bupropion and the autonomic nervous system
... The nervous system comprises the brain and various types of nerves, including afferent nerves (from the Latin, ad = towards; ferro = I carry), which carry sensory impulses from all parts of the body to the brain and efferent nerves (ex = from; ferro = I carry) through which "messages" are conducted ...
... The nervous system comprises the brain and various types of nerves, including afferent nerves (from the Latin, ad = towards; ferro = I carry), which carry sensory impulses from all parts of the body to the brain and efferent nerves (ex = from; ferro = I carry) through which "messages" are conducted ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... 2. The distal branches of a spinal nerve are more complex. (Fig. 13.13) a. Immediately after emerging from the intervertebral foramen, the nerve divides into an anterior ramus, and posterior ramus, and a small meningeal branch. i. Each spinal nerve branches on both ends: anterior and posterior roots ...
... 2. The distal branches of a spinal nerve are more complex. (Fig. 13.13) a. Immediately after emerging from the intervertebral foramen, the nerve divides into an anterior ramus, and posterior ramus, and a small meningeal branch. i. Each spinal nerve branches on both ends: anterior and posterior roots ...
Skeletal Reflexes - University of Houston College of Optometry
... muscle spindles. Stretch reflexes are important in maintaining normal posture and balance. Makes automatic adjustments in muscle tone. Stimulus is increasing muscle length Activates a sensory neuron that triggers a motor response which is contraction of the stretched muscle. This counteracts the sti ...
... muscle spindles. Stretch reflexes are important in maintaining normal posture and balance. Makes automatic adjustments in muscle tone. Stimulus is increasing muscle length Activates a sensory neuron that triggers a motor response which is contraction of the stretched muscle. This counteracts the sti ...
Trigeminal Neuralgia
... will recur. Bouts of pains tend to become more frequent as you become older. Are there any complications? The pain itself can be severe and distressing. If left untreated, this may make you depressed or anxious. You may neglect to clean your teeth or not eat for fear of ...
... will recur. Bouts of pains tend to become more frequent as you become older. Are there any complications? The pain itself can be severe and distressing. If left untreated, this may make you depressed or anxious. You may neglect to clean your teeth or not eat for fear of ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... Dendrites and axons are cytoplasmic extensions, or processes, that project from the cell body. They are sometimes referred to as fibers. Dendrites are usually, but not always, short and branching, which increases their surface area to receive signals from other neurons. The number of dendrites on a ...
... Dendrites and axons are cytoplasmic extensions, or processes, that project from the cell body. They are sometimes referred to as fibers. Dendrites are usually, but not always, short and branching, which increases their surface area to receive signals from other neurons. The number of dendrites on a ...
SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Each sensory receptor has an adequate stimulus, a particular form of energy to which it is most responsive. For example, thermoreceptors are more sensitive to temperature changes than to pressure, and mechanoreceptors respond preferentially to stimuli that deform the cell membrane, receptors in th ...
... • Each sensory receptor has an adequate stimulus, a particular form of energy to which it is most responsive. For example, thermoreceptors are more sensitive to temperature changes than to pressure, and mechanoreceptors respond preferentially to stimuli that deform the cell membrane, receptors in th ...
Spinal Cord and Nerves
... Bundles axons into fascicles CT Epineurium Bundles fascicles into a nerve Fibrous CT CT layers contain blood vessels ...
... Bundles axons into fascicles CT Epineurium Bundles fascicles into a nerve Fibrous CT CT layers contain blood vessels ...
Biology 13A
... 7. Typical sympathetic postganglionic fibers that release norepinephrine at neuroeffector junctions are classified as a. cholinergic b. adrenergic c. norephinephric d. nonsecretory e. none of the above 8. The sympathetic division of the ANS includes which of the following? a. three segmentally arran ...
... 7. Typical sympathetic postganglionic fibers that release norepinephrine at neuroeffector junctions are classified as a. cholinergic b. adrenergic c. norephinephric d. nonsecretory e. none of the above 8. The sympathetic division of the ANS includes which of the following? a. three segmentally arran ...
Bilateral communication between
... Bilateral communication between musculocutaneous and median nerve the MN in the middle of the arm, whereas in type III, the lateral root fibres of the MN pass along the MCN and after some distance, leave it to form the lateral root of the MN. In type IV, the MCN fibres join the lateral root of the ...
... Bilateral communication between musculocutaneous and median nerve the MN in the middle of the arm, whereas in type III, the lateral root fibres of the MN pass along the MCN and after some distance, leave it to form the lateral root of the MN. In type IV, the MCN fibres join the lateral root of the ...
A & P 240: Overview of the Human Nervous System
... 1. The N.S. helps control and integrate all body activities by sensing changes (sensory), interpreting them (integrative), and responding to them (motor). 2. The N.S. has two principal Divisions: the Central N.S. (CNS) and the Peripheral N.S. (PNS). 3. The CNS consists of the Brain and Spinal Cord. ...
... 1. The N.S. helps control and integrate all body activities by sensing changes (sensory), interpreting them (integrative), and responding to them (motor). 2. The N.S. has two principal Divisions: the Central N.S. (CNS) and the Peripheral N.S. (PNS). 3. The CNS consists of the Brain and Spinal Cord. ...
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
... reference. Even when motor action does occur, comparison of sensory input in one modality (e.g., vision) when compared with input from another modality (e.g., touch) can result in memories that lead to adjustment of the relation between the two modalities. This happens extensively during postnatal d ...
... reference. Even when motor action does occur, comparison of sensory input in one modality (e.g., vision) when compared with input from another modality (e.g., touch) can result in memories that lead to adjustment of the relation between the two modalities. This happens extensively during postnatal d ...
Chapter Eleven
... Myelin Sheath and Neurilemma • Formed by _________________ cells in the _ • A Schwann cell: – Envelopes an axon – Encloses the axon with its plasma membrane – Has concentric layers of membrane that make up the myelin sheath ...
... Myelin Sheath and Neurilemma • Formed by _________________ cells in the _ • A Schwann cell: – Envelopes an axon – Encloses the axon with its plasma membrane – Has concentric layers of membrane that make up the myelin sheath ...
Muscle
... • Muscles involved in movement can be classified as agonists, antagonists, and synergists. • Three types of muscle action are concentric, static, and eccentric. • Force production is increased by recruiting more motor units. ...
... • Muscles involved in movement can be classified as agonists, antagonists, and synergists. • Three types of muscle action are concentric, static, and eccentric. • Force production is increased by recruiting more motor units. ...
NEUROLOGIC INVESTIGATIONS
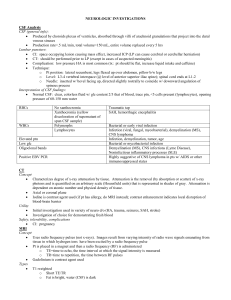
... o Sharp and spike wave discharges w/ or w/o accompanying slow wave interictal epileptiform findings o Rhythmic spike or sharp and slow wave discharges or rhythmic slow waves focal or generalized electrographic seizures Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) Electrical stimulus applied over a nerve, and ...
... o Sharp and spike wave discharges w/ or w/o accompanying slow wave interictal epileptiform findings o Rhythmic spike or sharp and slow wave discharges or rhythmic slow waves focal or generalized electrographic seizures Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) Electrical stimulus applied over a nerve, and ...
456 ss 96 final - People Server at UNCW
... 28. Which of the following is true of the primary visual cortex : a) it gives meaning to complex stimuli like faces b) it allocates a small proportion of its area to processing foveal vision c) it is not layered d) it is not organized in columns e) LGN inputs terminate at layer 4 29. The optic radia ...
... 28. Which of the following is true of the primary visual cortex : a) it gives meaning to complex stimuli like faces b) it allocates a small proportion of its area to processing foveal vision c) it is not layered d) it is not organized in columns e) LGN inputs terminate at layer 4 29. The optic radia ...
chapt12 neuron_lecture
... • Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Myelin sheath of CNS deteriorate and are replaced by scar tissue • Starts somewhere between 20s-40s, patients survive 7-32 years after the onset • Symptoms: depend on what part of CNS is involved: blindness, speech defects, tremors, neurosis • No cure, but it might be immun ...
... • Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Myelin sheath of CNS deteriorate and are replaced by scar tissue • Starts somewhere between 20s-40s, patients survive 7-32 years after the onset • Symptoms: depend on what part of CNS is involved: blindness, speech defects, tremors, neurosis • No cure, but it might be immun ...
Modeling and Imagery
... about rate control…see open & closed loop control later) • Made up of intrafusal muscle fibers and sensory receptors • Transmits info about amount and rate of stretch in muscle ...
... about rate control…see open & closed loop control later) • Made up of intrafusal muscle fibers and sensory receptors • Transmits info about amount and rate of stretch in muscle ...
Presentation
... Separate the recorded signal into different components. High frequencies (>500 Hz): ...
... Separate the recorded signal into different components. High frequencies (>500 Hz): ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... receives sensory information (input) from receptors transmits this information to the CNS. ...
... receives sensory information (input) from receptors transmits this information to the CNS. ...
Human Anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... receives sensory information (input) from receptors transmits this information to the CNS. ...
... receives sensory information (input) from receptors transmits this information to the CNS. ...
Nervous System
... • Vasomotor center: constricts or dilates the blood vessels, influencing blood pressure ...
... • Vasomotor center: constricts or dilates the blood vessels, influencing blood pressure ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... a. Cell bodies of motor neurons b. Cell bodies of sensory neurons c. Cell bodies of cortical neurons d. Cell bodies of smooth muscle cells e. Cell bodies of skeletal muscle cells ...
... a. Cell bodies of motor neurons b. Cell bodies of sensory neurons c. Cell bodies of cortical neurons d. Cell bodies of smooth muscle cells e. Cell bodies of skeletal muscle cells ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.