Read our 2014-15 Annual Report - Nuffield Department of Clinical
... was formed on 1 November 2010, and is one of 16 departments in the University of Oxford’s Medical Sciences Division. Its constituent parts are: the Division of Clinical Neurology; the Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology; the Nuffield Division of Anaesthetics; the Oxford Centre for Functional MRI of ...
... was formed on 1 November 2010, and is one of 16 departments in the University of Oxford’s Medical Sciences Division. Its constituent parts are: the Division of Clinical Neurology; the Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology; the Nuffield Division of Anaesthetics; the Oxford Centre for Functional MRI of ...
chapter 4
... auditory receptor cells. Taste receptors stimulate neurons that project to the medulla and pons in the hindbrain. From there, the information is carried along two neural pathways, one leading to the primary gustatory cortex, which allows identification of tastes, and the other leading to the limbic ...
... auditory receptor cells. Taste receptors stimulate neurons that project to the medulla and pons in the hindbrain. From there, the information is carried along two neural pathways, one leading to the primary gustatory cortex, which allows identification of tastes, and the other leading to the limbic ...
The Brain - Miami Arts Charter School
... These results show that both nature and nurture influence IQ, however other confounding variables could have skewed these results (like how they are treated based on their physical looks or being raised in similar environments) ...
... These results show that both nature and nurture influence IQ, however other confounding variables could have skewed these results (like how they are treated based on their physical looks or being raised in similar environments) ...
Contemporary Issues - psychlotron.org.uk
... and selective in the way it processes information Schemas are used to interpret experiences and reconstruct memories Alterations and biases in schemas can affect the accuracy of memory ...
... and selective in the way it processes information Schemas are used to interpret experiences and reconstruct memories Alterations and biases in schemas can affect the accuracy of memory ...
4 Brenda - Wawa Family Health Team
... walk into a room with some purpose in mind, only to completely forget what that purpose was? Turns out, doors themselves are to blame for these strange memory lapses. Psychologists at the University of Notre Dame have discovered that passing through a doorway triggers what's known as an event bounda ...
... walk into a room with some purpose in mind, only to completely forget what that purpose was? Turns out, doors themselves are to blame for these strange memory lapses. Psychologists at the University of Notre Dame have discovered that passing through a doorway triggers what's known as an event bounda ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 2
... researchers studying the effects of morphine and other opiates. To their surprise, the researchers learned there were special receptor sites for such drugs within the brain (Hughes et al., 1975). Why should such receptors exist? • Naturally occurring substances that closely resemble morphine in phys ...
... researchers studying the effects of morphine and other opiates. To their surprise, the researchers learned there were special receptor sites for such drugs within the brain (Hughes et al., 1975). Why should such receptors exist? • Naturally occurring substances that closely resemble morphine in phys ...
The nervous system - Science for Yr9@E
... The nervous system has three general functions: a sensory function, an interpretative function and a motor function. 1. Sensory nerves gather information from inside the body and the outside environment. The nerves then carry the information to central nervous system (CNS). 2. Sensory information br ...
... The nervous system has three general functions: a sensory function, an interpretative function and a motor function. 1. Sensory nerves gather information from inside the body and the outside environment. The nerves then carry the information to central nervous system (CNS). 2. Sensory information br ...
Memory Unit – 2 day lesson plan Lara Bruner Desert Vista High
... that all the students know from their campus, “Walt”, three words in a row that start with the same letter, etc. The PowerPoint is included in the documents to explore/modify to make the proper noun specific to the campus where it is used. A principal’s name or the teacher’s name may be substituted. ...
... that all the students know from their campus, “Walt”, three words in a row that start with the same letter, etc. The PowerPoint is included in the documents to explore/modify to make the proper noun specific to the campus where it is used. A principal’s name or the teacher’s name may be substituted. ...
Bio101Lab13
... spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (motor vs. sensory), given either a model of the spinal cord or a microscope slide. (use the same tw ...
... spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (motor vs. sensory), given either a model of the spinal cord or a microscope slide. (use the same tw ...
Thinking, Learning and Intelligence: The Brain Imagine a 500 pound
... and had temper tantrums. Thus, this complex area of the brain must play a large part in what we call social control as well as in our basic personalities. The size of this frontal association likely reflects intelligence level from one species to another. About 7% of the brain in a dog is devoted to ...
... and had temper tantrums. Thus, this complex area of the brain must play a large part in what we call social control as well as in our basic personalities. The size of this frontal association likely reflects intelligence level from one species to another. About 7% of the brain in a dog is devoted to ...
Nervous Regulation
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. ...
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. ...
Nervous System - science
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
Document
... • Controls automatic functions at subconscious level • Sympathetic nervous system - nerves emerge from thoracic and lumbar ...
... • Controls automatic functions at subconscious level • Sympathetic nervous system - nerves emerge from thoracic and lumbar ...
Slides
... muscular system to effect bodily movement, and monitors the operation of internal organs like the heart and lungs by two-way signals. The brain and the spinal cord are generally referred to as the central nervous system, and the nerve network as the peripheral nervous system. The remainder of this l ...
... muscular system to effect bodily movement, and monitors the operation of internal organs like the heart and lungs by two-way signals. The brain and the spinal cord are generally referred to as the central nervous system, and the nerve network as the peripheral nervous system. The remainder of this l ...
nervoussystemwebquest
... Emotions are the result of a complex interplay of many regions of the brain Prominent among these regions is the limbic system, a ring of structures around the brainstem The limbic system includes three parts of the cerebral cortex—the amygdala, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb—along with some inner ...
... Emotions are the result of a complex interplay of many regions of the brain Prominent among these regions is the limbic system, a ring of structures around the brainstem The limbic system includes three parts of the cerebral cortex—the amygdala, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb—along with some inner ...
Biology and Behavior
... A. PET and fMRI scans, which measure neuronal activity, have shown that brain functioning changes with age. 1. Newborns’ brain activity is high in the thalamus and low in the part of the forebrain related to smooth movement. This pattern of brain activity and motor function resembles that seen after ...
... A. PET and fMRI scans, which measure neuronal activity, have shown that brain functioning changes with age. 1. Newborns’ brain activity is high in the thalamus and low in the part of the forebrain related to smooth movement. This pattern of brain activity and motor function resembles that seen after ...
The Bio-Psychology Dictionary - Windsor C
... neuron - a nerve cell. Neurons have specialized projections (dendrites and axons) and communicate with each other via an electrochemical process. The word "neuron" was coined by the German scientist Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz in 1891 (he also coined the term "chromosome"). ...
... neuron - a nerve cell. Neurons have specialized projections (dendrites and axons) and communicate with each other via an electrochemical process. The word "neuron" was coined by the German scientist Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz in 1891 (he also coined the term "chromosome"). ...
vocab - sociallyconsciousbird.com
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
Your Amazing Brain
... Your brain contains about 100 billion microscopic cells called neurons—so many it would take you over 3,000 years to count them all. Whenever you dream, laugh, think, see, or move, it’s because tiny chemical and electrical signals are racing between these neurons along billions of tiny neuron highwa ...
... Your brain contains about 100 billion microscopic cells called neurons—so many it would take you over 3,000 years to count them all. Whenever you dream, laugh, think, see, or move, it’s because tiny chemical and electrical signals are racing between these neurons along billions of tiny neuron highwa ...
Slide ()
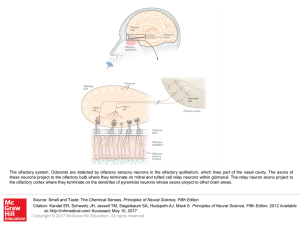
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
How does the Teenage Brain Work? (Teacher Version)
... A productive change in neural structure by ...
... A productive change in neural structure by ...
How the Brain Learns
... functions of learning are the same for everyone. Differences in learning occur not physiologically, but based on what each reader already knows. How Does this Chapter Connect to Chapters that will Follow? The cognitive strategies and habits of mind the reader will be learning in the following chapte ...
... functions of learning are the same for everyone. Differences in learning occur not physiologically, but based on what each reader already knows. How Does this Chapter Connect to Chapters that will Follow? The cognitive strategies and habits of mind the reader will be learning in the following chapte ...
Memory - Lascap
... Nickerson & Adams •Basic points: •Familiarity does not guarantee retention. •Even if there were literally thousands of presentations of the information. •Crucial are importance, which generally leads to the deployment of attention. •In the absence of these, memory is poor. •People are not necessari ...
... Nickerson & Adams •Basic points: •Familiarity does not guarantee retention. •Even if there were literally thousands of presentations of the information. •Crucial are importance, which generally leads to the deployment of attention. •In the absence of these, memory is poor. •People are not necessari ...