Every synaptic algebra has the monotone square root property
... If A is a commutative synaptic algebra, then A is a commutative, associative, partially ordered, Archimedean, real linear algebra with a unity element 1 that is an order unit; it is a normed linear algebra under the orderunit norm; and it may be regarded as its own enveloping algebra. By [11, Theore ...
... If A is a commutative synaptic algebra, then A is a commutative, associative, partially ordered, Archimedean, real linear algebra with a unity element 1 that is an order unit; it is a normed linear algebra under the orderunit norm; and it may be regarded as its own enveloping algebra. By [11, Theore ...
AGING PRESENTATION
... Ex: 100.000 neuron loss daily resulting in 19.7% loss at the age of 80 [Brody et al.]. With the advancements of neuron counting technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the st ...
... Ex: 100.000 neuron loss daily resulting in 19.7% loss at the age of 80 [Brody et al.]. With the advancements of neuron counting technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the st ...
Chapter 4
... Brain Plasticity • Plasticity – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
... Brain Plasticity • Plasticity – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
Chapter 4
... Brain Plasticity • Plasticity – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
... Brain Plasticity • Plasticity – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
slides
... Water maze task is complex and requires animals to learn the general task requirement as well as the specific location of the hidden platform Spatial pretraining can separate the two kinds of learning Rats first made familiar with the general task requirements and subsequently trained after receivin ...
... Water maze task is complex and requires animals to learn the general task requirement as well as the specific location of the hidden platform Spatial pretraining can separate the two kinds of learning Rats first made familiar with the general task requirements and subsequently trained after receivin ...
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
... Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the underside of the brain: 2 pairs arise from the cerebrum and 10 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brainstem. These cranial nerves are designated by numbers and names. The number indicates the order in which the nerve arises from the brain, form anter ...
... Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the underside of the brain: 2 pairs arise from the cerebrum and 10 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brainstem. These cranial nerves are designated by numbers and names. The number indicates the order in which the nerve arises from the brain, form anter ...
Nervous Systems
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
bulbar pseudobulbar
... nerves are innervated by the motor strip areas of both the left and right hemispheres. This redundancy is a safety mechanism. If there is a unilateral lesion on the pyramidal tract, both sides of body areas connected to cranial nerves will continue to receive motor messages from the cortex. The mess ...
... nerves are innervated by the motor strip areas of both the left and right hemispheres. This redundancy is a safety mechanism. If there is a unilateral lesion on the pyramidal tract, both sides of body areas connected to cranial nerves will continue to receive motor messages from the cortex. The mess ...
Slide 1
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
Brain Waves Volunteer Instructor Guide
... The size of sensory receiving areas, relative to different body parts, is shown by the unusual proportions of the homunculus. A larger area in the brain means a greater sensitivity of that body part, relative to other body parts. Very sensitive areas of the skin, like fingers, have very high densiti ...
... The size of sensory receiving areas, relative to different body parts, is shown by the unusual proportions of the homunculus. A larger area in the brain means a greater sensitivity of that body part, relative to other body parts. Very sensitive areas of the skin, like fingers, have very high densiti ...
Why Do We Sleep - The Dallas Philosophers Forum
... conscious experience of the brain has to be interrupted in order to integrate new memories without becoming oversaturated or obliterating older memories. Their hypothesis is that in order for the brain to return to its baseline, there has to be a weakening of some lines between neurons during sleep. ...
... conscious experience of the brain has to be interrupted in order to integrate new memories without becoming oversaturated or obliterating older memories. Their hypothesis is that in order for the brain to return to its baseline, there has to be a weakening of some lines between neurons during sleep. ...
Neurons and Synapses
... Students will collect information from pre-set resources to develop understanding of the nervous system, neurons, synapses, and neurotransmitters. Information gather from this lesson will help them build models and participate in neuron related activities of future lessons. Time Needed: 1+ Period(s) ...
... Students will collect information from pre-set resources to develop understanding of the nervous system, neurons, synapses, and neurotransmitters. Information gather from this lesson will help them build models and participate in neuron related activities of future lessons. Time Needed: 1+ Period(s) ...
Introduction to ANNs
... clap). A single neuron can only emit a pulse (“fires”) when the total input is above a certain threshold. This characteristic led to the McCulloch and Pitts model (1943) of the artificial neural network (ANN). Glance briefly at Figure 2. which illustrates how learning occurs in a biological neural n ...
... clap). A single neuron can only emit a pulse (“fires”) when the total input is above a certain threshold. This characteristic led to the McCulloch and Pitts model (1943) of the artificial neural network (ANN). Glance briefly at Figure 2. which illustrates how learning occurs in a biological neural n ...
HBTRC Tour - Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center
... Huntington’s slice is on the left. The Huntington’s striatum has severe atrophy, and because the cerebral cortex is connected to the striatum, Huntington’s Disease patients not only suffer from movement disorders but eventually become demented as well. ...
... Huntington’s slice is on the left. The Huntington’s striatum has severe atrophy, and because the cerebral cortex is connected to the striatum, Huntington’s Disease patients not only suffer from movement disorders but eventually become demented as well. ...
Discovering spatial working memory fields in prefrontal cortex
... substrate of the highest-level mental processes. Yet, despite the bewildering gamut and complexity of cognitive processes that depend on the prefrontal cortex, over the last decades significant progress has been made in linking the prefrontal function with its cellular and circuit mechanisms in a fi ...
... substrate of the highest-level mental processes. Yet, despite the bewildering gamut and complexity of cognitive processes that depend on the prefrontal cortex, over the last decades significant progress has been made in linking the prefrontal function with its cellular and circuit mechanisms in a fi ...
Anatomy Review - Interactive Physiology
... 28. (Page 7.) Chemical synapses transmit signals more slowly than __________ ________ but the signal may be either ________ or __________, and the signal can be modified as it passes from one neuron to the next. a. electrical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory b. chemical synapses, excitatory, inhibit ...
... 28. (Page 7.) Chemical synapses transmit signals more slowly than __________ ________ but the signal may be either ________ or __________, and the signal can be modified as it passes from one neuron to the next. a. electrical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory b. chemical synapses, excitatory, inhibit ...
Discovering spatial working memory fields in prefrontal cortex
... substrate of the highest-level mental processes. Yet, despite the bewildering gamut and complexity of cognitive processes that depend on the prefrontal cortex, over the last decades significant progress has been made in linking the prefrontal function with its cellular and circuit mechanisms in a fi ...
... substrate of the highest-level mental processes. Yet, despite the bewildering gamut and complexity of cognitive processes that depend on the prefrontal cortex, over the last decades significant progress has been made in linking the prefrontal function with its cellular and circuit mechanisms in a fi ...
the central nervous system
... explicit information, is often stored with the learning context, and is related to our conscious thoughts and our ability to manipulate symbols and language – Hippocampus and amygdala (both part of the limbic system) – Diencephalon (thalamus and ...
... explicit information, is often stored with the learning context, and is related to our conscious thoughts and our ability to manipulate symbols and language – Hippocampus and amygdala (both part of the limbic system) – Diencephalon (thalamus and ...
Sleep and Arousal
... • per, tim are needed for 24 hr rhythms. • Mutations lead to short, long or no rhythm. • dbt mutations alter enzyme, casein kinase, leading to short rhythm in Drosophila. • Homologous genes (per1-3, cry, tau) found in mice and humans. • Transcription factors Clock and Cycle start each cycle. These a ...
... • per, tim are needed for 24 hr rhythms. • Mutations lead to short, long or no rhythm. • dbt mutations alter enzyme, casein kinase, leading to short rhythm in Drosophila. • Homologous genes (per1-3, cry, tau) found in mice and humans. • Transcription factors Clock and Cycle start each cycle. These a ...
NMDA and AMPA Receptors: Development and Status Epilepticus
... isoxazol-4-yl) propanoic acid (AMPA) and kainate (KA). During early stages of postnatal development glutamate receptors of NMDA and AMPA type undergo intensive functional changes owing to modifications in their subunit composition (Carter et al. 1988, Watanabe et al. 1992, Monyer et al. 1994, Wenzel ...
... isoxazol-4-yl) propanoic acid (AMPA) and kainate (KA). During early stages of postnatal development glutamate receptors of NMDA and AMPA type undergo intensive functional changes owing to modifications in their subunit composition (Carter et al. 1988, Watanabe et al. 1992, Monyer et al. 1994, Wenzel ...
Understanding-Psychology-8th-Edition-Morris-Test-Bank
... A teacher grading papers opens the door of the room in which she has been working and becomes aware of loud rock music coming from her son's radio. When she asks him to turn it off, he asks why she is just noticing it now when he's had it on for over 20 minutes. Which of the following psychological ...
... A teacher grading papers opens the door of the room in which she has been working and becomes aware of loud rock music coming from her son's radio. When she asks him to turn it off, he asks why she is just noticing it now when he's had it on for over 20 minutes. Which of the following psychological ...
May 30, 04copy.doc
... weeks, indicating the dramatic, long-lasting effect of neonatal deprivation. What is the chemical basis of these physiological changes? Since GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in cortex, it was important to consider GABA and its receptors as suitable candidates responsible for these phys ...
... weeks, indicating the dramatic, long-lasting effect of neonatal deprivation. What is the chemical basis of these physiological changes? Since GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in cortex, it was important to consider GABA and its receptors as suitable candidates responsible for these phys ...
Descision making
... Directing attention toward relevant information as opposed to irrelevant information during goal-related decision making processes ...
... Directing attention toward relevant information as opposed to irrelevant information during goal-related decision making processes ...
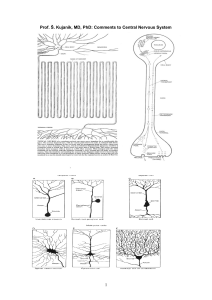
Study materials CNS
... § beta (14-30/s, 5-10 μV, after opening of the eyes, during input of informations to the brain or during any activity) § theta (4-7/s, 50 μV, in small children also in consciousness) § delta (1-4/s, 100-150 μV, slow waves with a high amplitude, in small children also in conscious stage, typical for ...
... § beta (14-30/s, 5-10 μV, after opening of the eyes, during input of informations to the brain or during any activity) § theta (4-7/s, 50 μV, in small children also in consciousness) § delta (1-4/s, 100-150 μV, slow waves with a high amplitude, in small children also in conscious stage, typical for ...