Theoretical Neuroscience: From Single Neuron to Network Dynamics
... – Insert such rules in networks, and study how inputs with prescribed statistics shape network attractor landscape – Study maximal storage capacity of the network, with different types of attractors – Learning rules that are able to reach maximal capacity? ...
... – Insert such rules in networks, and study how inputs with prescribed statistics shape network attractor landscape – Study maximal storage capacity of the network, with different types of attractors – Learning rules that are able to reach maximal capacity? ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... Some neurotransmitters excite the next cell into firing and some inhibit the next cell from firing. Specific neurotransmitters “bind” with specific POSTSYNAPTIC RECEPTORS. 1. “Lock and Key” model 2. Neurotransmitter—receptor binding causes postsynaptic changes 3. ION CHANNEL: closely “tied” to a r ...
... Some neurotransmitters excite the next cell into firing and some inhibit the next cell from firing. Specific neurotransmitters “bind” with specific POSTSYNAPTIC RECEPTORS. 1. “Lock and Key” model 2. Neurotransmitter—receptor binding causes postsynaptic changes 3. ION CHANNEL: closely “tied” to a r ...
Notes Module #1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... Removal of brain tissue or structures leads to an understanding of those cells/structures. (tumors/elective) ...
... Removal of brain tissue or structures leads to an understanding of those cells/structures. (tumors/elective) ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS-Central Nervous System PNS
... A by itself = no transmission A+D = transmission A + B + D = no transmission ...
... A by itself = no transmission A+D = transmission A + B + D = no transmission ...
The Nervous System
... environment stable, secrete chemicals to help restore damage, and respond to signals from neurons – enable neurons to function ...
... environment stable, secrete chemicals to help restore damage, and respond to signals from neurons – enable neurons to function ...
The Human Body Systems
... B. The Neuron – the basic unit of structure & function 1. Cells that carry information to, from & through the brain by way of nerve impulses. 2. Structure – cannot grow back if cut or broken a) Large cell body contains the nucleus and multiple thread-like extensions. (1) Dendrites – thread-like “fin ...
... B. The Neuron – the basic unit of structure & function 1. Cells that carry information to, from & through the brain by way of nerve impulses. 2. Structure – cannot grow back if cut or broken a) Large cell body contains the nucleus and multiple thread-like extensions. (1) Dendrites – thread-like “fin ...
questions from - AP Psychology: 6(A)
... 26. Neurons found in the center of the spinal cord that receive information from the sensory neurons and send commands to the muscles through the motor neurons are called __________. 27. Cameron touches a hot iron and immediately pulls his hand away. His quick response occurs because __________. 28 ...
... 26. Neurons found in the center of the spinal cord that receive information from the sensory neurons and send commands to the muscles through the motor neurons are called __________. 27. Cameron touches a hot iron and immediately pulls his hand away. His quick response occurs because __________. 28 ...
Module 2.1 Neurons: The Body`s Wiring Lecture Outline
... Neurons don’t actually touch; they are separated by a synapse The neural impulse reaches the axon’s terminal buttons and triggers the release of chemicals that either increase or decrease the likelihood that neighboring cells will fire (Figure 2.3) Neurotransmitters are either excitatory, making an ...
... Neurons don’t actually touch; they are separated by a synapse The neural impulse reaches the axon’s terminal buttons and triggers the release of chemicals that either increase or decrease the likelihood that neighboring cells will fire (Figure 2.3) Neurotransmitters are either excitatory, making an ...
Lecture 4 ppt
... • FROM THESE EVIDENCES WE CAN ACCEPT A WORKING HYPOTHESIS THAT EVERYTHING WE OBSERVE IS A RESULT OF PROCESSING BY CERTAIN BRAIN STRUCTURES. • THE QUESTION IS HOW THESE STRUCTURES OPERATE? THIS HAS TO BE VERY COMPLEX. CERTAIN BEHAVIORS ARE PROGRAMMED (ANIMALS) BUT THERE IS SIGNIFICANT LEARNING AND A ...
... • FROM THESE EVIDENCES WE CAN ACCEPT A WORKING HYPOTHESIS THAT EVERYTHING WE OBSERVE IS A RESULT OF PROCESSING BY CERTAIN BRAIN STRUCTURES. • THE QUESTION IS HOW THESE STRUCTURES OPERATE? THIS HAS TO BE VERY COMPLEX. CERTAIN BEHAVIORS ARE PROGRAMMED (ANIMALS) BUT THERE IS SIGNIFICANT LEARNING AND A ...
The human brain - "G. Galilei" – Pescara
... System: a branch of the autonomic nervous system responsible for mobilizing the body's energy and resources during times of stress and arousal. ...
... System: a branch of the autonomic nervous system responsible for mobilizing the body's energy and resources during times of stress and arousal. ...
Nervous system
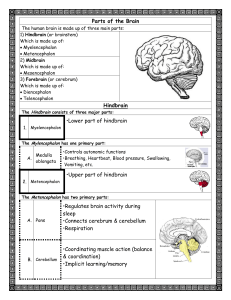
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...
Intellectual Development in Infants
... Dendrites = arms of neurons that receive information from the axons. They are like branches reaching out toward each other but never touch. Synapses = space /gap between dendrites ...
... Dendrites = arms of neurons that receive information from the axons. They are like branches reaching out toward each other but never touch. Synapses = space /gap between dendrites ...
CNS neurotransmitters
... Actions and Site of Actions Most of the serotonin in the brain is in the brainstem, specifically in the raphe nuclei; considerable amounts also are present in areas of the hypothalamus, the limbic system, and the pituitary gland. Current evidence indicates that serotonin is involved in the regula ...
... Actions and Site of Actions Most of the serotonin in the brain is in the brainstem, specifically in the raphe nuclei; considerable amounts also are present in areas of the hypothalamus, the limbic system, and the pituitary gland. Current evidence indicates that serotonin is involved in the regula ...
phys chapter 45 [10-24
... Neuropeptides usually cause more prolonged actions Vesicle portion of membrane invaginates back to inside of presynaptic terminal to be recycled; new vesicular membrane still contains appropriate enzyme proteins or transport proteins required for synthesizing and/or concentrating new transmitter sub ...
... Neuropeptides usually cause more prolonged actions Vesicle portion of membrane invaginates back to inside of presynaptic terminal to be recycled; new vesicular membrane still contains appropriate enzyme proteins or transport proteins required for synthesizing and/or concentrating new transmitter sub ...
Brain`s Building Blocks
... like GABA keys and open GABA receptors ◦ when GABA neurons are excited, they decrease neural activity ...
... like GABA keys and open GABA receptors ◦ when GABA neurons are excited, they decrease neural activity ...
Development of the Brain
... vacant receptors. • Cells that have lost their source of innervation release neurotrophins that induce axons to ...
... vacant receptors. • Cells that have lost their source of innervation release neurotrophins that induce axons to ...
Name: The nervous system Reference URL: http://faculty
... Go to: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/chmodel.html#string There are several ideas for making a model neuron or brain. Choose the model you wish to make. You will need to bring the materials you need (check out the requirements for each model). Your model must be completely labelled and you ne ...
... Go to: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/chmodel.html#string There are several ideas for making a model neuron or brain. Choose the model you wish to make. You will need to bring the materials you need (check out the requirements for each model). Your model must be completely labelled and you ne ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Extracellular calcium concentrations in the brain fluctuate during neuronal activities and may affect the behavior of brain cells. Microglia are highly dynamic immune cells of the brain. However, the effects of extracellular calcium concentrations on microglial dynamics have not been investigated. H ...
... Extracellular calcium concentrations in the brain fluctuate during neuronal activities and may affect the behavior of brain cells. Microglia are highly dynamic immune cells of the brain. However, the effects of extracellular calcium concentrations on microglial dynamics have not been investigated. H ...
There are about 3 million miles of axons in the human brain. The
... dilation, hearing and body movement ...
... dilation, hearing and body movement ...
B6 Brain and Mind revised - Blackpool Aspire Academy
... When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
PDF
... signalling patterns. These results provide new insights into gonadal sex determination and also define for the first time the critical time window in which a master gene that determines organ fate has to act. ...
... signalling patterns. These results provide new insights into gonadal sex determination and also define for the first time the critical time window in which a master gene that determines organ fate has to act. ...
PDF
... signalling patterns. These results provide new insights into gonadal sex determination and also define for the first time the critical time window in which a master gene that determines organ fate has to act. ...
... signalling patterns. These results provide new insights into gonadal sex determination and also define for the first time the critical time window in which a master gene that determines organ fate has to act. ...