Module 25 PowerPoint
... years later Recognition: the average person can view 2500 new faces and places, and later can notice with 90 percent accuracy which ones they’ve seen before Relearning: some people are unable to form new memories, especially of episodes; although they would not recall a puzzle-solving lesson, th ...
... years later Recognition: the average person can view 2500 new faces and places, and later can notice with 90 percent accuracy which ones they’ve seen before Relearning: some people are unable to form new memories, especially of episodes; although they would not recall a puzzle-solving lesson, th ...
Nervous System 2
... 3. Compare the parasympathetic and sympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system: a. Where do they branch off the spinal cord? b. Where do the pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic neurons synapse (Close to the spinal cord? Close to the peripheral location they innervate?) c. Which is primarily ...
... 3. Compare the parasympathetic and sympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system: a. Where do they branch off the spinal cord? b. Where do the pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic neurons synapse (Close to the spinal cord? Close to the peripheral location they innervate?) c. Which is primarily ...
Food for Thought: What Fuels Brain Cells?
... buffer the free radicals they produce because of their high oxidative metabolism. Astrocytes in turn, process glucose mostly glycolytically in an unselfish manner aimed at producing lactate to be used by neurons and other cells such as the myelin-forming oligidendrocytes. Astrocytes have a preferenc ...
... buffer the free radicals they produce because of their high oxidative metabolism. Astrocytes in turn, process glucose mostly glycolytically in an unselfish manner aimed at producing lactate to be used by neurons and other cells such as the myelin-forming oligidendrocytes. Astrocytes have a preferenc ...
Justin Smith - USD Biology
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
The Neural Control of Movement
... The PNS receives and sends information from the real world to the brain, and the brain has the responsibility of sorting out what’s important and what’s not. The nervous system uses structures called receptors to determine the status of thins in the real world. ...
... The PNS receives and sends information from the real world to the brain, and the brain has the responsibility of sorting out what’s important and what’s not. The nervous system uses structures called receptors to determine the status of thins in the real world. ...
chapter2
... here is how you can print the slides out without the dark background, in plain black and white. 1. click on print, when the print dialog box opens look to the lower left, for the menu called "print what". 2. use the mouse to select "handouts" 3. just below that menu is another menu called "Color/gra ...
... here is how you can print the slides out without the dark background, in plain black and white. 1. click on print, when the print dialog box opens look to the lower left, for the menu called "print what". 2. use the mouse to select "handouts" 3. just below that menu is another menu called "Color/gra ...
Tutorial 10: Temporal and Spatial Summation Figure 10: Temporal
... pathways, composed of sites where cells transmitted information to other cells. He called these sites synapses. In addition, Sherrington introduced the possible role of evolution in the development of the nervous system, with his suggestion that higher centers of the brain inhibit the excitatory fun ...
... pathways, composed of sites where cells transmitted information to other cells. He called these sites synapses. In addition, Sherrington introduced the possible role of evolution in the development of the nervous system, with his suggestion that higher centers of the brain inhibit the excitatory fun ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... summate, and if the net result is a threshold or greater amount of depolarization, an action potential occurs. VISUAL: Hold up Electrical wire—similarities to axon (insulation, send electrical impulse) and the main difference: no continuous signals/bursts of activity with periods to reset the chemic ...
... summate, and if the net result is a threshold or greater amount of depolarization, an action potential occurs. VISUAL: Hold up Electrical wire—similarities to axon (insulation, send electrical impulse) and the main difference: no continuous signals/bursts of activity with periods to reset the chemic ...
2. Literature Review
... indeterminestic. The special study should be done to deal with this signal i.e. special type of system with high precision and accuracy should be made to capture these brain signals. To capture these signals medically a sensor or transducer named electrode is made which could capture this signals wi ...
... indeterminestic. The special study should be done to deal with this signal i.e. special type of system with high precision and accuracy should be made to capture these brain signals. To capture these signals medically a sensor or transducer named electrode is made which could capture this signals wi ...
File
... brain: the brainstem and limbic system the outer, wrinkled “bark”: the cortex left, right, and split brains Questions about parts of the brain: Do you think that the brain is the sum of its parts, or is the brain actually about the way they are ...
... brain: the brainstem and limbic system the outer, wrinkled “bark”: the cortex left, right, and split brains Questions about parts of the brain: Do you think that the brain is the sum of its parts, or is the brain actually about the way they are ...
kn35l1SvSY1SkTqq
... brain: the brainstem and limbic system the outer, wrinkled “bark”: the cortex left, right, and split brains Questions about parts of the brain: Do you think that the brain is the sum of its parts, or is the brain actually about the way they are ...
... brain: the brainstem and limbic system the outer, wrinkled “bark”: the cortex left, right, and split brains Questions about parts of the brain: Do you think that the brain is the sum of its parts, or is the brain actually about the way they are ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers - AP Psychology
... brain: the brainstem and limbic system the outer, wrinkled “bark”: the cortex left, right, and split brains Questions about parts of the brain: Do you think that the brain is the sum of its parts, or is the brain actually about the way they are ...
... brain: the brainstem and limbic system the outer, wrinkled “bark”: the cortex left, right, and split brains Questions about parts of the brain: Do you think that the brain is the sum of its parts, or is the brain actually about the way they are ...
List of vocabulary used in understanding the nervous
... release of neurotransmitter chemicals from the axon terminal at the synapse may initiate an action potential in an adjacent neuron, propagating the impulse to a new cell. The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Humans have about 100 billion neurons in their brain alone! While variab ...
... release of neurotransmitter chemicals from the axon terminal at the synapse may initiate an action potential in an adjacent neuron, propagating the impulse to a new cell. The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Humans have about 100 billion neurons in their brain alone! While variab ...
memory and its learning implications
... factors determines if the new input will be used just for a moment or not. In the other hand, the new findings tell us that there is a prominent future to learn more about the memory and how some of its deficits could be managed by means of new drugs or molecules. In the same way, research can revea ...
... factors determines if the new input will be used just for a moment or not. In the other hand, the new findings tell us that there is a prominent future to learn more about the memory and how some of its deficits could be managed by means of new drugs or molecules. In the same way, research can revea ...
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Endocrine – Takes seconds for messages to trudge through the blood stream *** Hormonal Messages tend to last longer (outlast the effects of) 14. What role do the Adrenal Glands play. They secrete hormones (epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine) that help arouse body during stress. – Create ...
... Endocrine – Takes seconds for messages to trudge through the blood stream *** Hormonal Messages tend to last longer (outlast the effects of) 14. What role do the Adrenal Glands play. They secrete hormones (epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine) that help arouse body during stress. – Create ...
Lecture 6 Slides
... encoding, consolidation, and retrieval • Pre-existing memories are left intact by hippocampal damage • Memories are thought to be stored in the areas that initially processed given information ...
... encoding, consolidation, and retrieval • Pre-existing memories are left intact by hippocampal damage • Memories are thought to be stored in the areas that initially processed given information ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
... all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
Unit Three Nervous System
... • The actions of the nervous and endocrine systems control and regulate the body. • These two systems allow us to adjust to internal as well as external environmental changes. ...
... • The actions of the nervous and endocrine systems control and regulate the body. • These two systems allow us to adjust to internal as well as external environmental changes. ...
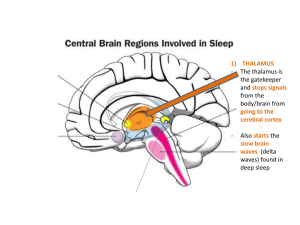
Sleep Brain Labelling
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...