Biology GuideBook
... D___________ is collected during an experiment and must be organized into T____________ or G_____________. A hypothesis may be Ch____________ if it isn’t supported by data. Scientific testing must have P__________ review and verification before being accepted and P_____________ in scientific j ...
... D___________ is collected during an experiment and must be organized into T____________ or G_____________. A hypothesis may be Ch____________ if it isn’t supported by data. Scientific testing must have P__________ review and verification before being accepted and P_____________ in scientific j ...
Document
... and DNA Replication Gene expression and DNA replication are compared in Table I-I-I. Transcription, the first stage in gene expression, involves transfer of information found in a double-stranded DNA molecule to the base sequence of a single-stranded RNA molecule. If the RNA molecule is a messenger ...
... and DNA Replication Gene expression and DNA replication are compared in Table I-I-I. Transcription, the first stage in gene expression, involves transfer of information found in a double-stranded DNA molecule to the base sequence of a single-stranded RNA molecule. If the RNA molecule is a messenger ...
Odyssey of Agrobacterium T-DNA.
... & Citovsky, 1997; Rossi et al., 1998; Zupan & Zambryski, 1997). In biotechnology this ability is widely used for plant transformation. During tumor induction Agrobacterium attaches to plant cells and then transfers part of .This ...
... & Citovsky, 1997; Rossi et al., 1998; Zupan & Zambryski, 1997). In biotechnology this ability is widely used for plant transformation. During tumor induction Agrobacterium attaches to plant cells and then transfers part of .This ...
for growth. fermentation end products and genes required growth of
... also observed (data not shown). The pattern of the fermentative end products of B. subtilis is similar to that observed for E. coli (1) or Bacillus licheniformis (29), although 2,3-butanediol and acetoin are not major products of E. coli fermentation and no formate peak of around 8 ppm was detected ...
... also observed (data not shown). The pattern of the fermentative end products of B. subtilis is similar to that observed for E. coli (1) or Bacillus licheniformis (29), although 2,3-butanediol and acetoin are not major products of E. coli fermentation and no formate peak of around 8 ppm was detected ...
Bacteria - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Genetic variation in bacteria is due to – mutation – mixing genetic material between different cells transformation conjugation transduction ...
... • Genetic variation in bacteria is due to – mutation – mixing genetic material between different cells transformation conjugation transduction ...
Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA gyrase ATPase domain structures
... its ATPase activity using a sensitive fluorescence assay which measures the production of Pi [28]. As the ATPase activity of the isolated ATPase domain is quite low, 15 μM protein was used. Figure 1 shows an ATP titration for the ATPase domain. An ATP-dependent increase in activity was observed, and ...
... its ATPase activity using a sensitive fluorescence assay which measures the production of Pi [28]. As the ATPase activity of the isolated ATPase domain is quite low, 15 μM protein was used. Figure 1 shows an ATP titration for the ATPase domain. An ATP-dependent increase in activity was observed, and ...
docx Helicobacter Infection
... system. H.pylori cells that have been associated with aggregates of Urease and a heat shock protein GroEL. The function of cryptic plasmids of strains of Helicobacter pylori is not well understood.pHe112, and pHe14 plasmids have mobilization regions for conjugative transfer. Bacterial conjugation is ...
... system. H.pylori cells that have been associated with aggregates of Urease and a heat shock protein GroEL. The function of cryptic plasmids of strains of Helicobacter pylori is not well understood.pHe112, and pHe14 plasmids have mobilization regions for conjugative transfer. Bacterial conjugation is ...
Improvement of poly-γ-glutamic acid (PGA)
... positions on four nitrogenous bases of the bacterial DNA, the best mutagenicity correlated with an addition of oxygen molecule at the sixth position of guanine to create an O-6- methyl guanine, leading to direct miss-pairing resulting in G:C A:T transitions at the next round of replication. The NTG ...
... positions on four nitrogenous bases of the bacterial DNA, the best mutagenicity correlated with an addition of oxygen molecule at the sixth position of guanine to create an O-6- methyl guanine, leading to direct miss-pairing resulting in G:C A:T transitions at the next round of replication. The NTG ...
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Biogenesis: Visualization and Duel
... only used BrdU alone (Amiri and Hollenbeck 2008) or have used the two thymidine analogs to measure nuclear DNA replication (Cappella et al. 2008; Salic and Mitchison 2008). In addition, the labeling procedure for EdU does not involve the harsh acid or enzyme digests needed for BrdU epitope recovery, ...
... only used BrdU alone (Amiri and Hollenbeck 2008) or have used the two thymidine analogs to measure nuclear DNA replication (Cappella et al. 2008; Salic and Mitchison 2008). In addition, the labeling procedure for EdU does not involve the harsh acid or enzyme digests needed for BrdU epitope recovery, ...
New Approach to Inactivation of Harmful and Pathogenic
... translocation of the photosensitizer into the cytoplasm must be possible; (iii) two ways are proposed to explain the lethal damage of bacteria: destruction of either DNA or membrane (Fig. 4). Breaks in both single- and double-stranded DNA have been detected in both Gram(+) and Gram(–) bacteria after ...
... translocation of the photosensitizer into the cytoplasm must be possible; (iii) two ways are proposed to explain the lethal damage of bacteria: destruction of either DNA or membrane (Fig. 4). Breaks in both single- and double-stranded DNA have been detected in both Gram(+) and Gram(–) bacteria after ...
Thermodynamic analysis of DNA binding by a Bacillus single
... (<10 mM NaCl), SSB binds ssDNA using two of its four subunits in a highly cooperative manner and occludes only 35 nucleotides [(SSB)35 mode]. On the other hand, at higher salt concentrations (>200 mM NaCl), it binds to ssDNA using all four subunits and protects ~65 nucleotides [(SSB)65 mode]. It is ...
... (<10 mM NaCl), SSB binds ssDNA using two of its four subunits in a highly cooperative manner and occludes only 35 nucleotides [(SSB)35 mode]. On the other hand, at higher salt concentrations (>200 mM NaCl), it binds to ssDNA using all four subunits and protects ~65 nucleotides [(SSB)65 mode]. It is ...
Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a novel Ca2+
... pink halo was produced around extracts of cells containing the empty vector (grid B1). Therefore, the cloned cDNA encodes a nuclease. This is the ¢rst report that a plant nuclease homolog is functional. We further tested e¡ects of the divalent cations, Ca2 , Mg2 , and Zn2 on the activity of the n ...
... pink halo was produced around extracts of cells containing the empty vector (grid B1). Therefore, the cloned cDNA encodes a nuclease. This is the ¢rst report that a plant nuclease homolog is functional. We further tested e¡ects of the divalent cations, Ca2 , Mg2 , and Zn2 on the activity of the n ...
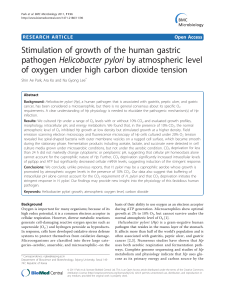
Stimulation of growth of the human gastric
... Results: We cultured Hp under a range of O2 levels with or without 10% CO2 and evaluated growth profiles, morphology, intracellular pH, and energy metabolism. We found that, in the presence of 10% CO2, the normal atmospheric level of O2 inhibited Hp growth at low density but stimulated growth at a h ...
... Results: We cultured Hp under a range of O2 levels with or without 10% CO2 and evaluated growth profiles, morphology, intracellular pH, and energy metabolism. We found that, in the presence of 10% CO2, the normal atmospheric level of O2 inhibited Hp growth at low density but stimulated growth at a h ...
Supplementary Table 1: WormBase IDs and given
... tat-1: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-1_1 and SL1 (SL2 did not produce a product), sequenced 4 clones fully, 4 partially; 3 ESTs sequenced (yk1228h06, yk34c11, yk1496c06); a singe poly(A) signal inferred from the ESTs; tat-2: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-2_1 and SL1 (SL2 did no ...
... tat-1: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-1_1 and SL1 (SL2 did not produce a product), sequenced 4 clones fully, 4 partially; 3 ESTs sequenced (yk1228h06, yk34c11, yk1496c06); a singe poly(A) signal inferred from the ESTs; tat-2: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-2_1 and SL1 (SL2 did no ...
results and discussion discussion
... partial digestion after 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 min respectively, Lane 8: λ BamHI/ EcoRI marker. ...
... partial digestion after 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 min respectively, Lane 8: λ BamHI/ EcoRI marker. ...
Purine nucleotide synthesis De novo
... The regulation of de novo pyrimidine synthesis CPS II is activated by PRPP and inhibited by UTP As cells approach the S-phase of the cell cycle CPS II becomes more sensitive to activation by PRPP and less sensitive? to inhibition by UTP phosphorylation of CPS II by MAP kinase at a specific site le ...
... The regulation of de novo pyrimidine synthesis CPS II is activated by PRPP and inhibited by UTP As cells approach the S-phase of the cell cycle CPS II becomes more sensitive to activation by PRPP and less sensitive? to inhibition by UTP phosphorylation of CPS II by MAP kinase at a specific site le ...
New peptide and gene coding for same
... Figure 7 represents a result of electrophoresis showing expression of a 7-hANP gene. Figure 8 represents a construction process of plasmid pS223-3 from plasmid pS83-3 and a DNA fragment containing a base sequence coding for amino acid sequence of 7-hANP, and a construction process of plasmid pS225-3 ...
... Figure 7 represents a result of electrophoresis showing expression of a 7-hANP gene. Figure 8 represents a construction process of plasmid pS223-3 from plasmid pS83-3 and a DNA fragment containing a base sequence coding for amino acid sequence of 7-hANP, and a construction process of plasmid pS225-3 ...
File
... Relate the relevance of biology to a person’s life. Describe the importance of biology in human society. List the characteristics of living things. Summarize the hierarchy of organization within complex multicellular organisms. Distinguish between homeostasis and metabolism and between growth, devel ...
... Relate the relevance of biology to a person’s life. Describe the importance of biology in human society. List the characteristics of living things. Summarize the hierarchy of organization within complex multicellular organisms. Distinguish between homeostasis and metabolism and between growth, devel ...
Expression of phosphofructokinase in Neisseria meningitidis
... Software) was used to design the forward (59-CAAGAAGACTTCCGGCAACA-39) and reverse oligonucleotide primers (59TGATAAGCGAAGCGCATCAG-39). Primers were synthesized by Sigma-Genosys. The forward primer anneals 55 bp upstream of the ATG start codon while the reverse primer anneals 79 bp downstream of the ...
... Software) was used to design the forward (59-CAAGAAGACTTCCGGCAACA-39) and reverse oligonucleotide primers (59TGATAAGCGAAGCGCATCAG-39). Primers were synthesized by Sigma-Genosys. The forward primer anneals 55 bp upstream of the ATG start codon while the reverse primer anneals 79 bp downstream of the ...
pdf
... Fig. 2. Evolution of the anticodon-binding pocket of PhProRS to charge different Af-tRNAPro anticodon variants. (A) Anticodon-binding site of ProRS in the crystal structure from T. thermophilus. The consensus sequence of the proline anticodon (GG), shown in magenta, interacts strongly with the amino ...
... Fig. 2. Evolution of the anticodon-binding pocket of PhProRS to charge different Af-tRNAPro anticodon variants. (A) Anticodon-binding site of ProRS in the crystal structure from T. thermophilus. The consensus sequence of the proline anticodon (GG), shown in magenta, interacts strongly with the amino ...
Biology: semester one: course outline
... Distinguish between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition. Describe the structure of a chloroplast, listing all membranes and compartments. Write a summary equation for photosynthesis, and describe the two main stages of photosynthesis. In general terms, explain the role of redox reactions in phot ...
... Distinguish between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition. Describe the structure of a chloroplast, listing all membranes and compartments. Write a summary equation for photosynthesis, and describe the two main stages of photosynthesis. In general terms, explain the role of redox reactions in phot ...
Transformation (genetics)
In molecular biology, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material (exogenous DNA) from its surroundings and taken up through the cell membrane(s). Transformation occurs naturally in some species of bacteria, but it can also be effected by artificial means in other cells. For transformation to happen, bacteria must be in a state of competence, which might occur as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density.Transformation is one of three processes by which exogenous genetic material may be introduced into a bacterial cell, the other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a bacteriophage virus into the host bacterium).""Transformation"" may also be used to describe the insertion of new genetic material into nonbacterial cells, including animal and plant cells; however, because ""transformation"" has a special meaning in relation to animal cells, indicating progression to a cancerous state, the term should be avoided for animal cells when describing introduction of exogenous genetic material. Introduction of foreign DNA into eukaryotic cells is often called ""transfection"".