CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves CNS
... But visceral reflex arc has two neurons in motor pathway Visceral pain afferents travel along same pathways as somatic pain fibers, contributing to phenomenon of referred pain ...
... But visceral reflex arc has two neurons in motor pathway Visceral pain afferents travel along same pathways as somatic pain fibers, contributing to phenomenon of referred pain ...
52 Nerve Tissue
... parallel-running microtubules. The cell membrane of most dendrites forms numerous minute projections called dendritic spines or gemmules that serve as areas for synaptic contact between neurons; an important function of dendrites is to receive impulses from other neurons. Dendrites provide most of t ...
... parallel-running microtubules. The cell membrane of most dendrites forms numerous minute projections called dendritic spines or gemmules that serve as areas for synaptic contact between neurons; an important function of dendrites is to receive impulses from other neurons. Dendrites provide most of t ...
TENS/5.
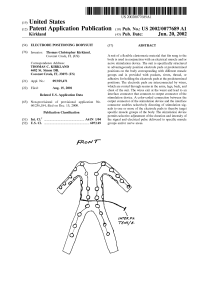
... [0002] The present invention relates generally to Trans cutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Elec trical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) devices for providing a stimulating Waveform and electrical pulses to select muscle groups and nerve areas of the body and, more particularly, ...
... [0002] The present invention relates generally to Trans cutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Elec trical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) devices for providing a stimulating Waveform and electrical pulses to select muscle groups and nerve areas of the body and, more particularly, ...
THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
... Area 17, granular cortex Afferents – visual pathway, thalamic lateral geniculate body. Overrepresentation of central part of retina. Efferents – thalamus (lateral geniculate body), area 18, 19, parietal cortex, temporal cortex. Dorsal stream – parietal cortex (where : rods, periphery of retina, area ...
... Area 17, granular cortex Afferents – visual pathway, thalamic lateral geniculate body. Overrepresentation of central part of retina. Efferents – thalamus (lateral geniculate body), area 18, 19, parietal cortex, temporal cortex. Dorsal stream – parietal cortex (where : rods, periphery of retina, area ...
Nerves Ganglia Spinal nerves Cranial nerves Afferent neurons
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
TSM34 - Chemical Senses
... The sensory receptors for taste are contained in discrete functional units – taste buds o Found in various positions on the surface of papillae on the tongue Laterally in circumvallate and foliate papillae Superiorly on fungiform papillae o Comprise a narrow pore through which chemicals can pass ...
... The sensory receptors for taste are contained in discrete functional units – taste buds o Found in various positions on the surface of papillae on the tongue Laterally in circumvallate and foliate papillae Superiorly on fungiform papillae o Comprise a narrow pore through which chemicals can pass ...
ISHIK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY
... The uncharged form of local anesthetics is more likely to penetrate the membrane but the charged form is more active in blocking the Na+ channel. At high pH, most local anesthetics are uncharged but also have a lower affinity for the sodium channel. At very low pH, there is a higher percentage of ch ...
... The uncharged form of local anesthetics is more likely to penetrate the membrane but the charged form is more active in blocking the Na+ channel. At high pH, most local anesthetics are uncharged but also have a lower affinity for the sodium channel. At very low pH, there is a higher percentage of ch ...
Nervous Sytem notes HS Spring
... The primary motor area is in the frontal lobe; this commands skeletal muscle. The primary somatosensory area is dorsal to the central sulcus or groove. ...
... The primary motor area is in the frontal lobe; this commands skeletal muscle. The primary somatosensory area is dorsal to the central sulcus or groove. ...
ESTH – Esthetician ESTH 1000 - Introduction to Esthetics 3.000
... Provides instruction on and application of techniques and theory in the treatment of the skin. Topics include skin analysis equipment, basic skin care products, basic electricity, men’s skin care products, post consultation and home care, mechanical versus chemical exfoliations, microdermabrasion, a ...
... Provides instruction on and application of techniques and theory in the treatment of the skin. Topics include skin analysis equipment, basic skin care products, basic electricity, men’s skin care products, post consultation and home care, mechanical versus chemical exfoliations, microdermabrasion, a ...
intro to psych ch3 biological bases of behavior
... Resting state is restored After firing, the neuron dips below resting level and is less willing to fire ...
... Resting state is restored After firing, the neuron dips below resting level and is less willing to fire ...
MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... 3. RED NUCLEUS A midbrain structure with ascending input to thalamic VA/VL nucleus and hence to motor cortex through its parvocellular subdivision to permit upper motoneurons to have rapid feedback about actual muscle state for ongoing movement; the magnocellular part contributes to the rubrospinal ...
... 3. RED NUCLEUS A midbrain structure with ascending input to thalamic VA/VL nucleus and hence to motor cortex through its parvocellular subdivision to permit upper motoneurons to have rapid feedback about actual muscle state for ongoing movement; the magnocellular part contributes to the rubrospinal ...
The autonomic nervous system (ANS)
... Nicotinic Receptors are located on: Motor end plates of skeletal muscles (somatic targets) All ganglionic neurons (sypathetic and parasympathetic) The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla ACh always produces a stimulatory effect when it binds with nicotinic receptors Muscarine Recept ...
... Nicotinic Receptors are located on: Motor end plates of skeletal muscles (somatic targets) All ganglionic neurons (sypathetic and parasympathetic) The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla ACh always produces a stimulatory effect when it binds with nicotinic receptors Muscarine Recept ...
a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve
... The fibers ol'the optic nerve are the axons orthe cells in the ganglionic layer of the retina. They converge on the o(1tic disc and exit li'ol11 the eye. about 3 or 4 mm to the nasal side of its center. as the optic nerve The libel's orthe optic nerve arc myelinated. but the sheaths arc j(JI'med li' ...
... The fibers ol'the optic nerve are the axons orthe cells in the ganglionic layer of the retina. They converge on the o(1tic disc and exit li'ol11 the eye. about 3 or 4 mm to the nasal side of its center. as the optic nerve The libel's orthe optic nerve arc myelinated. but the sheaths arc j(JI'med li' ...
Neurons - Jordan High School
... becomes more positive (depolarization) More open channels = more Na+ = more depolarization Repolarization vs. hyperpolarization ...
... becomes more positive (depolarization) More open channels = more Na+ = more depolarization Repolarization vs. hyperpolarization ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Neurons can facilitate - set off an excitatory response neurons can inhibit – a muscle does not fully contract all fibers at the same time. ...
... Neurons can facilitate - set off an excitatory response neurons can inhibit – a muscle does not fully contract all fibers at the same time. ...
MENNONITE COLLEGE OF NURSING AT ILLINOIS STATE
... worsen or improve the pain, duration and frequency of pain, associated symptoms (nausea, vomiting, duration and frequency of paresthesias, weakness, seizures, muscle stiffness or soreness, fever, weakness). Time of day of onset, age at previous onset, hospitalizations, drug therapy and effects. Fami ...
... worsen or improve the pain, duration and frequency of pain, associated symptoms (nausea, vomiting, duration and frequency of paresthesias, weakness, seizures, muscle stiffness or soreness, fever, weakness). Time of day of onset, age at previous onset, hospitalizations, drug therapy and effects. Fami ...
Ch 28-29
... Chapter 28 Sensory Input and Motor Output Chapter 29 Reproduction and Embryonic Development 28.1 The Senses ...
... Chapter 28 Sensory Input and Motor Output Chapter 29 Reproduction and Embryonic Development 28.1 The Senses ...
Cranial Nerves - Austin Community College
... - homunculus (little man)- portrays motor and sensory areas of body overlaying precentral and postcentral gyri of the cortex ...
... - homunculus (little man)- portrays motor and sensory areas of body overlaying precentral and postcentral gyri of the cortex ...
Neuro_Basis_of_AK__by_Dr._Walter_Schmitt
... all centrally generated effects at that moment, and observing changes in the patient's motor responses to that context…” ...
... all centrally generated effects at that moment, and observing changes in the patient's motor responses to that context…” ...
lower motor neurons
... • Pyramidal tract: in strict sense those fibers that course longitudinally in the pyramid of medulla oblongata. • It descends from the cortex, crosses corona radiata, posterior limb of internal capsule, cerebral peduncle, ventral pons, pyramid of upper medulla, crosses in lower medulla and continues ...
... • Pyramidal tract: in strict sense those fibers that course longitudinally in the pyramid of medulla oblongata. • It descends from the cortex, crosses corona radiata, posterior limb of internal capsule, cerebral peduncle, ventral pons, pyramid of upper medulla, crosses in lower medulla and continues ...
9.2 - 4ubiology
... Differentiating Between Warm & Hot The more intense the stimulus, the greater the frequency of impulses. Intense stimuli excite more neurons. Different ...
... Differentiating Between Warm & Hot The more intense the stimulus, the greater the frequency of impulses. Intense stimuli excite more neurons. Different ...
Chapter 12
... Somatic receptors include sensory receptors in skin, muscle, joints, ligaments Nerve impulses from general (somatic) receptors sent to the primary somatosensory area of parietal lobe of cerebral cortex Somatosensory area processes the information and perception of sensation happens here ...
... Somatic receptors include sensory receptors in skin, muscle, joints, ligaments Nerve impulses from general (somatic) receptors sent to the primary somatosensory area of parietal lobe of cerebral cortex Somatosensory area processes the information and perception of sensation happens here ...
Nervous System
... Kingdom, they have a network of nerves that conducts signals from sensory cells to muscle cells. But their nervous system is not centralized. 3) Many flatworms have a netlike nerve system like cnidarians but some have a more organized and complex system with a brain and spinal chord. The nervous sys ...
... Kingdom, they have a network of nerves that conducts signals from sensory cells to muscle cells. But their nervous system is not centralized. 3) Many flatworms have a netlike nerve system like cnidarians but some have a more organized and complex system with a brain and spinal chord. The nervous sys ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.