Neuron encyclopaedia fires up to reveal brain secrets
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
Higher brain functions
... • After intense stimulation of the presynaptic neuron, the amplitude of the post-synaptic neuron’s response increases. • The stimulus applied is generally of short duration (less than 1 second) but high frequency • In the postsynaptic neuron, this stimulus causes sufficient depolarization to evacua ...
... • After intense stimulation of the presynaptic neuron, the amplitude of the post-synaptic neuron’s response increases. • The stimulus applied is generally of short duration (less than 1 second) but high frequency • In the postsynaptic neuron, this stimulus causes sufficient depolarization to evacua ...
Neural Coalition and Main Theorem
... •What is memory? How is it physically stored and accessed? • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obt ...
... •What is memory? How is it physically stored and accessed? • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obt ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... • Localization of Function • Whether specific areas of the brain control specific abilities or behaviors ...
... • Localization of Function • Whether specific areas of the brain control specific abilities or behaviors ...
“The Physiology of Excitable Cells”
... intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive with respect to outside. The motion of each ion during each discrete time step is determined by, first, the net electrical force acting on it; secondly, the frictional force and, finally, r ...
... intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive with respect to outside. The motion of each ion during each discrete time step is determined by, first, the net electrical force acting on it; secondly, the frictional force and, finally, r ...
Structure of the Brain PowerPoint Notes
... _______________ branch out and end near dendrites of neighboring cells • ____________________ are the tips of the axon’s branches • A gap separates the axon terminals from dendrites - called the _________________ or synaptic gap • Presynaptic neuron – message-sending neuron • Postsynaptic neuron – ...
... _______________ branch out and end near dendrites of neighboring cells • ____________________ are the tips of the axon’s branches • A gap separates the axon terminals from dendrites - called the _________________ or synaptic gap • Presynaptic neuron – message-sending neuron • Postsynaptic neuron – ...
Ling411-02-Neurons - OWL-Space
... Result of this summation is the amount of incoming activation Determines how much activation will be transmitted along the axon (and its branches), hence to other neurons Degree of activation is implemented as frequency of spikes ...
... Result of this summation is the amount of incoming activation Determines how much activation will be transmitted along the axon (and its branches), hence to other neurons Degree of activation is implemented as frequency of spikes ...
Connectionism
... different letters are pronounced under different circumstances. (It has been argued that ''ghiti'' could be pronounced ''fish'' - ''gh'' from ''enough'' and ''ti'' from ''nation.'') • But once the system has evolved, it acts as though it knows the rules. They become implicitly coded in the network o ...
... different letters are pronounced under different circumstances. (It has been argued that ''ghiti'' could be pronounced ''fish'' - ''gh'' from ''enough'' and ''ti'' from ''nation.'') • But once the system has evolved, it acts as though it knows the rules. They become implicitly coded in the network o ...
Slide ()
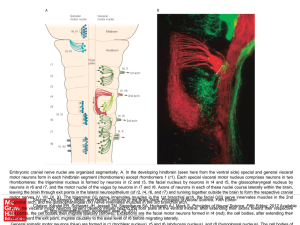
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Grant Clay
... a. Family Studies/Kinship Studies – Researchers compare Blood relatives to see how much they are similar in a trait; More similarity will be found among family members who share more genes ...
... a. Family Studies/Kinship Studies – Researchers compare Blood relatives to see how much they are similar in a trait; More similarity will be found among family members who share more genes ...
HPA Axis Activation and Hippocampal Atrophy
... hippocampal pyramidal neurons was first noticed in aging rats. Adrenalectomy performed on middle-aged rat can halt this process, while administration of glucocorticoid for 12 weeks resulted in neuronal loss in hippocampal formation. Chronic social stress can also decrease the amount of hippocampal n ...
... hippocampal pyramidal neurons was first noticed in aging rats. Adrenalectomy performed on middle-aged rat can halt this process, while administration of glucocorticoid for 12 weeks resulted in neuronal loss in hippocampal formation. Chronic social stress can also decrease the amount of hippocampal n ...
Document
... • The brain goes through dynamic change during adolescence, and alcohol can seriously damage long- and short-term growth processes. • Frontal lobe development and the refinement of pathways and connections continue until age 16, and a high rate of energy is used as the brain matures until age 20. • ...
... • The brain goes through dynamic change during adolescence, and alcohol can seriously damage long- and short-term growth processes. • Frontal lobe development and the refinement of pathways and connections continue until age 16, and a high rate of energy is used as the brain matures until age 20. • ...
Studying the Living Human Brain
... for integrating and acting on information received and processed by sensory areas. ...
... for integrating and acting on information received and processed by sensory areas. ...
The Brain - Gordon State College
... – Medulla: controls breathing, heart rate, swallowing, digestion, and posture ...
... – Medulla: controls breathing, heart rate, swallowing, digestion, and posture ...
The Biology of the Brain
... • d) carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. Different • a) have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons that bring information to and take it away from the cell body (respectively). • b) communicate with each other through electrochemical proces ...
... • d) carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. Different • a) have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons that bring information to and take it away from the cell body (respectively). • b) communicate with each other through electrochemical proces ...
Editorial: Cell Assemblies - CommuniGate Pro uni
... assembly, once a subset of its cells are stimulated, tends to be activated as a whole, it can be considered as an operational unit in the brain. Hebb related cell assemblies to the psychological level by proposing that they represent “objects” (or more abstract entities of thought). In the framework ...
... assembly, once a subset of its cells are stimulated, tends to be activated as a whole, it can be considered as an operational unit in the brain. Hebb related cell assemblies to the psychological level by proposing that they represent “objects” (or more abstract entities of thought). In the framework ...
Module 4 Notes
... A split brain is one whose corpus callosum, the wide band of axon fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres, has been severed. Experiments on split-brain patients have refined our knowledge of each hemisphere’s special functions. In the laboratory, investigators ask a split-brain patient to loo ...
... A split brain is one whose corpus callosum, the wide band of axon fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres, has been severed. Experiments on split-brain patients have refined our knowledge of each hemisphere’s special functions. In the laboratory, investigators ask a split-brain patient to loo ...
Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
... Axon terminal – the place where one axon ends and forms a synapse with another neuron ...
... Axon terminal – the place where one axon ends and forms a synapse with another neuron ...
File
... • Sends information/messages from sensory receptors (such as skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARDS the CNS. • Sensory neurons have specialised endings that are sensitive to a particular stimuli such as heat, pressure or light called Receptors. • Messages are sent as an electrical impulse along the ...
... • Sends information/messages from sensory receptors (such as skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARDS the CNS. • Sensory neurons have specialised endings that are sensitive to a particular stimuli such as heat, pressure or light called Receptors. • Messages are sent as an electrical impulse along the ...
slides - NYU Computation and Cognition Lab
... Information flows between neurons with action potentials and synaptic transmission (involving neurotransmitters) The likely mechanism for memory is the changes at the synapses in the form of LTP, dendritic growth, etc.. Circuits represent the collective action of interconnected networks of neurons C ...
... Information flows between neurons with action potentials and synaptic transmission (involving neurotransmitters) The likely mechanism for memory is the changes at the synapses in the form of LTP, dendritic growth, etc.. Circuits represent the collective action of interconnected networks of neurons C ...
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz
... active in executive functions such as judgment planning and inhibit action of impulses active in use of working memory and processing new memories Frontal line associating areas many functions in area behind sensory strip managing input from multiple senses performing spatial and mathema ...
... active in executive functions such as judgment planning and inhibit action of impulses active in use of working memory and processing new memories Frontal line associating areas many functions in area behind sensory strip managing input from multiple senses performing spatial and mathema ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... VI. Effects of Aging A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar region. (loss of muscle mass & increase fatigue) C. Size and weight of the brain decre ...
... VI. Effects of Aging A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar region. (loss of muscle mass & increase fatigue) C. Size and weight of the brain decre ...
Pasko Rakic`s Autobiography
... computerized animation of this dynamic process, based on my India ink drawings, is provided at (http://rakiclab.med.yale.edu/MigratingCorticalNeuron.html). Based on this discovery, I proposed a radial unit hypothesis of cortical development and evolution, which provides insight into how the complex, ...
... computerized animation of this dynamic process, based on my India ink drawings, is provided at (http://rakiclab.med.yale.edu/MigratingCorticalNeuron.html). Based on this discovery, I proposed a radial unit hypothesis of cortical development and evolution, which provides insight into how the complex, ...