CHAPTER 18
... polymerase-dependent DNA synthesis but does not depend upon premature termination. – It identifies the individual nucleotides as they are being incorporated by the polymerase in real time. ...
... polymerase-dependent DNA synthesis but does not depend upon premature termination. – It identifies the individual nucleotides as they are being incorporated by the polymerase in real time. ...
A crime scene often is rich in information that reveals the nature of
... involving homeland securities, for which forensic evidence can be gathered. The term “forensic science” encompasses a broad range of forensic disciplines, each with its own set of technologies and practices. Some of the forensic science disciplines are laboratory based (e.g., nuclear and mitochondri ...
... involving homeland securities, for which forensic evidence can be gathered. The term “forensic science” encompasses a broad range of forensic disciplines, each with its own set of technologies and practices. Some of the forensic science disciplines are laboratory based (e.g., nuclear and mitochondri ...
Big_Idea_3_Multiple_Choice_Questions-2013-03
... c. Locate the gene using a DNA sequencer, remove the gene from the genome, amplify the amount of DNA using polymerase chain reaction, insert the gene onto a plasmid, transform bacteria using the plasmid d. Locate the gene using a DNA sequencer, remove the gene from the genome, amplify the amount of ...
... c. Locate the gene using a DNA sequencer, remove the gene from the genome, amplify the amount of DNA using polymerase chain reaction, insert the gene onto a plasmid, transform bacteria using the plasmid d. Locate the gene using a DNA sequencer, remove the gene from the genome, amplify the amount of ...
Ch11 Answers to Concept Check Questions
... Concept check questions (in figure legends) FIGURE 11.1 Concept check: Explain why the mouse in part (d) died. Answer: In this experiment, the type R bacteria had taken up genetic material from the heat-killed type S bacteria, which converted the type R bacteria into type S. This enabled them to pro ...
... Concept check questions (in figure legends) FIGURE 11.1 Concept check: Explain why the mouse in part (d) died. Answer: In this experiment, the type R bacteria had taken up genetic material from the heat-killed type S bacteria, which converted the type R bacteria into type S. This enabled them to pro ...
Homework 1
... 1) _____ The human insulin gene and the cow insulin gene are: A) paralogs B) alleles C) orthologs D) mutations E) analogues 2) _____ The fastest method to search for the chicken insulin gene using the human insulin gene is: A) PCR B) BLAST! C) gene amplification D) crystallography E) DNA purificatio ...
... 1) _____ The human insulin gene and the cow insulin gene are: A) paralogs B) alleles C) orthologs D) mutations E) analogues 2) _____ The fastest method to search for the chicken insulin gene using the human insulin gene is: A) PCR B) BLAST! C) gene amplification D) crystallography E) DNA purificatio ...
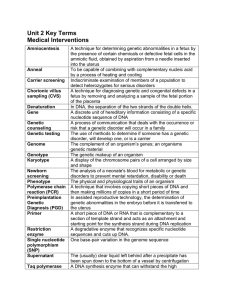
Unit 2 Terms
... risk that a genetic disorder will occur in a family The use of methods to determine if someone has a genetic disorder, will develop one, or is a carrier The complement of an organism’s genes; an organisms genetic material The genetic makeup of an organism A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell ...
... risk that a genetic disorder will occur in a family The use of methods to determine if someone has a genetic disorder, will develop one, or is a carrier The complement of an organism’s genes; an organisms genetic material The genetic makeup of an organism A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell ...
Genetics AIMS Review
... 26 Steven went to a farm and picked a bright red tomato from a broken branch on the plant. The tomato had a rotten spot with a worm inside of it. Instead of eating the tomato, Steven decided to plant the seeds and grow new tomato plants. Which characteristic of the tomato plant is inherited and coul ...
... 26 Steven went to a farm and picked a bright red tomato from a broken branch on the plant. The tomato had a rotten spot with a worm inside of it. Instead of eating the tomato, Steven decided to plant the seeds and grow new tomato plants. Which characteristic of the tomato plant is inherited and coul ...
Nucleic Acids
... • Nucleoside = nitrogenous base + sugar • There are two families of nitrogenous bases: ...
... • Nucleoside = nitrogenous base + sugar • There are two families of nitrogenous bases: ...
Chapter 16, Extranuclear inheritance
... • Chloroplasts have more genes than mitochondria (110 vs. 37). Most genes are involved in photosynthesis. • Corn has 20-40 chloroplasts per cell, with ...
... • Chloroplasts have more genes than mitochondria (110 vs. 37). Most genes are involved in photosynthesis. • Corn has 20-40 chloroplasts per cell, with ...
Protein Synthesis
... – Delivers amino acids to enzymes at ribosomes, in the order dictated by mRNA, to build correct polypeptide Where is RNA made? What two kinds of molecules make up a ribosome? Where do you find ribosomes in a cell? ...
... – Delivers amino acids to enzymes at ribosomes, in the order dictated by mRNA, to build correct polypeptide Where is RNA made? What two kinds of molecules make up a ribosome? Where do you find ribosomes in a cell? ...
File
... products? • Review: Gene = a section of DNA that codes for a physical trait • If a gene produces a trait, we can use technology to isolate the gene and insert it into another organism – Example: Gene for weight was inserted into mice in order to study obesity! ...
... products? • Review: Gene = a section of DNA that codes for a physical trait • If a gene produces a trait, we can use technology to isolate the gene and insert it into another organism – Example: Gene for weight was inserted into mice in order to study obesity! ...
Genetics Quiz – 18 October 2005
... 12. plant cell division differs in the formation of a cleavage furrow False 13. Mendel was the American involved in discovery of DNA structure False 14. the genetic code on DNA is first translated into mRNA and then transcribed into a poly peptide False 15. eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotes i ...
... 12. plant cell division differs in the formation of a cleavage furrow False 13. Mendel was the American involved in discovery of DNA structure False 14. the genetic code on DNA is first translated into mRNA and then transcribed into a poly peptide False 15. eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotes i ...
Biology UNIT 2 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of traits Big Ideas
... Each chromosome consists of a single very long DNA molecule, and each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of that DNA. The instructions for forming species’ characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes used (expressed) by the ...
... Each chromosome consists of a single very long DNA molecule, and each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of that DNA. The instructions for forming species’ characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes used (expressed) by the ...
DNA Review
... Complementary Strands Double Helix has two strands: • Complementary – means when you read the message on one strand, you automatically know the message on other strand • Not identical, because in reverse • “Antiparallel” strands • Exact same message on both strands ...
... Complementary Strands Double Helix has two strands: • Complementary – means when you read the message on one strand, you automatically know the message on other strand • Not identical, because in reverse • “Antiparallel” strands • Exact same message on both strands ...
DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
... 8. When grouping the nitrogen bases by similar characteristics, the pyrimidines have ________________(amt.) of rings and consist of the bases of _______________ and ___________________. 9. Singular ringed bases pair with double-ringed bases when forming DNA, what are the 2 combination of base pairs? ...
... 8. When grouping the nitrogen bases by similar characteristics, the pyrimidines have ________________(amt.) of rings and consist of the bases of _______________ and ___________________. 9. Singular ringed bases pair with double-ringed bases when forming DNA, what are the 2 combination of base pairs? ...
Introductory Biological Sequence Analysis Through Spreadsheets
... Recording the results of many trials Simresult Trial # alignment 0.271429 this is updated each time any cell is entered ...
... Recording the results of many trials Simresult Trial # alignment 0.271429 this is updated each time any cell is entered ...
Scientists Say They`ve Found a Code Beyond Genetics in DNA
... was “a profound insight if true,” because it would explain many aspects of how the DNA is controlled. The nucleosome is made up of proteins known as histones, which are among the most highly conserved in evolution, meaning that they change very little from one species to another. A histone of peas a ...
... was “a profound insight if true,” because it would explain many aspects of how the DNA is controlled. The nucleosome is made up of proteins known as histones, which are among the most highly conserved in evolution, meaning that they change very little from one species to another. A histone of peas a ...
DNA Technology Notes (13.1 & 13.2)
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/clickandclone/ ...
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/clickandclone/ ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.