Lecture_2_f01_p2
... If a constant input is to be applied to an IC from outside, it is generally a good idea to include a resistance between the ground or supply and the input for the following reasons: o prevents a large current at the input for some technologies at power-up that can cause damage or disable the IC. o a ...
... If a constant input is to be applied to an IC from outside, it is generally a good idea to include a resistance between the ground or supply and the input for the following reasons: o prevents a large current at the input for some technologies at power-up that can cause damage or disable the IC. o a ...
16-V to +80-V, Low - Texas Instruments
... – 0.6-V Internal Voltage Reference Quiescent Current: 1800 μA (Max) Latch-Up Exceeds 100 mA per JESD78 Package: VSSOP-8 ...
... – 0.6-V Internal Voltage Reference Quiescent Current: 1800 μA (Max) Latch-Up Exceeds 100 mA per JESD78 Package: VSSOP-8 ...
Data Sheet General Description
... The AUR9807 selects the power source automatically. In the absence of the input source (AC adapter or USB), the battery is chosen to power the system. Under this circumstance, the AUR9807 consumes less than 5µ Ampere; the power path resistance from the battery to the system is only 40mΩ (3); all the ...
... The AUR9807 selects the power source automatically. In the absence of the input source (AC adapter or USB), the battery is chosen to power the system. Under this circumstance, the AUR9807 consumes less than 5µ Ampere; the power path resistance from the battery to the system is only 40mΩ (3); all the ...
Single-Cell Li-Ion Charge Management IC for PDAs and Internet
... The bq2400x series ICs are advanced Li-Ion linear charge management devices for highly integrated and space-limited applications. They combine highaccuracy current and voltage regulation; FET passtransistor and reverse-blocking Schottky; battery conditioning, temperature, or input-power monitoring; ...
... The bq2400x series ICs are advanced Li-Ion linear charge management devices for highly integrated and space-limited applications. They combine highaccuracy current and voltage regulation; FET passtransistor and reverse-blocking Schottky; battery conditioning, temperature, or input-power monitoring; ...
V Loading Effects and Input Resistance
... Cards with desirable low output resistance include op-amp circuits, comparators, and logic gates. Op-amp circuits can also be linear, which helps to account for their ubiquity. Cards with desirable high input resistance include comparators, logic gates, and op-amp circuits where inputs are connected ...
... Cards with desirable low output resistance include op-amp circuits, comparators, and logic gates. Op-amp circuits can also be linear, which helps to account for their ubiquity. Cards with desirable high input resistance include comparators, logic gates, and op-amp circuits where inputs are connected ...
Instructions for Using Circuit System Design Method Cards
... Cards with desirable low output resistance include op-amp circuits, comparators, and logic gates. Op-amp circuits can also be linear, which helps to account for their ubiquity. Cards with desirable high input resistance include comparators, logic gates, and op-amp circuits where inputs are connected ...
... Cards with desirable low output resistance include op-amp circuits, comparators, and logic gates. Op-amp circuits can also be linear, which helps to account for their ubiquity. Cards with desirable high input resistance include comparators, logic gates, and op-amp circuits where inputs are connected ...
60VIN, 3A Synchronous Buck Regulator
... return path for the step-down regulator power stage and should be tied together. The negative terminal of the input decoupling capacitor should be placed as close as possible to these pins. Switch Node. The SW pins are the internal power switch outputs. These pins should be tied together and connect ...
... return path for the step-down regulator power stage and should be tied together. The negative terminal of the input decoupling capacitor should be placed as close as possible to these pins. Switch Node. The SW pins are the internal power switch outputs. These pins should be tied together and connect ...
LM3916 Dot/Bar Display Driver (Rev. A)
... LM3916 is set up with 10V full scale across its voltage divider, the turn-on point for the first LED is only 450 mV. A simple silicon diode rectifier won’t work well at the low end due to the 600 mV diode threshold. The half-wave peak detector in Figure 3 uses a PNP emitter-follower in front of the ...
... LM3916 is set up with 10V full scale across its voltage divider, the turn-on point for the first LED is only 450 mV. A simple silicon diode rectifier won’t work well at the low end due to the 600 mV diode threshold. The half-wave peak detector in Figure 3 uses a PNP emitter-follower in front of the ...
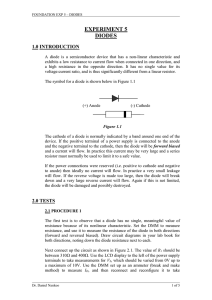
Diodes - staff.city.ac.uk
... a high resistance in the opposite direction. It has no single value for its voltage:current ratio, and is thus significantly different from a linear resistor. The symbol for a diode is shown below in Figure 1.1 ...
... a high resistance in the opposite direction. It has no single value for its voltage:current ratio, and is thus significantly different from a linear resistor. The symbol for a diode is shown below in Figure 1.1 ...
CHAPTER 3: ANALOGUE SUB-SYSTEMS DESIGN
... transistors have aspect ratios of 5/1 and 15/1, respectively. The basic concept of its operation is based on using various stages of current mirrors to keep “mirroring” the IREF from the beta-multiplier. Since IREF is mirrored through the PMOS and NMOS cascode current mirror structures and since the ...
... transistors have aspect ratios of 5/1 and 15/1, respectively. The basic concept of its operation is based on using various stages of current mirrors to keep “mirroring” the IREF from the beta-multiplier. Since IREF is mirrored through the PMOS and NMOS cascode current mirror structures and since the ...
FAN2306 / FAN2306M TinyBuck™ 6 A Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator F A
... Analog ground for the analog portions of the IC and for substrate ...
... Analog ground for the analog portions of the IC and for substrate ...
A 3-V, 6-Bit C-2C Digital-to-Analog Converter Using Complementary
... twice that of the unit capacitor and thus significantly reducing the time constants. Furthermore, a 6-bit binary-weighted DAC requires 64 unit capacitors, which is a large sum that is difficult to accomplish with high yield at this nascent stage of process development. A 6-bit C-2C DAC only requires ...
... twice that of the unit capacitor and thus significantly reducing the time constants. Furthermore, a 6-bit binary-weighted DAC requires 64 unit capacitors, which is a large sum that is difficult to accomplish with high yield at this nascent stage of process development. A 6-bit C-2C DAC only requires ...
A Transient-Enhanced Low-Quiescent Current Low
... prevent an accidental turn off or resetting of the portable device. These four major performance requirements of the LDO, including low dropout voltage, high output current, low no-load quiescent current, and small output transient undershoots and overshoots are, however, difficult to achieve simult ...
... prevent an accidental turn off or resetting of the portable device. These four major performance requirements of the LDO, including low dropout voltage, high output current, low no-load quiescent current, and small output transient undershoots and overshoots are, however, difficult to achieve simult ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.