PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM DISEASES
... Judgement and reasoning Orientation in time and space Language processing Appropriate use of objects Planning and execution of voluntary movements ...
... Judgement and reasoning Orientation in time and space Language processing Appropriate use of objects Planning and execution of voluntary movements ...
Information Processing SG AK
... a) sensory neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse to the central nervous system b) motor neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse away from the central nervous system and towards the muscle or gland that needs to respond c) interneurons—nerve cells found only in the brain and spinal co ...
... a) sensory neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse to the central nervous system b) motor neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse away from the central nervous system and towards the muscle or gland that needs to respond c) interneurons—nerve cells found only in the brain and spinal co ...
Neurotransmisson Practice
... some of these extensions are insulated by a layer of fatty cells called the ______________, which help speed the neuron’s impulses. 3. The neural impulse, or ______________________-, is a brief electrical charge that travels down a neuron. 4. The junction between two neurons is called a ____________ ...
... some of these extensions are insulated by a layer of fatty cells called the ______________, which help speed the neuron’s impulses. 3. The neural impulse, or ______________________-, is a brief electrical charge that travels down a neuron. 4. The junction between two neurons is called a ____________ ...
26 - Henderson State University
... Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 26 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 10 ...
... Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 26 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 10 ...
Visual system - cloudfront.net
... shield to keep out germs, dust, and other harmful matter. It also acts like a lens.A lens changes shape to refract light to be focused on the retina ,which is on the back of the eye. ...
... shield to keep out germs, dust, and other harmful matter. It also acts like a lens.A lens changes shape to refract light to be focused on the retina ,which is on the back of the eye. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Named according to their vertebrae Each spinal nerve has 2 roots: dorsal and ventral ...
... Named according to their vertebrae Each spinal nerve has 2 roots: dorsal and ventral ...
eVox Powerpoint
... purchase the eVox system was because of the reimbursement, it’s a great way for my practice to make money. 50% of my practice is on medicare, so eVox has been great in determining signs of dementia from ordinary brain fatigue.” Dr. Ashley, Spokane, WA Medical Specialty: Family Practice ...
... purchase the eVox system was because of the reimbursement, it’s a great way for my practice to make money. 50% of my practice is on medicare, so eVox has been great in determining signs of dementia from ordinary brain fatigue.” Dr. Ashley, Spokane, WA Medical Specialty: Family Practice ...
The Nervous System
... cell body - the cell body of the neuron; it contains the nucleus (also called the soma) dendrites - the branching structure of a neuron that receives messages (attached to the cell body) myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers node of Ranvier - one of the ma ...
... cell body - the cell body of the neuron; it contains the nucleus (also called the soma) dendrites - the branching structure of a neuron that receives messages (attached to the cell body) myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers node of Ranvier - one of the ma ...
Top Memory Improvement Tips
... Memory refers to the processes that are used to acquire, store, retain and later retrieve information. There are three major processes involved in memory: encoding, storage and retrieval2. In order to form new memories, information must be changed into a usable form, which occurs through the process ...
... Memory refers to the processes that are used to acquire, store, retain and later retrieve information. There are three major processes involved in memory: encoding, storage and retrieval2. In order to form new memories, information must be changed into a usable form, which occurs through the process ...
Teen Brain - CDS--The-Tech
... We court risk more avidly as teens than at any other time . . . The period from roughly 15 to 25 brings peaks in all sorts of risky ventures and ugly outcomes. This age group dies of accidents of almost every sort (other than work accidents) at high rates. Most long-term drug or alcohol abuse start ...
... We court risk more avidly as teens than at any other time . . . The period from roughly 15 to 25 brings peaks in all sorts of risky ventures and ugly outcomes. This age group dies of accidents of almost every sort (other than work accidents) at high rates. Most long-term drug or alcohol abuse start ...
Focus on Vocabulary Chapter 07
... To discard the clutter of useless information . . . is surely a blessing. We tend to focus on the importance of remembering and recalling information. However, to be able to get rid of—or throw away (discard)—messy, untidy, irrelevant material (the clutter of useless information) is something to be ...
... To discard the clutter of useless information . . . is surely a blessing. We tend to focus on the importance of remembering and recalling information. However, to be able to get rid of—or throw away (discard)—messy, untidy, irrelevant material (the clutter of useless information) is something to be ...
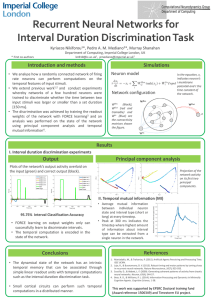
Recurrent Neural Networks for Interval Duration Discrimination Task
... • We analyse how a randomly connected network of firing rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stim ...
... • We analyse how a randomly connected network of firing rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stim ...
Memory: Introduction - People Server at UNCW
... Dementia from Latin: “de” - to depart, “mens” - mind, being out of one's mind. ...
... Dementia from Latin: “de” - to depart, “mens” - mind, being out of one's mind. ...
File
... neurotransmitter at a synapse. 2) Them membrane depolarizes due to voltage-gated Na+ channels opening and Na+ rapidly moving in. 3) The membrane repolarizes due to voltage-gated K+ channels opening and K+ slowly moving out. 4) The membrane returns to the resting potential due to the eventual movemen ...
... neurotransmitter at a synapse. 2) Them membrane depolarizes due to voltage-gated Na+ channels opening and Na+ rapidly moving in. 3) The membrane repolarizes due to voltage-gated K+ channels opening and K+ slowly moving out. 4) The membrane returns to the resting potential due to the eventual movemen ...
Learning Objectives
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
Ch 3 Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Tap your right finger when you see a command on a screen. It's a simple maneuver, yet carrying it out requires a vastly complicated series of actions. First, the image of the words on the screen (telling you to tap your finger) enters your eyes and strikes the retinas. The retinas then convert the ...
... • Tap your right finger when you see a command on a screen. It's a simple maneuver, yet carrying it out requires a vastly complicated series of actions. First, the image of the words on the screen (telling you to tap your finger) enters your eyes and strikes the retinas. The retinas then convert the ...
The Nervous System
... unilateral facial paralysis due to disorder of facial nerve partial paralysis & lack of muscular coordination due to damage to cerebrum during birth ...
... unilateral facial paralysis due to disorder of facial nerve partial paralysis & lack of muscular coordination due to damage to cerebrum during birth ...
anatomy of a neuron worksheet
... carry proteins and other substances through the cell. Locate the microtubules and label them. 4. The tree-like structures on the cell body/soma are called dendrites , the term comes from a Greek word meaning “tree”. Dendrites direct incoming electrochemical signals toward the cell body/soma. Locate ...
... carry proteins and other substances through the cell. Locate the microtubules and label them. 4. The tree-like structures on the cell body/soma are called dendrites , the term comes from a Greek word meaning “tree”. Dendrites direct incoming electrochemical signals toward the cell body/soma. Locate ...
Lecture3
... to treating many brain-related disorders • Parkinson’s Disease – Parkinson’s Disease is a condition in which the individual has trouble executing voluntary movements, and has tremors, rigidity and a ...
... to treating many brain-related disorders • Parkinson’s Disease – Parkinson’s Disease is a condition in which the individual has trouble executing voluntary movements, and has tremors, rigidity and a ...
The Nervous System
... • Myelin sheath: fatty white tissue that covers some axons • Terminal knobs: part of neuron that attaches to another cell • Synapse: connection between terminal knob of one axon and dendrite of another ...
... • Myelin sheath: fatty white tissue that covers some axons • Terminal knobs: part of neuron that attaches to another cell • Synapse: connection between terminal knob of one axon and dendrite of another ...
Remembering What Matters
... People consider Working Memory (WM) to be a collection of various subunits because one can disrupt visual WM with a visual task (following a dot moving on the screen) and verbal WM with a verbal task (repeating the word “the”). However, one cannot disrupt verbal WM with a visual task nor visual WM ...
... People consider Working Memory (WM) to be a collection of various subunits because one can disrupt visual WM with a visual task (following a dot moving on the screen) and verbal WM with a verbal task (repeating the word “the”). However, one cannot disrupt verbal WM with a visual task nor visual WM ...
The relationship between heart-brain dynamics, positive emotions
... long term memory. It has been proven now that heartneurons also have long and shortterm memory. The heart needs functional memory to do it´s job right, fast reactions are impossible if a signal has to be sent to the brain first for approval. Carl Eislyy: ´It is not possible to localise memory to a n ...
... long term memory. It has been proven now that heartneurons also have long and shortterm memory. The heart needs functional memory to do it´s job right, fast reactions are impossible if a signal has to be sent to the brain first for approval. Carl Eislyy: ´It is not possible to localise memory to a n ...