Direct Electrode Stimulation Direct electrode stimulation involves
... field pulse through the skull and temporarily activates or disrupts the normal activity of neurons in a specific area of the cerebral cortex. In this procedure, patients are sat in a chair while a magnetic field pulse is transmitted from a small copper electromagnetic coil placed next to the scalp. ...
... field pulse through the skull and temporarily activates or disrupts the normal activity of neurons in a specific area of the cerebral cortex. In this procedure, patients are sat in a chair while a magnetic field pulse is transmitted from a small copper electromagnetic coil placed next to the scalp. ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... neuron, receiving input from other neurons. Dendrites are covered with synapses. Each synapse has many receptors for neurotransmitters of various kinds. Dendritic spines – specialized dendrites that isolate reactions at some synapses. ...
... neuron, receiving input from other neurons. Dendrites are covered with synapses. Each synapse has many receptors for neurotransmitters of various kinds. Dendritic spines – specialized dendrites that isolate reactions at some synapses. ...
Introduction to the brain and behaviour
... Cortical areas 1. Sensory cortex areas – receive and process information from the senses. 2. Motor cortex area – receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements. 3. Association cortex areas – integrate sensory, motor and other information and are involved in complex menta ...
... Cortical areas 1. Sensory cortex areas – receive and process information from the senses. 2. Motor cortex area – receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements. 3. Association cortex areas – integrate sensory, motor and other information and are involved in complex menta ...
Research Interests: Reading neural codes Current:
... receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what the monkey was watching when the LGN spike occurred. Much of the data is still being analyzed. Whereas the ...
... receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what the monkey was watching when the LGN spike occurred. Much of the data is still being analyzed. Whereas the ...
The Nervous System
... • Carries fine touch, pressure, proprioception (position) • Ascending neurons synapse in medulla oblongata • Axons cross over and synapse in thalamus • Thalamus sends axons to primary sensory cortex • Organized as sensory homunculus ...
... • Carries fine touch, pressure, proprioception (position) • Ascending neurons synapse in medulla oblongata • Axons cross over and synapse in thalamus • Thalamus sends axons to primary sensory cortex • Organized as sensory homunculus ...
Fast thinking article 1
... share and debate ideas. But when people compete for recognition, they stop sharing information. Creativity was shown also to suffer greatly during a downsizing of team structures and infrastructures - an important lesson for many senior managers too often attracted by processes of “rationalisation”. ...
... share and debate ideas. But when people compete for recognition, they stop sharing information. Creativity was shown also to suffer greatly during a downsizing of team structures and infrastructures - an important lesson for many senior managers too often attracted by processes of “rationalisation”. ...
Consciousness, Thought, and Memory
... cortices -> medial temporal lobe (hippocampus and temporal cortical areas) -> thalmus and prefrontal cortex <-basal forebrain Memories are retrieved when the same sets of neurons that were initially involved in memory formation are stimulated. ...
... cortices -> medial temporal lobe (hippocampus and temporal cortical areas) -> thalmus and prefrontal cortex <-basal forebrain Memories are retrieved when the same sets of neurons that were initially involved in memory formation are stimulated. ...
The Human Nervous System
... such as the knee jerk reflex, follows. 1. A tap on the knee stimulates sensory receptors (tendon), generating a nerve signal. 2. The signal travels along a nerve to the spinal cord. 3. In the spinal cord, the signal is transmitted from the sensory nerve to a motor nerve. 4. The motor nerve sends the ...
... such as the knee jerk reflex, follows. 1. A tap on the knee stimulates sensory receptors (tendon), generating a nerve signal. 2. The signal travels along a nerve to the spinal cord. 3. In the spinal cord, the signal is transmitted from the sensory nerve to a motor nerve. 4. The motor nerve sends the ...
Abbreviations: LTP= long
... declarative memory, things that are transiently stored in parts of the brain, like the hippocampus, and then stored in the cortex. c. We know this because we all have pneumonics that we use to remember things. d. The reason associative memory is useful is because it is like storing information by im ...
... declarative memory, things that are transiently stored in parts of the brain, like the hippocampus, and then stored in the cortex. c. We know this because we all have pneumonics that we use to remember things. d. The reason associative memory is useful is because it is like storing information by im ...
Slide ()
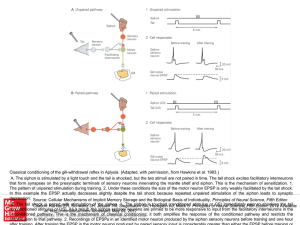
... A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses on the presynaptic terminals of sensory neurons innervating the mantle shelf and siphon. This is the mechanism of sens ...
... A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses on the presynaptic terminals of sensory neurons innervating the mantle shelf and siphon. This is the mechanism of sens ...
The Nervous System
... between different parts of the body and the body's interactions with the environment. c. Students know how feedback loops in the nervous and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. d. Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochem ...
... between different parts of the body and the body's interactions with the environment. c. Students know how feedback loops in the nervous and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. d. Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochem ...
Synaptogenesis
... Excessive depolarization (slicing) results in rapid increase of inhibitory synapse number ...
... Excessive depolarization (slicing) results in rapid increase of inhibitory synapse number ...
Nervous system (Brain and Plexi)
... 1. The central nervous system (CNS) 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) The central nervous system consist of Brain and Spinal Cord, The peripheral nervous system is composed of all nerves outside the central system (Spinal nerves and cranial nerves) The rat have 34 pairs of spinal nerves: 8 c ...
... 1. The central nervous system (CNS) 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) The central nervous system consist of Brain and Spinal Cord, The peripheral nervous system is composed of all nerves outside the central system (Spinal nerves and cranial nerves) The rat have 34 pairs of spinal nerves: 8 c ...
BRAIN
... (upregulating AMPA and NMDA receptors, increase in dendrites and overall surface area of postsynaptic neuron) Retrograde Signaling: Postsynaptic cell also releases an unknown paracrine (once thought to be Nitric Oxide, but scientists are now unsure) that acts on the presynaptic cell to enhance gluta ...
... (upregulating AMPA and NMDA receptors, increase in dendrites and overall surface area of postsynaptic neuron) Retrograde Signaling: Postsynaptic cell also releases an unknown paracrine (once thought to be Nitric Oxide, but scientists are now unsure) that acts on the presynaptic cell to enhance gluta ...
TeachingwiththeBrain-BasedNaturalHumanFACES_forprint
... Each person's special learning needs might be different from any other person's and also difficult to diagnose. When my granddaughter went to first grade, we thought she’d be a great reader. Her parents always read to her, and she could read her books. No, she had memorized them, as many children do ...
... Each person's special learning needs might be different from any other person's and also difficult to diagnose. When my granddaughter went to first grade, we thought she’d be a great reader. Her parents always read to her, and she could read her books. No, she had memorized them, as many children do ...
Cellular Neuroscience - How Your Brain Works
... • A common side-effect of L-DOPA therapy • The case shown here is quite severe ...
... • A common side-effect of L-DOPA therapy • The case shown here is quite severe ...
PNS Study Guide
... 10. ***Draw a neuron. Label the neuron, dendrites, cell body, axon, Schwann cells, nodes of Ranvier, axon terminals, synapse and synaptic cleft. *** 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called ...
... 10. ***Draw a neuron. Label the neuron, dendrites, cell body, axon, Schwann cells, nodes of Ranvier, axon terminals, synapse and synaptic cleft. *** 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called ...
Gluck_OutlinePPT_Ch02
... single neurons as they become active (“fire”). Implanted electrodes deliver electrical charges that stimulate a neuron into activity. Observe evoked behavior. ...
... single neurons as they become active (“fire”). Implanted electrodes deliver electrical charges that stimulate a neuron into activity. Observe evoked behavior. ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions. The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cortex that carries the functions out have been identified) but it is i ...
... brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions. The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cortex that carries the functions out have been identified) but it is i ...
Making Waves With Your Brain!!!!
... detected on the outside of your brain • They result from the total average electrical activity inside your brain • You cannot get a shock from them, they are very small voltages • The signals change in size at regular intervals between 1/10 and 60 times a second depending how active the brain is. • ...
... detected on the outside of your brain • They result from the total average electrical activity inside your brain • You cannot get a shock from them, they are very small voltages • The signals change in size at regular intervals between 1/10 and 60 times a second depending how active the brain is. • ...
Brain Development - Pottstown School District
... rapidly at 2 to 4 months of age, peaking in intensity at 8 months. It is no coincidence that babies begin to take notice of the world during this period. Scientists believe that language is acquired most easily during the first ten years of life. During these years, the circuits in children’s brains ...
... rapidly at 2 to 4 months of age, peaking in intensity at 8 months. It is no coincidence that babies begin to take notice of the world during this period. Scientists believe that language is acquired most easily during the first ten years of life. During these years, the circuits in children’s brains ...