Biopsychology and the Foundations of Neuroscience Chapter 3
... You and your siblings probably look similar, but not exactly the same. This is because what you inherit from your parents is a random shuffling of genes. ◦ This random shuffling and variation is what Darwin viewed as the raw material for evolution and genetic differences. ...
... You and your siblings probably look similar, but not exactly the same. This is because what you inherit from your parents is a random shuffling of genes. ◦ This random shuffling and variation is what Darwin viewed as the raw material for evolution and genetic differences. ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
Nervous System
... (fibres) of sensory and motor nerve cells. Nerve cells are also known as neurons. ...
... (fibres) of sensory and motor nerve cells. Nerve cells are also known as neurons. ...
Mind Is Matter
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous System
... have residual neurological deficit & > 25% require chronic care • Includes all disorders in which an area of the brain is transiently or permanently affected by ischemia or bleeding and one or more of the cerebral blood vessels are involved in the pathological process • Ischemic stroke: accounts for ...
... have residual neurological deficit & > 25% require chronic care • Includes all disorders in which an area of the brain is transiently or permanently affected by ischemia or bleeding and one or more of the cerebral blood vessels are involved in the pathological process • Ischemic stroke: accounts for ...
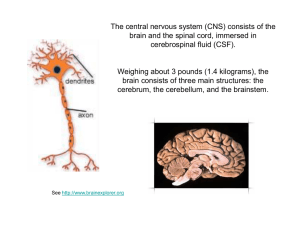
The Nervous System
... Ø Do not transfer any information Ø Provide metabolic support and protection for neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems Ø More numerous than neurons? ...
... Ø Do not transfer any information Ø Provide metabolic support and protection for neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems Ø More numerous than neurons? ...
consciousness
... • between conscious and unconscious elements of memory • between forms of brain damage that selectively impair conscious process and those that don’t • between wakefulness and unconsciousness • between new and habituated events ...
... • between conscious and unconscious elements of memory • between forms of brain damage that selectively impair conscious process and those that don’t • between wakefulness and unconsciousness • between new and habituated events ...
Nervous System
... 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain & Spinal Cord – process incoming & outgoing messages 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves – connects all neurons to the central nervous system ...
... 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain & Spinal Cord – process incoming & outgoing messages 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves – connects all neurons to the central nervous system ...
Невротрансмитери в ЦНС
... Glutamate is the excitatory amino acid transmitter in the CNS. It acts at NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) and other receptors. NMDA receptors are involved in the development of adaptive responses that modulate synaptic transmission, known as synaptic plasticity.These responses have a role in both physi ...
... Glutamate is the excitatory amino acid transmitter in the CNS. It acts at NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) and other receptors. NMDA receptors are involved in the development of adaptive responses that modulate synaptic transmission, known as synaptic plasticity.These responses have a role in both physi ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
Nerve
... stimulus. The external stimulus may be electrical, microelectrodes are inserted into cells, membrane (axons ...
... stimulus. The external stimulus may be electrical, microelectrodes are inserted into cells, membrane (axons ...
Unit 3B Study Guide
... The once friendly, soft-spoken Gage became irritable and dishonest. Gage's case provided evidence that which region of the brain plays a role in personality and behavior? A) temporal lobes B) sensory cortex C) frontal lobes D) parietal lobes E) Broca's area 14. To trigger a person's hand to make a f ...
... The once friendly, soft-spoken Gage became irritable and dishonest. Gage's case provided evidence that which region of the brain plays a role in personality and behavior? A) temporal lobes B) sensory cortex C) frontal lobes D) parietal lobes E) Broca's area 14. To trigger a person's hand to make a f ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... 2. Functional Plasticity – When an area of the brain takes up a new function to replace a damaged area of the brain. ...
... 2. Functional Plasticity – When an area of the brain takes up a new function to replace a damaged area of the brain. ...
Deanne Boules presentation pdf
... medicine, genetics and applied disciplines such as psychology ...
... medicine, genetics and applied disciplines such as psychology ...
Worksheet - Humble ISD
... connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense organs to the brain. The electrical signal of the neuron is carried toward the ________________ by the _____________ and away from the nucleus of the neuron by the _______________, which is surrounded ...
... connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense organs to the brain. The electrical signal of the neuron is carried toward the ________________ by the _____________ and away from the nucleus of the neuron by the _______________, which is surrounded ...
Quiz
... 11. The brief period of time immediately after the initiation of an action potential when it is impossible to initiate another one in the same neuron is called the a. Threshold of excitation b. Threshold ...
... 11. The brief period of time immediately after the initiation of an action potential when it is impossible to initiate another one in the same neuron is called the a. Threshold of excitation b. Threshold ...
Chapter 6
... not completely understood, motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord begin to disintegrate. (58) 4. Potential causes or contributors to ALS include an excess amount of the neurotransmitter _____. (59) 5. Scientists have now identified several genes that are responsible for some forms of ALS. The mo ...
... not completely understood, motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord begin to disintegrate. (58) 4. Potential causes or contributors to ALS include an excess amount of the neurotransmitter _____. (59) 5. Scientists have now identified several genes that are responsible for some forms of ALS. The mo ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... This communication system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. Our nervous system allows us to feel pain. ...
... This communication system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. Our nervous system allows us to feel pain. ...
PAC Newsletter - March 2015
... connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use through our experiences in our environment creating pathways. These repetitions create pathways of memory. The development of your child’s brain is interdependent upon the genetic structure and life experiences, especially with you ...
... connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use through our experiences in our environment creating pathways. These repetitions create pathways of memory. The development of your child’s brain is interdependent upon the genetic structure and life experiences, especially with you ...
5 levels of Neural Theory of Language
... to arrive at biological accounts of perceptual, motor, cognitive and language learning Biological Learning is concerned with this topic. ...
... to arrive at biological accounts of perceptual, motor, cognitive and language learning Biological Learning is concerned with this topic. ...
Lecture #19 - Suraj @ LUMS
... An action potential is a temporary reversal of the electrical. potential along the membrane for a few milliseconds. 1. Stimulus (pressure, chemical, electrical) alters shape of membrane carrier proteins. 2. Some Na + rushes in = depolarization. Inside of cell becomes locally + instead of –. 3. Local ...
... An action potential is a temporary reversal of the electrical. potential along the membrane for a few milliseconds. 1. Stimulus (pressure, chemical, electrical) alters shape of membrane carrier proteins. 2. Some Na + rushes in = depolarization. Inside of cell becomes locally + instead of –. 3. Local ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... • Cell body (soma): contains nucleus • Axon: long tail-like end of neuron which transmits (sends) messages ...
... • Cell body (soma): contains nucleus • Axon: long tail-like end of neuron which transmits (sends) messages ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...