Neural basis of learning and memory
... perspective, but also biologically as they both involve and are influenced by many of the same neural mechanisms and processes. All memory involves neurological changes that occur as a result of learning. Memory is not a recorded ‘snapshot’ of an event but a neurological representation of the event. ...
... perspective, but also biologically as they both involve and are influenced by many of the same neural mechanisms and processes. All memory involves neurological changes that occur as a result of learning. Memory is not a recorded ‘snapshot’ of an event but a neurological representation of the event. ...
Alzheimer`s disease: when the mind goes astray
... diagnose with precision but also to know when it begins since early symptoms are so similar to the first signs of the normal ageing process of the brain. It all starts with small failings of the memory such as mild forgetfulness that can be bothersome in every day living, or words that will not come ...
... diagnose with precision but also to know when it begins since early symptoms are so similar to the first signs of the normal ageing process of the brain. It all starts with small failings of the memory such as mild forgetfulness that can be bothersome in every day living, or words that will not come ...
Coding and learning of behavioral sequences
... fields (Figure 1b), rate coding is sufficient [10,11,29,30] and a precise temporal code is not required. The development of asymmetric place fields [24,30] or, similarly, of visual receptive fields [31,32] could therefore be interpreted as a system-level signature of asymmetric Hebbian plasticity. I ...
... fields (Figure 1b), rate coding is sufficient [10,11,29,30] and a precise temporal code is not required. The development of asymmetric place fields [24,30] or, similarly, of visual receptive fields [31,32] could therefore be interpreted as a system-level signature of asymmetric Hebbian plasticity. I ...
Membrane potential
... • Brain’s capacity to store and retrieve information about past sensory input • Stored in stages – Temporary storage in cerebral cortex ...
... • Brain’s capacity to store and retrieve information about past sensory input • Stored in stages – Temporary storage in cerebral cortex ...
Part 1: True/False
... Referred Pain. Pain neurons that monitor the heart synapse onto the same dorsal spinal cord neurons that receive information from the skin along their arms. Therefore the signal from the spinal cord eventually ends up in the arm representation of the somatosensory cortex. ...
... Referred Pain. Pain neurons that monitor the heart synapse onto the same dorsal spinal cord neurons that receive information from the skin along their arms. Therefore the signal from the spinal cord eventually ends up in the arm representation of the somatosensory cortex. ...
CNS Autonomic NS
... • Coding and processing of stimuli allows us to determine the stimulus type, intensity, location, and duration • Type determined by the cortex in response to where the input comes from; 1:1 association between type of receptor and sensation is called labeled line coding • Location determined by whic ...
... • Coding and processing of stimuli allows us to determine the stimulus type, intensity, location, and duration • Type determined by the cortex in response to where the input comes from; 1:1 association between type of receptor and sensation is called labeled line coding • Location determined by whic ...
Message Transmission
... So, what happens at the end of the axon? • You run into a synapse. – This is the junction between any two communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic ...
... So, what happens at the end of the axon? • You run into a synapse. – This is the junction between any two communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic ...
I. Introduction to class
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
Chapter 28: Nervous System
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
Biological Impact
... • Agonists mimic the neurotransmitter by binding to the receptor sites just as the neurotransmitters do and having the same effect on the receiving neuron. Agonists are used when it is believed that there is not enough neurotransmitter • Antagonists BLOCK the neurotransmitter by binding to the recep ...
... • Agonists mimic the neurotransmitter by binding to the receptor sites just as the neurotransmitters do and having the same effect on the receiving neuron. Agonists are used when it is believed that there is not enough neurotransmitter • Antagonists BLOCK the neurotransmitter by binding to the recep ...
UNIT II: THE HUMAN BRAIN
... • Nerves (but not neurons) have the ability to regrow • Gives us the ability to reattach limbs • Difference between nerve and neuron: – Neuron is individual cell – Nerve is a group of neurons • Think of nerves as the superfast lane of highway neurons use to get signals to your brain ...
... • Nerves (but not neurons) have the ability to regrow • Gives us the ability to reattach limbs • Difference between nerve and neuron: – Neuron is individual cell – Nerve is a group of neurons • Think of nerves as the superfast lane of highway neurons use to get signals to your brain ...
Your Body Is Nothing Without A Brain
... This author was able to solve the problem of paraplegic and quadriplegic injuries in young children and adults resulting in blows to the steel face mask used in football. The weight of the new face mask, commercialized and licensed to Riddell, was less than half the weight of the pre-existing steel ...
... This author was able to solve the problem of paraplegic and quadriplegic injuries in young children and adults resulting in blows to the steel face mask used in football. The weight of the new face mask, commercialized and licensed to Riddell, was less than half the weight of the pre-existing steel ...
biophysiology show 1
... • Based on the idea that the human being is a type of animal • Therefore it is valid to make inferences about human behaviour based on animal research because the mechanisms that underlie behaviour are the core similarity we share ...
... • Based on the idea that the human being is a type of animal • Therefore it is valid to make inferences about human behaviour based on animal research because the mechanisms that underlie behaviour are the core similarity we share ...
Nervous System Poster
... o Right and left cerebral hemispheres in humans Note: You DO NOT need to know the types of nervous systems, details of various structures and features of the brain parts, and details of specific neurologic processes. ...
... o Right and left cerebral hemispheres in humans Note: You DO NOT need to know the types of nervous systems, details of various structures and features of the brain parts, and details of specific neurologic processes. ...
Adolescents Brain Development
... • Use it or lose it • Adolescence and young adulthood is a time of great potential for change and development ...
... • Use it or lose it • Adolescence and young adulthood is a time of great potential for change and development ...
The Human Brain 101
... The left hemisphere has 186 million more neurons than the right hemisphere The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph, as “slow” as Bugatti EB 16.4 Veyron which clocked at 253 mph More electrical impulses are generated in one day by the brain than by all the teleph ...
... The left hemisphere has 186 million more neurons than the right hemisphere The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph, as “slow” as Bugatti EB 16.4 Veyron which clocked at 253 mph More electrical impulses are generated in one day by the brain than by all the teleph ...
CNS Brain 241North
... movements with current body position to produce smooth, exact movement • Involved in learning new balance-intensive activities – Riding a bike, yoga, climbing ...
... movements with current body position to produce smooth, exact movement • Involved in learning new balance-intensive activities – Riding a bike, yoga, climbing ...
Cranial and Nerves
... Verbal 1 No response 2 Incomprehensible sounds 3 Inappropriate words 4 Disoriented and converses 5 Oriented and converses ...
... Verbal 1 No response 2 Incomprehensible sounds 3 Inappropriate words 4 Disoriented and converses 5 Oriented and converses ...
Following the discussion about mirror neurons and imagery we want
... stimulus-figure, trough the transduction on the muscular system and propriocective afferences could perceive the emotional meaning of the stimulus, experienced by his own body. So connotative (micro-emotional), denotative (cognitive) components of the stimulus are unified. In this way a bridge betw ...
... stimulus-figure, trough the transduction on the muscular system and propriocective afferences could perceive the emotional meaning of the stimulus, experienced by his own body. So connotative (micro-emotional), denotative (cognitive) components of the stimulus are unified. In this way a bridge betw ...
File
... exist within, and contribute to the structure of the CNS itself. -- the action potential (nerve impulse) does NOT diminish in strength as its journey along an axon persists. -- synaptic endings are swellings at the end of an axon. -- synaptic endings serve as the link between the neuron and either a ...
... exist within, and contribute to the structure of the CNS itself. -- the action potential (nerve impulse) does NOT diminish in strength as its journey along an axon persists. -- synaptic endings are swellings at the end of an axon. -- synaptic endings serve as the link between the neuron and either a ...
Slide ()
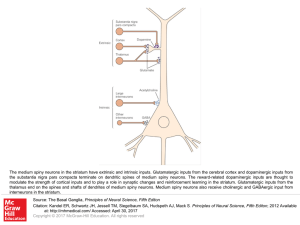
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
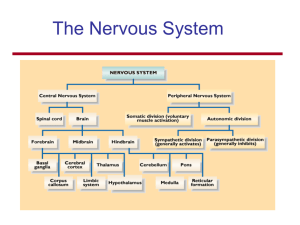
The Nervous System
... Thalamus: serves as a relay station for almost all information that comes and goes to the cortex Limbic system (includes hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus) Amygdala: emotional reactions Hippocampus: memory ...
... Thalamus: serves as a relay station for almost all information that comes and goes to the cortex Limbic system (includes hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus) Amygdala: emotional reactions Hippocampus: memory ...