The Field Effect Transistor
... drain current decreases with the gate voltage until a point where it is essentially zero. This is the so-called pinch-off voltage. ...
... drain current decreases with the gate voltage until a point where it is essentially zero. This is the so-called pinch-off voltage. ...
Exam questions
... scale the output voltage waveform from (a) A half-wave rectifier (b) A bridge rectifier Assume that silicon diodes are used in each case. 11. Explain why a smoothing capacitor is used in conjunction with rectifier circuits. Sketch the circuit of a simple half-wave rectifier showing how the smoothing ...
... scale the output voltage waveform from (a) A half-wave rectifier (b) A bridge rectifier Assume that silicon diodes are used in each case. 11. Explain why a smoothing capacitor is used in conjunction with rectifier circuits. Sketch the circuit of a simple half-wave rectifier showing how the smoothing ...
8. Logic Gates. - Badhan Education
... Look at two input of AND gate at figure (A). When both switches are in the ground position both diode are conducting and the output is low. If SI is switched to +5 v and S-II is left in ground position then the output is still low because D-2 still conducts continuously. If S-I is in ground position ...
... Look at two input of AND gate at figure (A). When both switches are in the ground position both diode are conducting and the output is low. If SI is switched to +5 v and S-II is left in ground position then the output is still low because D-2 still conducts continuously. If S-I is in ground position ...
Risistor
... LDRs or Light Dependent Resistors are very useful especially in light/dark sensor circuits. ...
... LDRs or Light Dependent Resistors are very useful especially in light/dark sensor circuits. ...
Operational_Amplifiers
... non-inverting and inverting inputs; use operational amplifiers which require a single power supply, i.e. 3140 IC; use an operational amplifier as a comparator and an inverting amplifier; know how to limit the gain of an operational amplifier by using an input resistor and a feedback resistor (negati ...
... non-inverting and inverting inputs; use operational amplifiers which require a single power supply, i.e. 3140 IC; use an operational amplifier as a comparator and an inverting amplifier; know how to limit the gain of an operational amplifier by using an input resistor and a feedback resistor (negati ...
realization of ternary-logic based shift up, shift down using mosfet
... bit input there is only the possibility of constructing four gates. Hence, it is apparent that the lack of hitherto unseen logic gates in the field of ternary logic has hampered further research in it. The use of new gates permits us to radically redesign familiar elements such as adders, subtractor ...
... bit input there is only the possibility of constructing four gates. Hence, it is apparent that the lack of hitherto unseen logic gates in the field of ternary logic has hampered further research in it. The use of new gates permits us to radically redesign familiar elements such as adders, subtractor ...
Unit 10 (Electricity) - Ms. Voit`s Physics Wiki
... Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Redraw the circuit with its equivalent resistance. Find the current through the battery. Using ohm’s law, find the current through and voltage drop across each resistor. (6A, 4A & 8V, 1.33A & 8V, 6.67A & 8V) V = 8 volts s ...
... Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Redraw the circuit with its equivalent resistance. Find the current through the battery. Using ohm’s law, find the current through and voltage drop across each resistor. (6A, 4A & 8V, 1.33A & 8V, 6.67A & 8V) V = 8 volts s ...
Ohm`s Law Foldable
... V is Voltage, measured in Volts Voltage is usually provided by a battery voltage drops across each resistor in a series and will change the elecric potential Voltage drops in parallel, always equal to the total voltage series batteries are added to increase voltage parallel batteries equal the volta ...
... V is Voltage, measured in Volts Voltage is usually provided by a battery voltage drops across each resistor in a series and will change the elecric potential Voltage drops in parallel, always equal to the total voltage series batteries are added to increase voltage parallel batteries equal the volta ...
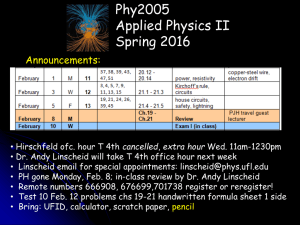
View Presentation
... •Reduce the ISC leading to “double reduction”: lower VDD and lower ISC •Reduce leakage power by 2.5 to 9 times. ...
... •Reduce the ISC leading to “double reduction”: lower VDD and lower ISC •Reduce leakage power by 2.5 to 9 times. ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.