Selective Breeding
... Insertion of gene may interfere with workings of other genes causing disease A superior transgenic organism that escaped into the environment may damage the ecosystem (food chains) ...
... Insertion of gene may interfere with workings of other genes causing disease A superior transgenic organism that escaped into the environment may damage the ecosystem (food chains) ...
Chapter 15 Genetic Engeneering
... – Introducing mutations has allowed scientists to develop hundreds of useful bacterial strains, including bacteria that can clean up oil spills. ...
... – Introducing mutations has allowed scientists to develop hundreds of useful bacterial strains, including bacteria that can clean up oil spills. ...
Advanced Environmental Biotechnology II
... it would be good to study nucleic acids directly from environmental samples. This would be representative of the microbial genomes in the samples. The analysis of DNA can give information on the structural diversity of environmental samples, or on the presence or absence of certain functional genes ...
... it would be good to study nucleic acids directly from environmental samples. This would be representative of the microbial genomes in the samples. The analysis of DNA can give information on the structural diversity of environmental samples, or on the presence or absence of certain functional genes ...
Transcription/Translation Notes Handout
... the DNA once the gene is transcribed. Transcription makes three types of RNA. – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a _______________. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of _______________________________ where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings _____ ...
... the DNA once the gene is transcribed. Transcription makes three types of RNA. – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a _______________. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of _______________________________ where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings _____ ...
E. coli - Sonoma Valley High School
... Separate DNA fragments by size Gel made of agarose or polyacrylamide Submersed in buffer that can carry current Subjected to an electrical field Negatively-charged DNA migrates towards the ...
... Separate DNA fragments by size Gel made of agarose or polyacrylamide Submersed in buffer that can carry current Subjected to an electrical field Negatively-charged DNA migrates towards the ...
CS262 Discussion Section 4
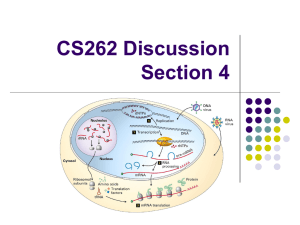
... regions are classified according to their effect on the protein synthesized. ...
... regions are classified according to their effect on the protein synthesized. ...
http://www - TeacherWeb
... How is DNA technology used to screen for cancer and other disease causing cells? How can DNA technology treat cancers and other diseases? Introduction: There are more than 4,000 genetic diseases currently identified - most are very rare, but some are relatively widespread, especially within certain ...
... How is DNA technology used to screen for cancer and other disease causing cells? How can DNA technology treat cancers and other diseases? Introduction: There are more than 4,000 genetic diseases currently identified - most are very rare, but some are relatively widespread, especially within certain ...
DNA
... Nucleotides and bases" • Nucleotides are the individual units of DNA." • A DNA nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, the sugar deoxyribose, and one or more ...
... Nucleotides and bases" • Nucleotides are the individual units of DNA." • A DNA nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, the sugar deoxyribose, and one or more ...
pGLO Transformation
... green color under ultraviolet light. In this activity, you will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria naturally contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usuall ...
... green color under ultraviolet light. In this activity, you will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria naturally contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usuall ...
Welcome to DNA Replication 101
... If one cell is going to divide to produce two new cells, the first cell must copy all of its parts before it can split in half. The cell grows, makes more organelles, and copies its genetic information (the DNA) so that the new cells each have a copy of everything they need. Cells use a process call ...
... If one cell is going to divide to produce two new cells, the first cell must copy all of its parts before it can split in half. The cell grows, makes more organelles, and copies its genetic information (the DNA) so that the new cells each have a copy of everything they need. Cells use a process call ...
Lecture#23 - Cloning genes by complementation
... 1. The isolation of genes proceeds via screening libraries for a gene of interest. 2. A clone containing a specific gene may be identified if it is able to complement a host mutation (single cell organisms). 3. Unfortunately, most genes in most organisms, especially eukaryotes, cannot be isolated by ...
... 1. The isolation of genes proceeds via screening libraries for a gene of interest. 2. A clone containing a specific gene may be identified if it is able to complement a host mutation (single cell organisms). 3. Unfortunately, most genes in most organisms, especially eukaryotes, cannot be isolated by ...
Biology Topic 2
... Each sugar of the backbone (sides of the "ladder") is covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base. Each of these bases forms hydrogen bonds with its complimentary nitrogenous base, forming the '"rungs" of the "ladder". The sides of the ladder are composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups. The r ...
... Each sugar of the backbone (sides of the "ladder") is covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base. Each of these bases forms hydrogen bonds with its complimentary nitrogenous base, forming the '"rungs" of the "ladder". The sides of the ladder are composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups. The r ...
genetics-1 - MacsScienceSpace
... d) changes in chromosome number or structure 52) Breeders have developed corn with 15-foot stalks and pumpkins weighing 300 pounds. Which method did these breeders most likely use to develop these new varieties? a) regeneration b) natural selection c) artificial selection d) grafting 53) What is the ...
... d) changes in chromosome number or structure 52) Breeders have developed corn with 15-foot stalks and pumpkins weighing 300 pounds. Which method did these breeders most likely use to develop these new varieties? a) regeneration b) natural selection c) artificial selection d) grafting 53) What is the ...
Lab 9 - Cloning GFP Lab
... green color under ultraviolet light. In this activity, you will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria naturally contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usuall ...
... green color under ultraviolet light. In this activity, you will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria naturally contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usuall ...
DNA Replication - Toronto District Christian High School
... on what we can and cannot clone? There are, many ways in which we currently use cloning. For example, cloning is used in agriculture to produce many copies of the same high-quality crop plant. In medicine, cloning is used to produce identical strains of bacteria for research. More common than the cl ...
... on what we can and cannot clone? There are, many ways in which we currently use cloning. For example, cloning is used in agriculture to produce many copies of the same high-quality crop plant. In medicine, cloning is used to produce identical strains of bacteria for research. More common than the cl ...
RNA base pairing Worksheet
... When a cell creates RNA (transcription), the original DNA ladder is broken apart and new RNA nucleotides are added to one of the strands (template strand). This creates a single stranded RNA molecule. ...
... When a cell creates RNA (transcription), the original DNA ladder is broken apart and new RNA nucleotides are added to one of the strands (template strand). This creates a single stranded RNA molecule. ...
iProof™ High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase - Bio-Rad
... iProof polymerase in HF buffer (4.4 x 10-7) is lower than that in GC buffer (9.5 x 10-7). Therefore, the HF buffer should be used as the default buffer for high fidelity amplification. However, the GC buffer can improve iProof performance on certain difficult or long templates, i.e. GC rich template ...
... iProof polymerase in HF buffer (4.4 x 10-7) is lower than that in GC buffer (9.5 x 10-7). Therefore, the HF buffer should be used as the default buffer for high fidelity amplification. However, the GC buffer can improve iProof performance on certain difficult or long templates, i.e. GC rich template ...
DNA and the Genetic Code
... Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA (messenger RNA) from DNA The two DNA strands separate from one another. One strand is used for replication. The other is used for transcription. mRNA is the complement strand of the original DNA except with thymine replaced with uracil (U). mRNA carries genetic ...
... Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA (messenger RNA) from DNA The two DNA strands separate from one another. One strand is used for replication. The other is used for transcription. mRNA is the complement strand of the original DNA except with thymine replaced with uracil (U). mRNA carries genetic ...
Biology1FinalExam I F'04(2-3-4).doc
... 26.Snapdragons have a single gene (locus) that determines flower color. The allele R is for red flowers and it shows incomplete dominance over the recessive allele r for white flowers. What color flowers are produced by Rr plants? a. All red b. Mixed red and white (some flowers of each color) c. pin ...
... 26.Snapdragons have a single gene (locus) that determines flower color. The allele R is for red flowers and it shows incomplete dominance over the recessive allele r for white flowers. What color flowers are produced by Rr plants? a. All red b. Mixed red and white (some flowers of each color) c. pin ...
Genetic engineering: the state of the art
... knowledge about the pivotal role of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in the development of all organ isms has accelerated relentlessly. To achieve the current understanding. scientists had to develop techniques for manipu la ting DNA . In 1958 the first enzyme capable of the test-tube synthesis of DNA wa ...
... knowledge about the pivotal role of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in the development of all organ isms has accelerated relentlessly. To achieve the current understanding. scientists had to develop techniques for manipu la ting DNA . In 1958 the first enzyme capable of the test-tube synthesis of DNA wa ...
Lec206
... Trans-heterozygous phenotypes • When two genes are in the same “pathway” mutants heterozygous for both genes will display a phenotype even though each individual heterozygous mutant does not • Can be combined with ENU mutagenesis to screen for genes in the same pathway as another known “knocked out ...
... Trans-heterozygous phenotypes • When two genes are in the same “pathway” mutants heterozygous for both genes will display a phenotype even though each individual heterozygous mutant does not • Can be combined with ENU mutagenesis to screen for genes in the same pathway as another known “knocked out ...
BIOL 2416 Genetics
... • Seeks to compare all or part of the genomes of two or more strains or species • Allows researchers to hone in on crucial genetic differences between strains/species/cell types. For example: – Using computer analysis: • May discover which gene(s) cause one virus to be more virulent than another • C ...
... • Seeks to compare all or part of the genomes of two or more strains or species • Allows researchers to hone in on crucial genetic differences between strains/species/cell types. For example: – Using computer analysis: • May discover which gene(s) cause one virus to be more virulent than another • C ...
DNA - Paxon Biology
... DNA is a double helix, however, only 1 of these strands is transcribed. The strand that is transcribed is called the template strand. The other strand is NOT transcribed and is called the non-template strand; it serves as a template for making a new strand during replication. An mRNA will be complem ...
... DNA is a double helix, however, only 1 of these strands is transcribed. The strand that is transcribed is called the template strand. The other strand is NOT transcribed and is called the non-template strand; it serves as a template for making a new strand during replication. An mRNA will be complem ...
DNA SEQUENCING DNA sequencing
... More importantly, these methods do not require PCR, which creates mutations in clonally amplified templates that masquerade as sequence variants. AT-rich and GC-rich target sequences may also show amplification bias in product yield, which results in their under representation in genome alignments a ...
... More importantly, these methods do not require PCR, which creates mutations in clonally amplified templates that masquerade as sequence variants. AT-rich and GC-rich target sequences may also show amplification bias in product yield, which results in their under representation in genome alignments a ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.