Neural Development - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... a newborn colt or calf is essentially functional at birth. This is necessary because the herd is always on the move. Many animals, including people, do much of their development after birth and activity-dependent mechanisms can exploit experience in the real world. ...
... a newborn colt or calf is essentially functional at birth. This is necessary because the herd is always on the move. Many animals, including people, do much of their development after birth and activity-dependent mechanisms can exploit experience in the real world. ...
1 CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK 2.1. Character
... It is supported with Lloyd and Peterson experiment about limited life span of information in STM. The participants demonstrated combination of three consonants (such as L, R, P) and was asked to remember it then counted backwards to keep them still remember the letter workout. Each individual is the ...
... It is supported with Lloyd and Peterson experiment about limited life span of information in STM. The participants demonstrated combination of three consonants (such as L, R, P) and was asked to remember it then counted backwards to keep them still remember the letter workout. Each individual is the ...
Slide 1
... • Patterns of neuronal electrical activity • Generated by synaptic activity in the cortex • Each person’s brain waves are unique • Can be grouped into four classes based on frequency measured as Hertz (Hz) ...
... • Patterns of neuronal electrical activity • Generated by synaptic activity in the cortex • Each person’s brain waves are unique • Can be grouped into four classes based on frequency measured as Hertz (Hz) ...
Bremen School District 228 Social Studies Common Assessment
... 8. Which of the following is true for those assigned to a control group? A) The experimenter exerts the greatest influence on participants' behavior. B) The research participants are exposed to all the different experimental treatments. C) The research participants are exposed to the most favorable ...
... 8. Which of the following is true for those assigned to a control group? A) The experimenter exerts the greatest influence on participants' behavior. B) The research participants are exposed to all the different experimental treatments. C) The research participants are exposed to the most favorable ...
Comparative approaches to cortical microcircuits
... (ORN) convergence on projection neurons (PNs) [60,61]. Gain reduction for strong signals, by contrast, relies on fast vesicle depletion (hence strong short term depression) at the ORN-PN synapse [59]. Adaptive homeostatic mechanisms appear to be involved also, whereby unitary EPSCs are tuned to PN i ...
... (ORN) convergence on projection neurons (PNs) [60,61]. Gain reduction for strong signals, by contrast, relies on fast vesicle depletion (hence strong short term depression) at the ORN-PN synapse [59]. Adaptive homeostatic mechanisms appear to be involved also, whereby unitary EPSCs are tuned to PN i ...
The Nervous System - Fulton County Schools
... The polio virus causes inflammation of the gray matter in the anterior horn motor neurons. These neurons innervate muscles Symptoms: causes muscle paralysis ...
... The polio virus causes inflammation of the gray matter in the anterior horn motor neurons. These neurons innervate muscles Symptoms: causes muscle paralysis ...
The Nervous System - Canton Local Schools
... Central Nervous System (CNS): The brain and spinal chord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Two parts: 1. Autonomatic (ANS): controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs. AUTOMATIC 2. Somatic (SNS) ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): The brain and spinal chord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Two parts: 1. Autonomatic (ANS): controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs. AUTOMATIC 2. Somatic (SNS) ...
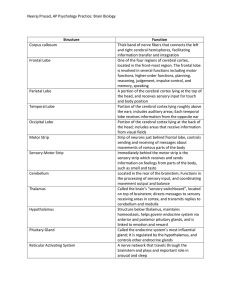
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... One of the four regions of cerebral cortex, located in the front-most region. The frontal lobe is involved in several functions including motor functions, higher-order functions, planning, reasoning, judgement, impulse control, and memory, speaking A portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top o ...
... One of the four regions of cerebral cortex, located in the front-most region. The frontal lobe is involved in several functions including motor functions, higher-order functions, planning, reasoning, judgement, impulse control, and memory, speaking A portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top o ...
Wider Than the Sky: The Phenomenal Gift of Consciousness
... ent areas of the brain. That an area may be essential or necessary for consciousness does not mean it is sufficient. Furthermore, a given neuron may contribute to conscious activity at one moment and not at the next. There are a number of other important aspects of consciousness as a process that m ...
... ent areas of the brain. That an area may be essential or necessary for consciousness does not mean it is sufficient. Furthermore, a given neuron may contribute to conscious activity at one moment and not at the next. There are a number of other important aspects of consciousness as a process that m ...
The Blank Slate
... brain-centered analysis of human behavior. Pinker argues that cognitive science, neuroscience, behavioral genetics, and evolutionary psychology bridge the divide between biology and culture, thus radically rewriting those aspects of the concepts of the Blank Slate, the Noble Savage, and the Ghost in ...
... brain-centered analysis of human behavior. Pinker argues that cognitive science, neuroscience, behavioral genetics, and evolutionary psychology bridge the divide between biology and culture, thus radically rewriting those aspects of the concepts of the Blank Slate, the Noble Savage, and the Ghost in ...
The Nervous System - Zen Shiatsu Chicago
... • Functions of the Nervous System o Sensory Input—monitoring changes both inside and outside the body o Integration—processing and interpreting sensory input and deciding on course of action o Motor Output—a response based on the integration of sensory input; activating effector organs (i.e., muscle ...
... • Functions of the Nervous System o Sensory Input—monitoring changes both inside and outside the body o Integration—processing and interpreting sensory input and deciding on course of action o Motor Output—a response based on the integration of sensory input; activating effector organs (i.e., muscle ...
Nervous System
... which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. • They are also found at the axon endings of motor neurons, where they stimulate the muscle fibers. • They and their close relatives are produced by some glands such as the pituitary and the adrenal glands. ...
... which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. • They are also found at the axon endings of motor neurons, where they stimulate the muscle fibers. • They and their close relatives are produced by some glands such as the pituitary and the adrenal glands. ...
DOWN - Ubiquitous Computing Lab
... A deadlock problem was the key feature of the short story in which Asimov first introduced the laws. He constructed the type of stand- off commonly referred to as the "Buridan's ass" problem. It involved a balance between a strong third- law self- protection tendency, causing the robot to try to av ...
... A deadlock problem was the key feature of the short story in which Asimov first introduced the laws. He constructed the type of stand- off commonly referred to as the "Buridan's ass" problem. It involved a balance between a strong third- law self- protection tendency, causing the robot to try to av ...
Nervous System
... which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. • They are also found at the axon endings of motor neurons, where they stimulate the muscle fibers. • They and their close relatives are produced by some glands such as the pituitary and the adrenal glands. ...
... which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. • They are also found at the axon endings of motor neurons, where they stimulate the muscle fibers. • They and their close relatives are produced by some glands such as the pituitary and the adrenal glands. ...
Answer Key - Psychological Associates of South Florida
... C) unprovable assumption about the unobservable processes that underlie psychological functioning. D) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. ...
... C) unprovable assumption about the unobservable processes that underlie psychological functioning. D) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. ...
Paradigm Shifts in Neurobiology Towards a New Theory of Perception
... cognitive scientists have couverted to the idea that functions like perception, problem-solving or memory emerge from complex interactions in highly distributed neuronal networks which, unlike conventional information-processing systems, are shaped by learning and experiencedependent plasticity. In ...
... cognitive scientists have couverted to the idea that functions like perception, problem-solving or memory emerge from complex interactions in highly distributed neuronal networks which, unlike conventional information-processing systems, are shaped by learning and experiencedependent plasticity. In ...
Chapter 23 take home test File
... 1. Which organ system(s) control or regulate body activities? a) nervous system b) endocrine system c) immune system d) circulatory system e) Both a) and b) control or regulate body activity. 2. Which of the following organisms does NOT have a brain? a) house flies b) ants c) fleas d) None of the ab ...
... 1. Which organ system(s) control or regulate body activities? a) nervous system b) endocrine system c) immune system d) circulatory system e) Both a) and b) control or regulate body activity. 2. Which of the following organisms does NOT have a brain? a) house flies b) ants c) fleas d) None of the ab ...
concept of buddhi, mana and memory processes in
... The memory is the process in which information is encoded, stored, and retrieved. Encoding allows information that is from the outside world to reach our senses in the form of chemical and physical stimuli. The thinking and intellectual power of brain has an unlimited measureless capacity. Buddhi (i ...
... The memory is the process in which information is encoded, stored, and retrieved. Encoding allows information that is from the outside world to reach our senses in the form of chemical and physical stimuli. The thinking and intellectual power of brain has an unlimited measureless capacity. Buddhi (i ...
File
... All-or-None Response: When the depolarizing current exceeds the threshold, a neuron will fire. If the depolarizing current fails to exceed the threshold, a neuron will not fire. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... All-or-None Response: When the depolarizing current exceeds the threshold, a neuron will fire. If the depolarizing current fails to exceed the threshold, a neuron will not fire. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Primary motor cortex
... when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially active when subjects hear words through ear-phones, as seen in the PET scan on the right. To create thes ...
... when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially active when subjects hear words through ear-phones, as seen in the PET scan on the right. To create thes ...
neurons
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...