero. This means the voltage drop across the resistive and reactive components of the transformer's primary side becomes very small. What's the net effect? In a noload situation, the voltage on the primary is almost equal to the supply voltage, and the se ...
A Comprehensive Study of Voltage Balancing Problem of Cascaded
... been presented, and successful operation has been demonstrated with DC capacitor balance maintained[11-18]. In [11], a voltage-balancing control algorithm including “clustered balancing control” between the three clusters and “individual balancing control” between the three cascaded H-bridge convert ...
... been presented, and successful operation has been demonstrated with DC capacitor balance maintained[11-18]. In [11], a voltage-balancing control algorithm including “clustered balancing control” between the three clusters and “individual balancing control” between the three cascaded H-bridge convert ...
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS for the RESIDUAL VOLTAGE
... 3. Total current of protected circuits must not exceed maximum current rating of the RCD/RCBO. 4. Fixed appliances such as ovens and hot water services should be connected on individual circuits as RCD/RCBO’s can be sensitive with these products. 5. Ensure the ‘Main Earth’ and ‘Main Neutral’ are in ...
... 3. Total current of protected circuits must not exceed maximum current rating of the RCD/RCBO. 4. Fixed appliances such as ovens and hot water services should be connected on individual circuits as RCD/RCBO’s can be sensitive with these products. 5. Ensure the ‘Main Earth’ and ‘Main Neutral’ are in ...
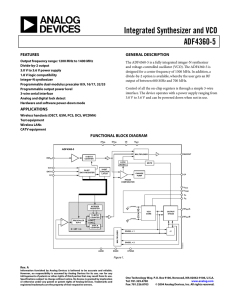
ADF4360-5 VCO-PLL - University of Toronto Physics
... Programmable dual-modulus prescaler 8/9, 16/17, 32/33 Programmable output power level 3-wire serial interface Analog and digital lock detect Hardware and software power-down mode ...
... Programmable dual-modulus prescaler 8/9, 16/17, 32/33 Programmable output power level 3-wire serial interface Analog and digital lock detect Hardware and software power-down mode ...
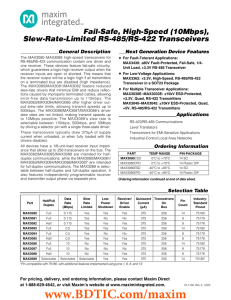
Fail-Safe, High-Speed (10Mbps), Slew-Rate-Limited RS-485/RS-422 Transceivers General Description Next Generation Device Features
... slew-rate drivers that minimize EMI and reduce reflections caused by improperly terminated cables, allowing error-free data transmission up to 115kbps. The MAX3083/MAX3084/MAX3085 offer higher driver output slew-rate limits, allowing transmit speeds up to 500kbps. The MAX3086/MAX3087/MAX3088’s drive ...
... slew-rate drivers that minimize EMI and reduce reflections caused by improperly terminated cables, allowing error-free data transmission up to 115kbps. The MAX3083/MAX3084/MAX3085 offer higher driver output slew-rate limits, allowing transmit speeds up to 500kbps. The MAX3086/MAX3087/MAX3088’s drive ...
Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using PIC16F877A Controller
... applications. They typically synthesize the stair-case voltage waveform (from several dc sources) which has reduced harmonic content. In this work hardware model of five level single phase cascade H-bridge multilevel inverter has been developed using MOSFET switches. The gating pulses are given to M ...
... applications. They typically synthesize the stair-case voltage waveform (from several dc sources) which has reduced harmonic content. In this work hardware model of five level single phase cascade H-bridge multilevel inverter has been developed using MOSFET switches. The gating pulses are given to M ...
AD7888 数据手册DataSheet下载
... Reference Input/Output. The on-chip reference is available on this pin for use external to the AD7888. Alternatively, the internal reference can be disabled and an external reference applied to this input. The voltage range for the external reference is from 1.2 V to VDD. Power Supply Input. The VDD ...
... Reference Input/Output. The on-chip reference is available on this pin for use external to the AD7888. Alternatively, the internal reference can be disabled and an external reference applied to this input. The voltage range for the external reference is from 1.2 V to VDD. Power Supply Input. The VDD ...
Clipper Circuits
... +10V), the 6V zener turns on and clips at +6.0V. The 8V zener is now a forward biased diode, which has another 0.7V drop across it, for a total of 6.7V. This configuration is fairly common. If you want to protect an electronic device from abuse, two zeners are often placed across the input pins as s ...
... +10V), the 6V zener turns on and clips at +6.0V. The 8V zener is now a forward biased diode, which has another 0.7V drop across it, for a total of 6.7V. This configuration is fairly common. If you want to protect an electronic device from abuse, two zeners are often placed across the input pins as s ...
Keysight Technologies Sheet Resistance/Resistivity Measurement
... the total EMF in the voltage measurement path. Because these errors are included in both measurements, taking subtraction of these two measurements can provide the R, eliminating these error factors. Here the thermo-EMF is assumed the same for both Isp and Isn. When considering drift factors, it is ...
... the total EMF in the voltage measurement path. Because these errors are included in both measurements, taking subtraction of these two measurements can provide the R, eliminating these error factors. Here the thermo-EMF is assumed the same for both Isp and Isn. When considering drift factors, it is ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.