Exercise 13
... they are outside the CNS and Tracts inside the brain and spinal cord • The cell bodies are clustered in groups in the CNS and are called nuclei • Brain gray matter is made up of millions of nuclei. • It is gray because there is no myelin around the cell bodies ...
... they are outside the CNS and Tracts inside the brain and spinal cord • The cell bodies are clustered in groups in the CNS and are called nuclei • Brain gray matter is made up of millions of nuclei. • It is gray because there is no myelin around the cell bodies ...
What is the Nervous System?
... Autonomic Nervous System Another part of the nervous system is the Autonomic Nervous System. It has three parts: • the sympathetic nervous system • the parasympathetic nervous system • the enteric nervous system This nervous system controls the nerves of the inner organs of the body on which humans ...
... Autonomic Nervous System Another part of the nervous system is the Autonomic Nervous System. It has three parts: • the sympathetic nervous system • the parasympathetic nervous system • the enteric nervous system This nervous system controls the nerves of the inner organs of the body on which humans ...
Interference
... If two light waves are present at the same place at the same time, their electric and magnetic fields add according to the superposition principle. If the two waves are in phase, they add constructively to produce a new wave with greater amplitude. If the two waves are 180° out of phase and have th ...
... If two light waves are present at the same place at the same time, their electric and magnetic fields add according to the superposition principle. If the two waves are in phase, they add constructively to produce a new wave with greater amplitude. If the two waves are 180° out of phase and have th ...
Memory research
... Information on any topic should be presented to students in a variety of formats including spatial, linguistic and sequential. For example, if students are presented with an outline, it may be given in the traditional sequential way as well as with using a strategy called "mind mapping". Mind mappin ...
... Information on any topic should be presented to students in a variety of formats including spatial, linguistic and sequential. For example, if students are presented with an outline, it may be given in the traditional sequential way as well as with using a strategy called "mind mapping". Mind mappin ...
Chapter 7: Memory
... Long term memory forgetting often occurs b/c memory is recalled incorrectly or is mixed up w/ new information ...
... Long term memory forgetting often occurs b/c memory is recalled incorrectly or is mixed up w/ new information ...
Chapter 12- Intro to NS
... A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, dendrites, axon. These cells live for many years, do not under mitosis, and are highly dependant on oxygen due to a high metabolic rate. 1. The cell body (soma)- ...
... A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, dendrites, axon. These cells live for many years, do not under mitosis, and are highly dependant on oxygen due to a high metabolic rate. 1. The cell body (soma)- ...
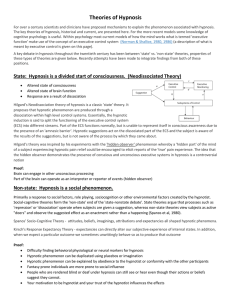
Hypnosis Handout - Updated 2016
... For over a century scientists and clinicians have proposed mechanisms to explain the phenomenon associated with hypnosis. The key theories of hypnosis, historical and current, are presented here. For the more recent models some knowledge of cognitive psychology is useful. Within psychology most curr ...
... For over a century scientists and clinicians have proposed mechanisms to explain the phenomenon associated with hypnosis. The key theories of hypnosis, historical and current, are presented here. For the more recent models some knowledge of cognitive psychology is useful. Within psychology most curr ...
Key Terms - Intro
... by computer, creating an image that represents a slice through the brain. 32. The PET (positron emission tomography) scan measures the levels of activity of different areas of the brain by tracing their consumption of glucose, the brain’s fuel. 33. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic fiel ...
... by computer, creating an image that represents a slice through the brain. 32. The PET (positron emission tomography) scan measures the levels of activity of different areas of the brain by tracing their consumption of glucose, the brain’s fuel. 33. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic fiel ...
Slide 1
... the heart and diaphragm • Some cranial nerves carry only sensory fibers, others carry only motor fibers, and others carry both types of fibers. ...
... the heart and diaphragm • Some cranial nerves carry only sensory fibers, others carry only motor fibers, and others carry both types of fibers. ...
Overview of Addiction Related Brain Regions Nucleus Accumbens
... pleasure. Its size is positively correlated with aggressive behavior across species. In humans, it is the most sexually-dimorphic brain structure, and shrinks by more than 30% in males upon castration. Conditions such as anxiety, autism, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and phobias are su ...
... pleasure. Its size is positively correlated with aggressive behavior across species. In humans, it is the most sexually-dimorphic brain structure, and shrinks by more than 30% in males upon castration. Conditions such as anxiety, autism, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and phobias are su ...
The Biology of Mind
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
What is brain dynamics - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... • (Heterogeneous) Those which require synaptic interactions between two or more populations of neurons, for example CA1 pyramidal neurons together with fast-spiking CA1 interneurons. ...
... • (Heterogeneous) Those which require synaptic interactions between two or more populations of neurons, for example CA1 pyramidal neurons together with fast-spiking CA1 interneurons. ...
Improved detection sensitivity in functional MRI data
... activated region with size and shape similar to the one of the filter are best detected. Since activated regions can in principle have any size or shape, multifiltering or multi-scale approaches have been investigated [11, 14]. However, the greater the filter size the less precise are the boundaries ...
... activated region with size and shape similar to the one of the filter are best detected. Since activated regions can in principle have any size or shape, multifiltering or multi-scale approaches have been investigated [11, 14]. However, the greater the filter size the less precise are the boundaries ...
3 slides
... Z Distributed practice produces memories that are retained for long durations Z Massed practice produces memories that are retained well over short intervals (a few days) but are not retained well for longer durations Z Effects of massed vs. distributed practice depend on the timing of the retention ...
... Z Distributed practice produces memories that are retained for long durations Z Massed practice produces memories that are retained well over short intervals (a few days) but are not retained well for longer durations Z Effects of massed vs. distributed practice depend on the timing of the retention ...
Encoding in Long
... new material can be fitted into the existing organization organization allows material to be grouped (chunked) ...
... new material can be fitted into the existing organization organization allows material to be grouped (chunked) ...
Encoding - Cloudfront.net
... memory, emotions or moods serve as retrieval cues State Dependent Memory what is learned in one state (while one is high, drunk or depressed) can more easily be remembered when in same state ...
... memory, emotions or moods serve as retrieval cues State Dependent Memory what is learned in one state (while one is high, drunk or depressed) can more easily be remembered when in same state ...
Chapter 13: The Nervous System
... K gates close relatively slowly and the outside of the cell becomes even more positively charged than the resting membrane as K ions continue to move out of the cell. This excessive diffusion is called ...
... K gates close relatively slowly and the outside of the cell becomes even more positively charged than the resting membrane as K ions continue to move out of the cell. This excessive diffusion is called ...
unit 6 - nervous system / special senses
... Interneurons are only located in the CNS. They are located between sensory and motor neurons and are responsible for the analysis of sensory inputs and coordinating the motor outputs. 3. There are three basic parts of a neuron -- the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. a. The dendrites are short ...
... Interneurons are only located in the CNS. They are located between sensory and motor neurons and are responsible for the analysis of sensory inputs and coordinating the motor outputs. 3. There are three basic parts of a neuron -- the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. a. The dendrites are short ...
Technology and the Biological Basis of Learning
... pass signals, is virtually the same in the adult as in the newborn. A great deal of the increase in mass is due to the growth of the individual neurons in the form of long projections called axons, and the protective cells that surround them. The development of the mental and motor faculties we thin ...
... pass signals, is virtually the same in the adult as in the newborn. A great deal of the increase in mass is due to the growth of the individual neurons in the form of long projections called axons, and the protective cells that surround them. The development of the mental and motor faculties we thin ...
Chapter 5 as PowerPoint
... • Kind of information being processed changes and different parts of brain may be used • processes that underlie memory retention and recall seem similar throughout the lifespan • but the quantity of information stored and recalled does differ markedly as infants develop. ...
... • Kind of information being processed changes and different parts of brain may be used • processes that underlie memory retention and recall seem similar throughout the lifespan • but the quantity of information stored and recalled does differ markedly as infants develop. ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... Interneurons are only located in the CNS. They are located between sensory and motor neurons and are responsible for the analysis of sensory inputs and coordinating the motor outputs. 3. There are three basic parts of a neuron -- the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. a. The dendrites are short ...
... Interneurons are only located in the CNS. They are located between sensory and motor neurons and are responsible for the analysis of sensory inputs and coordinating the motor outputs. 3. There are three basic parts of a neuron -- the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. a. The dendrites are short ...