Nucleotide Sequence of the Osmoregulatory proU Operon of
... two sets, respectively, and the arrows leading from them delineate the direction and extent of sequence determined by the dideoxynucleotide chain-termination method (40) in each of these clones. Specific clones that were used for probe preparation in the primer extension experiment described in the ...
... two sets, respectively, and the arrows leading from them delineate the direction and extent of sequence determined by the dideoxynucleotide chain-termination method (40) in each of these clones. Specific clones that were used for probe preparation in the primer extension experiment described in the ...
A set reduction and pattern matching problem motivated by Allele
... 3. Design a primer pair to amplify the desired allele from the pool of sequences produced using the locus specific primer (Fig. 3). The three steps seem quite similar due to their common purpose: reduction of the existing set. However, they are distinct as the primers must be designed to leverage di ...
... 3. Design a primer pair to amplify the desired allele from the pool of sequences produced using the locus specific primer (Fig. 3). The three steps seem quite similar due to their common purpose: reduction of the existing set. However, they are distinct as the primers must be designed to leverage di ...
Bioinformatics - Sequences and Computers
... Learn how information-bearing sequences are different from random sequences and become familiar with bioinformatics tools for the analysis of sequences. Language and DNA use sequences to communicate information. The sequence elements in language are letters and punctuation, in DNA they are the nucle ...
... Learn how information-bearing sequences are different from random sequences and become familiar with bioinformatics tools for the analysis of sequences. Language and DNA use sequences to communicate information. The sequence elements in language are letters and punctuation, in DNA they are the nucle ...
RESEARCH ARTICLES
... Fig. 2. Analysis of the assembly intermediates. (A) Not I and Sbf I double restriction digestion analysis of assembly 341350 purified from E. coli. These restriction enzymes release the vector fragments (5.5 and 3.4 kb) from the 10-kb insert. Insert DNA was separated from the vector DNA on a 0.8% E ...
... Fig. 2. Analysis of the assembly intermediates. (A) Not I and Sbf I double restriction digestion analysis of assembly 341350 purified from E. coli. These restriction enzymes release the vector fragments (5.5 and 3.4 kb) from the 10-kb insert. Insert DNA was separated from the vector DNA on a 0.8% E ...
PDF version - EpiGeneSys
... 1. DNA arrays are constructed using the Widom 601 nucleosome positioning DNA sequence. DNA arrays containing between 12 and 80 tandem 601 DNA repeats with different nucleosome repeat lengths (NRLs) (167 to 237bp) have been constructed (Huynh et al, 2005; Robinson et al, 2006; Routh et al, 2008). 2. ...
... 1. DNA arrays are constructed using the Widom 601 nucleosome positioning DNA sequence. DNA arrays containing between 12 and 80 tandem 601 DNA repeats with different nucleosome repeat lengths (NRLs) (167 to 237bp) have been constructed (Huynh et al, 2005; Robinson et al, 2006; Routh et al, 2008). 2. ...
pcr (polymerase chain reaction)
... Next we will transform the In-Fusion reaction into both electrocompetent and chemically competent cells. The electrocompetent cells produce lacI from the chromosome so that you can control the circuit’s function with the addition of IPTG to express either GFP or RFP. However, the transformation effi ...
... Next we will transform the In-Fusion reaction into both electrocompetent and chemically competent cells. The electrocompetent cells produce lacI from the chromosome so that you can control the circuit’s function with the addition of IPTG to express either GFP or RFP. However, the transformation effi ...
Cloning and Sequencing of a Gene from Bacillus
... primary sequences derived from the nucleotide sequences of the two genes were also compared. The gene from B. amyloliquefaciens coded for a protein of 344 amino acid residues, one more than the protein coded by the corresponding gene from B. subtilis. Comparison of the primary amino acid sequences o ...
... primary sequences derived from the nucleotide sequences of the two genes were also compared. The gene from B. amyloliquefaciens coded for a protein of 344 amino acid residues, one more than the protein coded by the corresponding gene from B. subtilis. Comparison of the primary amino acid sequences o ...
Table S1.
... binding sites in window (XXX stands for any transcription factor with a known binding matrix – all TFs starting with the same three letters are assumed to for a group and are counted together) ...
... binding sites in window (XXX stands for any transcription factor with a known binding matrix – all TFs starting with the same three letters are assumed to for a group and are counted together) ...
Introduction to Gel Electrophorsis
... • The voltage applied to the gel affects how quickly the gel runs • The higher the voltage, the more quickly the gel runs………But that often reduces the quality of the DNA separation • >>>>>>>>>>It also generates heat which reduces the quality of the DNA separation ...
... • The voltage applied to the gel affects how quickly the gel runs • The higher the voltage, the more quickly the gel runs………But that often reduces the quality of the DNA separation • >>>>>>>>>>It also generates heat which reduces the quality of the DNA separation ...
Explaining the Likelihood Ratio in DNA Mixture Interpretation
... social science. The LR is a standard measure of information that summarizes in a single number the data support for a hypothesis. It is a way of accounting for all the evidence in favor of or against a particular hypothesis (or proposition) (1). The LR is also the match statistic that is used in DNA ...
... social science. The LR is a standard measure of information that summarizes in a single number the data support for a hypothesis. It is a way of accounting for all the evidence in favor of or against a particular hypothesis (or proposition) (1). The LR is also the match statistic that is used in DNA ...
DNA Mismatch Repair and Synonymous Codon Evolution in
... let A&,,, be the probability that a base pair of type b (C:G or A:T ) becomes a mismatch of type m (C:T, C:A, G:T, G:A) per cell generation. In all that follows, the subscript “b” can either be “S,” for a C:G (or G:C) base pair, or “W,” for an A:T (or T:A) base pair (IUPAC codes). Once a mismatch is ...
... let A&,,, be the probability that a base pair of type b (C:G or A:T ) becomes a mismatch of type m (C:T, C:A, G:T, G:A) per cell generation. In all that follows, the subscript “b” can either be “S,” for a C:G (or G:C) base pair, or “W,” for an A:T (or T:A) base pair (IUPAC codes). Once a mismatch is ...
DNA -‐ Compsci 201
... The code in the class DNABenchMark can be used to benchmark the cutAndSplice method. The code given to you will pop-‐up a file-‐dialog box — when run you can use this to nav ...
... The code in the class DNABenchMark can be used to benchmark the cutAndSplice method. The code given to you will pop-‐up a file-‐dialog box — when run you can use this to nav ...
Wheat, Fusarium toxins and disease: the good, the bad and the ugly
... crop in Canada, with Manitoba exporting wheat to approximately 66 different countries. It is processed into flour, cereal food, animal feed and industrial products such as ethanol. ¾THE BAD: Fusarium head blight (FHB) is the most serious disease in wheat around the world. Fusarium graminearum is the ...
... crop in Canada, with Manitoba exporting wheat to approximately 66 different countries. It is processed into flour, cereal food, animal feed and industrial products such as ethanol. ¾THE BAD: Fusarium head blight (FHB) is the most serious disease in wheat around the world. Fusarium graminearum is the ...
Ionic distribution around simple DNA models. I
... which has its origin in the DNA axis, about 9 Å. With respect to the DNA charged site, the mobile ion behaves as a pointlike charge, and collapses into it. In most simulations of discretely charged structures the problem does not arise due to the use of hard potentials.13 Gordon and Goldman23 simula ...
... which has its origin in the DNA axis, about 9 Å. With respect to the DNA charged site, the mobile ion behaves as a pointlike charge, and collapses into it. In most simulations of discretely charged structures the problem does not arise due to the use of hard potentials.13 Gordon and Goldman23 simula ...
The rapidly evolving field of plant centromeres
... satellite evolution is driven by the selection and coevolution of satellites and centromere-binding proteins, rather than by random genetic drift. This requires that certain centromere satellite variants confer a selective advantage upon meiotic cells (i.e. eggs and sperm), a process known as meioti ...
... satellite evolution is driven by the selection and coevolution of satellites and centromere-binding proteins, rather than by random genetic drift. This requires that certain centromere satellite variants confer a selective advantage upon meiotic cells (i.e. eggs and sperm), a process known as meioti ...
Production of Recombinant Molecules
... P (a radioactive isotope of phosphorus incorporated into the phosphodiester bond in the probe DNA) or Digoxigenin, which is non- radioactive antibody-based marker. DNA sequences or RNA transcripts that have moderate to high sequence similarity to the probe are then detected by visualizing the hybrid ...
... P (a radioactive isotope of phosphorus incorporated into the phosphodiester bond in the probe DNA) or Digoxigenin, which is non- radioactive antibody-based marker. DNA sequences or RNA transcripts that have moderate to high sequence similarity to the probe are then detected by visualizing the hybrid ...
pSAT vectors: a modular series of plasmids for autofluorescent
... CA), respectively, and cloned into the NcoI-XbaI sites of pSAT6-EGFP-C1, replacing EGFP-C1MCS. To produce pSAT6-Citrine-C1, the Citrine-YFP ORF was PCR-amplified from pRSETBCitrine (Griesbeck et al., 2001) and cloned into the NcoI-XhoI sites of pSAT6-EGFP-C1, replacing EGFP. The Citrine-YFP PCR frag ...
... CA), respectively, and cloned into the NcoI-XbaI sites of pSAT6-EGFP-C1, replacing EGFP-C1MCS. To produce pSAT6-Citrine-C1, the Citrine-YFP ORF was PCR-amplified from pRSETBCitrine (Griesbeck et al., 2001) and cloned into the NcoI-XhoI sites of pSAT6-EGFP-C1, replacing EGFP. The Citrine-YFP PCR frag ...
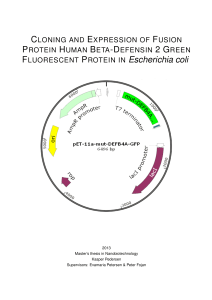
FLUORESCENT PROTEIN IN Escherichia coli
... The discovery of penicillin in 1928 by Sir Alexander Fleming was a huge breakthrough and became a shift in paradigm to how infections were treated. Since then many other antiobiotics were developed, e.g. streptomycin against tuberculosis. This meant that the leading cause of death changed from being ...
... The discovery of penicillin in 1928 by Sir Alexander Fleming was a huge breakthrough and became a shift in paradigm to how infections were treated. Since then many other antiobiotics were developed, e.g. streptomycin against tuberculosis. This meant that the leading cause of death changed from being ...
PDF
... Fig. 1. Modified DamID approach to identify DSXbinding regions. (A)Schematic drawing of the flip-on Dam-fusion constructs. The proteins are expressed from the basal level of the UAS sequence after the FRTstop-FRT cassette is removed by expression of FLPase. (B)Example of an Illumina sequencing lib ...
... Fig. 1. Modified DamID approach to identify DSXbinding regions. (A)Schematic drawing of the flip-on Dam-fusion constructs. The proteins are expressed from the basal level of the UAS sequence after the FRTstop-FRT cassette is removed by expression of FLPase. (B)Example of an Illumina sequencing lib ...
Association of (rs1801133) Polymorphism with Breast
... International Journal of Pure and Applied Biomedical Sciences; Vol. 2016.1.2; pp. 24-35. DNA sequence variation which is common in the main population. So in this case no single allele is taken as the standard sequence. Instead there are two or more equally acceptable alternatives. SNPs are biologi ...
... International Journal of Pure and Applied Biomedical Sciences; Vol. 2016.1.2; pp. 24-35. DNA sequence variation which is common in the main population. So in this case no single allele is taken as the standard sequence. Instead there are two or more equally acceptable alternatives. SNPs are biologi ...
Nucleotide sequence analysis - Bioinformatics Unit
... •Is it contaminated with vector sequences? •Is it an already known gene? •Is it related to any other genes either by having a common ancestor? •Is it similar in function to other genes via convergent evolution? •What could the protein sequence be for this nucleotide fra ...
... •Is it contaminated with vector sequences? •Is it an already known gene? •Is it related to any other genes either by having a common ancestor? •Is it similar in function to other genes via convergent evolution? •What could the protein sequence be for this nucleotide fra ...
HL7 V2.5.1 Genetic Test Result Message
... genomic and healthcare IT data standards may use this guide to extend these standards for support of clinical sequencing. Users of this guide must be familiar with the details of HL7 message construction and processing. This guide is not intended to be a tutorial on that subject. ...
... genomic and healthcare IT data standards may use this guide to extend these standards for support of clinical sequencing. Users of this guide must be familiar with the details of HL7 message construction and processing. This guide is not intended to be a tutorial on that subject. ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).