Reflex Arc - Point Loma High School
... The sensory neurons pass through the spinal cord which allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of steering signals through the brain, although the brain will receive sensory input while the reflex action occurs. ...
... The sensory neurons pass through the spinal cord which allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of steering signals through the brain, although the brain will receive sensory input while the reflex action occurs. ...
What we*ll sense and perceive* in this chapter:
... When light reaches the back of the retina, it triggers chemical changes in two types of receptor cells: Rods help us see the black and white actions in our peripheral view and in the dark. Cones help us see sharp colorful details in bright light. ...
... When light reaches the back of the retina, it triggers chemical changes in two types of receptor cells: Rods help us see the black and white actions in our peripheral view and in the dark. Cones help us see sharp colorful details in bright light. ...
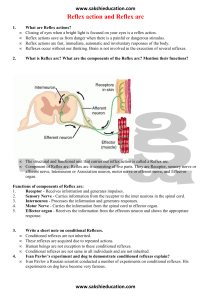
Reflex action and Reflex arc
... Closing of eyes when a bright light is focused on your eyes is a reflex action. Reflex actions save us from danger when there is a painful or dangerous stimulus. Reflex actions are fast, immediate, automatic and involuntary responses of the body. Reflexes occur without our thinking. Brain is not inv ...
... Closing of eyes when a bright light is focused on your eyes is a reflex action. Reflex actions save us from danger when there is a painful or dangerous stimulus. Reflex actions are fast, immediate, automatic and involuntary responses of the body. Reflexes occur without our thinking. Brain is not inv ...
Neuron
... Are covered by thorny spines (gemmules) which are sites of synaptic contact. Receive stimuli from sensory cells and other neurons and transmit them towards the soma. So they can be regarded as major sites of information input into neuron. Axon: Fig.(2) Single, long, cylindrical process of a ne ...
... Are covered by thorny spines (gemmules) which are sites of synaptic contact. Receive stimuli from sensory cells and other neurons and transmit them towards the soma. So they can be regarded as major sites of information input into neuron. Axon: Fig.(2) Single, long, cylindrical process of a ne ...
NS Review
... If people are in the same mood they were in during an event, they may have an easier time recalling the event ...
... If people are in the same mood they were in during an event, they may have an easier time recalling the event ...
MUSCLE ORIGIN/INSERTION ACTION INNERVATION
... pterygoid plate to joint capsule and articular disk of TMJ and pterygoid fovea on anteromedial aspect of condyloid process of mandible Medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate and pyramidal process of palatine bone and tuberosity of maxilla to medial surface of ramus of mandible inferior to mandibu ...
... pterygoid plate to joint capsule and articular disk of TMJ and pterygoid fovea on anteromedial aspect of condyloid process of mandible Medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate and pyramidal process of palatine bone and tuberosity of maxilla to medial surface of ramus of mandible inferior to mandibu ...
STUDY GUIDE 8
... If a drug prevents an excitatory neurotransmitter from binding to receptors of the postsynaptic neuNo How might such a drug be useful in a clinical situation? ron, will synaptic transmission occur? _____ Such a drug would be useful when it is desirable to prevent or reduce the transmission of impuls ...
... If a drug prevents an excitatory neurotransmitter from binding to receptors of the postsynaptic neuNo How might such a drug be useful in a clinical situation? ron, will synaptic transmission occur? _____ Such a drug would be useful when it is desirable to prevent or reduce the transmission of impuls ...
L7- Brainstem Studen..
... • Ventral view of the pons •Between the basal pons, cranial nerve 6 (abducens), 7 (facial) and 8 (vestibulocochlear) emerge (medial to lateral). •At the level of the midpons, the large trigeminal ...
... • Ventral view of the pons •Between the basal pons, cranial nerve 6 (abducens), 7 (facial) and 8 (vestibulocochlear) emerge (medial to lateral). •At the level of the midpons, the large trigeminal ...
Color Atlas of Neurology
... Reflexes Reflexes are involuntary and relatively stereotyped responses to specific stimuli. Afferent nerve fibers conduct the impulses generated by activated receptors to neurons in the central nervous system, which fire impulses that are then transmitted through efferent nerve fibers to the cells, ...
... Reflexes Reflexes are involuntary and relatively stereotyped responses to specific stimuli. Afferent nerve fibers conduct the impulses generated by activated receptors to neurons in the central nervous system, which fire impulses that are then transmitted through efferent nerve fibers to the cells, ...
Sher`s Neurology Pre-Quiz Quiz
... 69. Receptor, receptor potential, threshold, action potential 70. Amplitude, receptor potential, frequency, receptor potential 71. Adaptation 72. High, lower 73. Tonic 74. Rate, movement, phasic, detect 75. A, larger, myelinated 76. Alpha, beta, gamma, delta 77. Half, peripheral, post-ganglionic 78. ...
... 69. Receptor, receptor potential, threshold, action potential 70. Amplitude, receptor potential, frequency, receptor potential 71. Adaptation 72. High, lower 73. Tonic 74. Rate, movement, phasic, detect 75. A, larger, myelinated 76. Alpha, beta, gamma, delta 77. Half, peripheral, post-ganglionic 78. ...
The Nervous System
... • Controls skeletal muscle contraction, center for learning, emotion, memory, and perception • The cerebral cortex is vital for perception, voluntary movement, and learning. • The corpus callosum is a structure that enables the right and left hemispheres to communicate. • Deep in the white matter th ...
... • Controls skeletal muscle contraction, center for learning, emotion, memory, and perception • The cerebral cortex is vital for perception, voluntary movement, and learning. • The corpus callosum is a structure that enables the right and left hemispheres to communicate. • Deep in the white matter th ...
The Nervous System
... • Impulses are transmitted from cell to cell by the release of chemicals called ...
... • Impulses are transmitted from cell to cell by the release of chemicals called ...
vollllllkkks_1
... may be synthesized and released as a neurotransmitter by the NANC neurons after their excitation by either electrical or chemical stimulation. In this regard we have suggested that NO is highly labile; therefore, it cannot be stored as a preformed neurotransmitter. There are at least three distinct ...
... may be synthesized and released as a neurotransmitter by the NANC neurons after their excitation by either electrical or chemical stimulation. In this regard we have suggested that NO is highly labile; therefore, it cannot be stored as a preformed neurotransmitter. There are at least three distinct ...
File
... • Myelinated cat fiber = carry impulses up to 100 m/s • Unmyelinated cat fiber = carry impulses only 5 m/s ...
... • Myelinated cat fiber = carry impulses up to 100 m/s • Unmyelinated cat fiber = carry impulses only 5 m/s ...
File nervous system, ppt
... pituitary glands; therefore it indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands Contains centers for controlling appetite, wakefulness, pleasure, etc. ...
... pituitary glands; therefore it indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands Contains centers for controlling appetite, wakefulness, pleasure, etc. ...
4.27.05 Respiration and Nervous
... • The dorsal root of a spinal nerve contains sensory fibers that conduct sensory impulses from sensory receptors toward the spinal cord. • Dorsal root ganglia near the spinal cord contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons. • The ventral root of a spinal nerve contains motor fibers that conduct imp ...
... • The dorsal root of a spinal nerve contains sensory fibers that conduct sensory impulses from sensory receptors toward the spinal cord. • Dorsal root ganglia near the spinal cord contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons. • The ventral root of a spinal nerve contains motor fibers that conduct imp ...
BIOLOGY 3201
... 1. What are the two major divisions of the human nervous system? Abbreviations are fine. 2. __?__ are three protective membranes surrounding the brain . 3. grey matter: brownish-grey nerve tissue consisting of mainly __?__ within the brain and spinal cord 4. Which part of the autonomic nervous syste ...
... 1. What are the two major divisions of the human nervous system? Abbreviations are fine. 2. __?__ are three protective membranes surrounding the brain . 3. grey matter: brownish-grey nerve tissue consisting of mainly __?__ within the brain and spinal cord 4. Which part of the autonomic nervous syste ...
Nervous System (1)
... The Central Nervous System includes the: Brain and the Spinal Chord CEREBRUM ...
... The Central Nervous System includes the: Brain and the Spinal Chord CEREBRUM ...
Nervous System - WordPress.com
... With regard to pain pathways, all the following are true EXCEPT: a) peripheral afferents are transmitted along A (delta) and C fibres b) an intact cerebral cortex is necessary for pain sensation c) the synaptic transmitter released by primary afferent fibres subserving pain is substance P d) afferen ...
... With regard to pain pathways, all the following are true EXCEPT: a) peripheral afferents are transmitted along A (delta) and C fibres b) an intact cerebral cortex is necessary for pain sensation c) the synaptic transmitter released by primary afferent fibres subserving pain is substance P d) afferen ...
Lecture 13: Insect nerve system (NS)
... By the direction of information that they send (function) • Afferent (sensory) neurons --bipolar or multipolar cells have dendrites that are associated with sense organs. They carry information TOWARD the central nervous system (CNS). • Efferent (motor) neurons -- unipolar cells that conduct signals ...
... By the direction of information that they send (function) • Afferent (sensory) neurons --bipolar or multipolar cells have dendrites that are associated with sense organs. They carry information TOWARD the central nervous system (CNS). • Efferent (motor) neurons -- unipolar cells that conduct signals ...
Mullins
... Determine the best position for the child and her toys to accommodate for central field loss. ...
... Determine the best position for the child and her toys to accommodate for central field loss. ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.