3-2_UniqueFt_of_Neurons
... - well developed rough endoplasmatic reticulum system units can be found ...
... - well developed rough endoplasmatic reticulum system units can be found ...
Lesson Plan
... do that? How does it make your muscle get so big and strong? Explain the brain sends a connection called a nerve down the spine and to the muscles. How about people who can’t move their muscles? Some people have to be in wheelchairs because they can’t use their brain to move their muscles. Sometimes ...
... do that? How does it make your muscle get so big and strong? Explain the brain sends a connection called a nerve down the spine and to the muscles. How about people who can’t move their muscles? Some people have to be in wheelchairs because they can’t use their brain to move their muscles. Sometimes ...
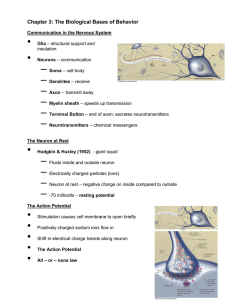
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... When a Neurotransmitter Binds: The Postsynaptic Potential ...
... When a Neurotransmitter Binds: The Postsynaptic Potential ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... 1. Neurons are nerve cells. There are a few types to know… 1. Sensory neurons – Take messages from the body, up the spinal cord, to the brain. There are millions of these. 2. Motor neurons – Take messages from the brain to the body. There are millions of these. 3. Interneurons – Are neurons within t ...
... 1. Neurons are nerve cells. There are a few types to know… 1. Sensory neurons – Take messages from the body, up the spinal cord, to the brain. There are millions of these. 2. Motor neurons – Take messages from the brain to the body. There are millions of these. 3. Interneurons – Are neurons within t ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... Early Twenties Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
... Early Twenties Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
Scientific priorities for the BRAIN Initiative
... temporal resolution with minimal disruption. We must also invest heavily in optical neurophysiology to generate more and better genetically encoded probes, both for stimulating neurons and for recording calcium and voltage dynamics. In addition, better microscopes will be needed if they are to be us ...
... temporal resolution with minimal disruption. We must also invest heavily in optical neurophysiology to generate more and better genetically encoded probes, both for stimulating neurons and for recording calcium and voltage dynamics. In addition, better microscopes will be needed if they are to be us ...
Human Learning & Memory
... Myelin: Fatty layer of tissue that coats axons ◦ Multiple Sclerosis (MS) occurs when myelin layer is destroyed; numbness, weakness, and paralysis occur Neurogenesis: Production of new brain cells ...
... Myelin: Fatty layer of tissue that coats axons ◦ Multiple Sclerosis (MS) occurs when myelin layer is destroyed; numbness, weakness, and paralysis occur Neurogenesis: Production of new brain cells ...
nervous system
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
Information Processing and Memory
... used to assist schema refinement if it varies in only one way from the designated example. H. Simon (1974) has estimated that each new bit of information takes ten seconds to process in order to be stored in long-term memory. The implications for lecture-based instruction are significant. On a neuro ...
... used to assist schema refinement if it varies in only one way from the designated example. H. Simon (1974) has estimated that each new bit of information takes ten seconds to process in order to be stored in long-term memory. The implications for lecture-based instruction are significant. On a neuro ...
The CNS - Mr. Lesiuk
... The cerebral cortex is a thin, highly convoluted outer layer of gray matter covering both hemispheres. The primary motor area is in the frontal lobe; this commands skeletal muscle. The primary somatosensory area is dorsal to the central sulcus or groove. The primary visual area is at the back occipi ...
... The cerebral cortex is a thin, highly convoluted outer layer of gray matter covering both hemispheres. The primary motor area is in the frontal lobe; this commands skeletal muscle. The primary somatosensory area is dorsal to the central sulcus or groove. The primary visual area is at the back occipi ...
Neuron is the basic working unit of the nervous system, specialized
... excitable axon extends from the cell body and often gives rise to many smaller ...
... excitable axon extends from the cell body and often gives rise to many smaller ...
Central Nervous system - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Chemical signal exchange between pre and postsynaptic neurons is needed A variety of signals act on developing neurons Neurons seldom stimulated soon lose their synapses, a process called synaptic pruning. ...
... Chemical signal exchange between pre and postsynaptic neurons is needed A variety of signals act on developing neurons Neurons seldom stimulated soon lose their synapses, a process called synaptic pruning. ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... 1. Remove part of the brain & see what effect it has on behavior 2. Examine humans who have suffered brain damage ...
... 1. Remove part of the brain & see what effect it has on behavior 2. Examine humans who have suffered brain damage ...
Biopsychology
... A large enough depolarization causes the inside of the cell to become positive with respect to the outside at the point of stimulation. Is contagious & results in the info being carried down the length of the cell. Is all-or-none. Summary Synaptic Transmission The Synapse Exocytosis Ov ...
... A large enough depolarization causes the inside of the cell to become positive with respect to the outside at the point of stimulation. Is contagious & results in the info being carried down the length of the cell. Is all-or-none. Summary Synaptic Transmission The Synapse Exocytosis Ov ...
MIND CONTROLLED ROBOT
... The EEG is used to evaluate several types of brain disorders like epilepsy, lesions in the brain which can result from tumors or stroke, Alzheimer's disease, certain psychoses, and a sleep disorder called narcolepsy. The EEG is also used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain to e ...
... The EEG is used to evaluate several types of brain disorders like epilepsy, lesions in the brain which can result from tumors or stroke, Alzheimer's disease, certain psychoses, and a sleep disorder called narcolepsy. The EEG is also used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain to e ...
Consciousness_12
... whole image can still be extracted from any of them (although with some loss of clarity). Pribram uses the term "holonomy" to refer to a dynamic (or changing) hologram. The Hologram Relationship The basic idea of a hologram can be understood without even considering the holograms found in novelty st ...
... whole image can still be extracted from any of them (although with some loss of clarity). Pribram uses the term "holonomy" to refer to a dynamic (or changing) hologram. The Hologram Relationship The basic idea of a hologram can be understood without even considering the holograms found in novelty st ...
Theoretical neuroscience: Single neuron dynamics and computation
... • Overview of the brain, experimental tools, spatial scales, temporal scales • Outline of the course ...
... • Overview of the brain, experimental tools, spatial scales, temporal scales • Outline of the course ...
MBBC Junior Neuroscience E-Book v1
... contains nucleus and cytoplasm, and is the cell’s control center. The electrically excitable axon extends from the cell body and often gives rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals. The larger the axon, the faster it transmits information. Some axons have an outer layer called ...
... contains nucleus and cytoplasm, and is the cell’s control center. The electrically excitable axon extends from the cell body and often gives rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals. The larger the axon, the faster it transmits information. Some axons have an outer layer called ...
Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...