Learning Objectives
... neurons of mesencephleic nucleus of 5th CN single axon & single dendrite, eg … ...
... neurons of mesencephleic nucleus of 5th CN single axon & single dendrite, eg … ...
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the
... a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out signals of their own and are considered the basic building blocks of the brain’s anatomy are called neurons b. Cells that aid in the transferring of a signal and help keep the basic structure of the nervous system intact and are neces ...
... a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out signals of their own and are considered the basic building blocks of the brain’s anatomy are called neurons b. Cells that aid in the transferring of a signal and help keep the basic structure of the nervous system intact and are neces ...
Document
... If the stimulus is strong enough to bring the inside to about -55 mv, a THRESHOLD has been reached. Once this occurs, the sodium channels immediately open wide and potassium channels close. ...
... If the stimulus is strong enough to bring the inside to about -55 mv, a THRESHOLD has been reached. Once this occurs, the sodium channels immediately open wide and potassium channels close. ...
Holography
... viewpoint, which is defined by the position of the camera lens. The hologram is not an image, but an encoding system which enables the scattered light field to be reconstructed. Images can then be formed from any point in the reconstructed beam either with a camera or by eye. It was very common in t ...
... viewpoint, which is defined by the position of the camera lens. The hologram is not an image, but an encoding system which enables the scattered light field to be reconstructed. Images can then be formed from any point in the reconstructed beam either with a camera or by eye. It was very common in t ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
the nervous system - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... pertaining to the control of skeletal muscle (somatic motor) activity or sensory information from skeletal muscles, tendons, and joints (somatic sensory) pertaining to the control of functions, such as digestion, circulation, etc. (visceral motor) or sensory information from visceral organs (viscera ...
... pertaining to the control of skeletal muscle (somatic motor) activity or sensory information from skeletal muscles, tendons, and joints (somatic sensory) pertaining to the control of functions, such as digestion, circulation, etc. (visceral motor) or sensory information from visceral organs (viscera ...
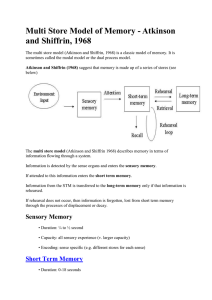
Memory 1
... • is very brief storage of raw or unencoded information at receptor sites • relates directly to our sensory system • we have a sensory register for each sense, which holds information from a fraction of a second and several seconds. • the duration varies from one sense to another • this information ...
... • is very brief storage of raw or unencoded information at receptor sites • relates directly to our sensory system • we have a sensory register for each sense, which holds information from a fraction of a second and several seconds. • the duration varies from one sense to another • this information ...
Sending Signals Notes
... Small Gap or Space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron is called the Synapse. • One importance of the presence of Synapses is that they ensures one-way transmission of impulses in a living person. • The Axon Terminals at a Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These ...
... Small Gap or Space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron is called the Synapse. • One importance of the presence of Synapses is that they ensures one-way transmission of impulses in a living person. • The Axon Terminals at a Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These ...
Ch 13 - lanoue
... The “Dropper” – hold ruler vertical and drop it between your partner’s thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites ...
... The “Dropper” – hold ruler vertical and drop it between your partner’s thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites ...
Chapter 7: Memory
... Long term memory forgetting often occurs b/c memory is recalled incorrectly or is mixed up w/ new information ...
... Long term memory forgetting often occurs b/c memory is recalled incorrectly or is mixed up w/ new information ...
List of References
... forgets less than one thinks or fears.” (Ricoeur 2006: 416) Memories are therefore never truly forgotten because, conforming to its description as a storehouse for memory (Bergson 1912: 81), the brain has the ability to organize stored information into appropriate memory ...
... forgets less than one thinks or fears.” (Ricoeur 2006: 416) Memories are therefore never truly forgotten because, conforming to its description as a storehouse for memory (Bergson 1912: 81), the brain has the ability to organize stored information into appropriate memory ...
8 CHAPTER Memory Chapter Preview Memory is the persistence of
... picture images better than we remember abstract, low-imagery words. We remember concrete nouns better than abstract nouns because, for example, we can associate both an image and a meaning with fire but only a meaning with process. In the peg-word system, people remember new items by using a visual ...
... picture images better than we remember abstract, low-imagery words. We remember concrete nouns better than abstract nouns because, for example, we can associate both an image and a meaning with fire but only a meaning with process. In the peg-word system, people remember new items by using a visual ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
Memory
... into our brains (encoding), retain that information (storage), and later get it back out (retrieval). A computer encodes, stores, and retrieves too. First, it translates input (keystrokes) into an electronic language, much like the brain encodes sensory information into a ...
... into our brains (encoding), retain that information (storage), and later get it back out (retrieval). A computer encodes, stores, and retrieves too. First, it translates input (keystrokes) into an electronic language, much like the brain encodes sensory information into a ...
Neurons and Astrocytes
... • So the brain is boss, but it can't do it alone. It needs some nerves — actually a lot of them. And it needs the spinal cord, which is a long bundle of nerves inside your spinal column, the vertebrae that protect it. It's the spinal cord and nerves — known as the nervous system — that let messages ...
... • So the brain is boss, but it can't do it alone. It needs some nerves — actually a lot of them. And it needs the spinal cord, which is a long bundle of nerves inside your spinal column, the vertebrae that protect it. It's the spinal cord and nerves — known as the nervous system — that let messages ...
Models hand out File
... Participants were presented with a series of 60 words about which they had to answer one of three questions. Some questions required the participants to process the word in a deep way (e.g. semantic) and others in a shallow way (e.g. structural and phonemic). For example: Structural / visual process ...
... Participants were presented with a series of 60 words about which they had to answer one of three questions. Some questions required the participants to process the word in a deep way (e.g. semantic) and others in a shallow way (e.g. structural and phonemic). For example: Structural / visual process ...
Slides - Mathematics of Networks meetings
... Work started as an individual basic research project, motivated by a critical look at modeling biological neurons, rather than using popular connectionist models Biological characteristics of the model needed to include: - Action potential “Signals” in the form of spikes of fixed amplitude - Modelin ...
... Work started as an individual basic research project, motivated by a critical look at modeling biological neurons, rather than using popular connectionist models Biological characteristics of the model needed to include: - Action potential “Signals” in the form of spikes of fixed amplitude - Modelin ...
The Newborn`s Reflexes
... A nerve cell includes dendrites that receive information, a cell body has life-sustaining machinery, and, for sending information, an axon that ends in terminal buttons. ...
... A nerve cell includes dendrites that receive information, a cell body has life-sustaining machinery, and, for sending information, an axon that ends in terminal buttons. ...
Introduction to ANNs
... and Cajal who received a Nobel Prize in 1906. You can see roundish neurons with their output axons. Some leave the area (those at the bottom which form the ‘optic nerve’) and other axons input into other neurons via their input connections called dendrites. Neuron e receives its input from four othe ...
... and Cajal who received a Nobel Prize in 1906. You can see roundish neurons with their output axons. Some leave the area (those at the bottom which form the ‘optic nerve’) and other axons input into other neurons via their input connections called dendrites. Neuron e receives its input from four othe ...
Biological Bases of Behavior: Neural Processing and the Endocrine
... • Larger body systems are made up of smaller and smaller sub systems. As these systems condense, they create specific organs, such as heart and lungs. These are then involved in larger systems, such as your circulatory system These systems then become part of the an even larger system, the individua ...
... • Larger body systems are made up of smaller and smaller sub systems. As these systems condense, they create specific organs, such as heart and lungs. These are then involved in larger systems, such as your circulatory system These systems then become part of the an even larger system, the individua ...
3 Basic Nerve Cells
... are critical for thinking and reasoning. Although many functions, such as touch, are found in b oth the right and left cereb ral hemisp heres, some functions are found p redominantly in only one hemisp here. For examp le, in most p eop le, language ab ilities are localized in the left hemisp here. E ...
... are critical for thinking and reasoning. Although many functions, such as touch, are found in b oth the right and left cereb ral hemisp heres, some functions are found p redominantly in only one hemisp here. For examp le, in most p eop le, language ab ilities are localized in the left hemisp here. E ...



![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015149816_1-9d495749ad340ee903e25aea78e4f4ae-300x300.png)
![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010706021_1-9baf14474201fd4015c7c6d48d77223e-300x300.png)