File - my Carlow weebly!
... The Brain/Body Connection: Re-wiring the Brain Through Movement surface helps strengthen and align the cervical and lumbar spine. From two and a half to seven months the baby organizes movement into an upper-lower pattern (pressing the upper body and grounding the lower body.) Next in the pattern o ...
... The Brain/Body Connection: Re-wiring the Brain Through Movement surface helps strengthen and align the cervical and lumbar spine. From two and a half to seven months the baby organizes movement into an upper-lower pattern (pressing the upper body and grounding the lower body.) Next in the pattern o ...
Hearing the Call of Neurons PowerPoint
... many different shapes and sizes. A midget bipolar and ...
... many different shapes and sizes. A midget bipolar and ...
From circuits to behavior: a bridge too far?
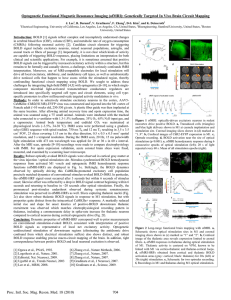
... least approximately, at various stages in the visual system6, in the auditory system7 and in the somatosensory system8. It may also be involved in motor systems, where neural activity can specify force fields obeying linear superposition9. Divisive normalization, in turn, is an operation in whic ...
... least approximately, at various stages in the visual system6, in the auditory system7 and in the somatosensory system8. It may also be involved in motor systems, where neural activity can specify force fields obeying linear superposition9. Divisive normalization, in turn, is an operation in whic ...
What is meant by the term `dementia`?
... between them (synapses) with the help of neurotransmitters (chemical messengers). These chemical and electrical signals are necessary in controlling our bodily functions – for example, language, decision-making, memory, personality, behaviour, sensing and interpreting our environment, and controllin ...
... between them (synapses) with the help of neurotransmitters (chemical messengers). These chemical and electrical signals are necessary in controlling our bodily functions – for example, language, decision-making, memory, personality, behaviour, sensing and interpreting our environment, and controllin ...
BIO 141 Unit 5 Learning Objectives
... e. primary somatosensory cortex. 25. Briefly explain the function of the areas listed below, a. primary motor cortex and premotor cortex. b. motor speech area (Broca’s area) and Wernicke’s area. c. primary auditory ...
... e. primary somatosensory cortex. 25. Briefly explain the function of the areas listed below, a. primary motor cortex and premotor cortex. b. motor speech area (Broca’s area) and Wernicke’s area. c. primary auditory ...
Brain and Nervous System— Your Information Superhighway
... autonomic nervous system (ANS): The part of the PNS which involves involuntary movement, meaning it manages functions we cannot consciously control such as digestion, respiration, the contraction of the irises in the eyes, and regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, and metabolism. beta waves: Bra ...
... autonomic nervous system (ANS): The part of the PNS which involves involuntary movement, meaning it manages functions we cannot consciously control such as digestion, respiration, the contraction of the irises in the eyes, and regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, and metabolism. beta waves: Bra ...
Neurotransmitter and Neuromodulator Activity in
... papillae, all of which are connected to the same second order neuron (Vogt and Mistretta, 1990). Combined functional and structural studies suggest that multipolar neurons might receive a major portion of the converging input (Mistretta and Labyak, 1994). Despite the considerable knowledge derived f ...
... papillae, all of which are connected to the same second order neuron (Vogt and Mistretta, 1990). Combined functional and structural studies suggest that multipolar neurons might receive a major portion of the converging input (Mistretta and Labyak, 1994). Despite the considerable knowledge derived f ...
The Brain and Behaviour
... The sensory area that receives and processes visual information is called the primary visual cortex. It is located in the occipital lobe. The sensory area that processes auditory information is called the primary auditory cortex and is located in the temporal lobe. Sensory information from the skin ...
... The sensory area that receives and processes visual information is called the primary visual cortex. It is located in the occipital lobe. The sensory area that processes auditory information is called the primary auditory cortex and is located in the temporal lobe. Sensory information from the skin ...
The mind`s mirror
... The difference between the imaging studies in humans and the electrophysiological studies in monkeys is one of scale, explains psychologist Christian Keysers, PhD, who studies the human mirror-neuron system at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands. "When we record signals from neurons in mo ...
... The difference between the imaging studies in humans and the electrophysiological studies in monkeys is one of scale, explains psychologist Christian Keysers, PhD, who studies the human mirror-neuron system at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands. "When we record signals from neurons in mo ...
The Brain and Behaviour
... The sensory neurons then transmit the information to the . The brain then organises and interprets the information in a meaningful way, which enables you to know how hot the flame is. If you decide it is too hot, the brain sends messages via the neurons which are part of the and then the which are p ...
... The sensory neurons then transmit the information to the . The brain then organises and interprets the information in a meaningful way, which enables you to know how hot the flame is. If you decide it is too hot, the brain sends messages via the neurons which are part of the and then the which are p ...
Supplemental Text Box 1 The Neurobiology of Arousal The defense
... muscles are affected first (to raise the body and stabilize it), followed by limb muscles— although at this stage no actual movement has occurred. In brief, all muscles, both smooth and striated, are toned up. The mind is awake, and the body is prepared. The brain region most important for the expre ...
... muscles are affected first (to raise the body and stabilize it), followed by limb muscles— although at this stage no actual movement has occurred. In brief, all muscles, both smooth and striated, are toned up. The mind is awake, and the body is prepared. The brain region most important for the expre ...
Distinct Requirements for Evoked and Spontaneous Release of
... incision, and the flaps of cuticle were glued to the slide. The gut, fat bodies, and connective tissue then were removed to expose the C NS and musculature. Dissections were performed in HL3 physiological solution, as described by Stewart et al. (1994). The dissected preparations were fixed in Bouin ...
... incision, and the flaps of cuticle were glued to the slide. The gut, fat bodies, and connective tissue then were removed to expose the C NS and musculature. Dissections were performed in HL3 physiological solution, as described by Stewart et al. (1994). The dissected preparations were fixed in Bouin ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM AND REFLEXES Introduction:
... the body to the CNS are the major structures of the Peripheral Nervous System. The nerves of the PNS function to bring sensory information to the central nervous system and to carry the commands of the CNS to cells of the body. Neurons are the cells of the nervous system which conduct electrical imp ...
... the body to the CNS are the major structures of the Peripheral Nervous System. The nerves of the PNS function to bring sensory information to the central nervous system and to carry the commands of the CNS to cells of the body. Neurons are the cells of the nervous system which conduct electrical imp ...
Lecture 2: Structure and function of the NS
... neurons, as described in Chapters 7 and 8. The pink segments covering the axon represent the myelin sheath that coats many axons (see Figs. 1-24 and 1-30), and the gap in the axon represents a missing extent that might be as long as a meter in the longest axons. ...
... neurons, as described in Chapters 7 and 8. The pink segments covering the axon represent the myelin sheath that coats many axons (see Figs. 1-24 and 1-30), and the gap in the axon represents a missing extent that might be as long as a meter in the longest axons. ...
Polarization theory of motivations, emotions and
... hyperpolarization deviation of MP is obligatory primary reaction of nervous cells on any impact (Vvedenskiy, 1901; Vasiliyev, 1925), the state forming at that, in all probability, reflects mobilization of adaptive intracellular mechanisms. The fact that during hyperpolarization adaptive reserves of ...
... hyperpolarization deviation of MP is obligatory primary reaction of nervous cells on any impact (Vvedenskiy, 1901; Vasiliyev, 1925), the state forming at that, in all probability, reflects mobilization of adaptive intracellular mechanisms. The fact that during hyperpolarization adaptive reserves of ...
Introduction - University of Toronto
... cingulate cortex than typical controls on an occulomotor spatial working memory task. This body of research may help to explain the lack of consistent evidence of abnormal frontal lobe structures; rather than specific structural abnormalities, perhaps the deficits seen in autism result from atypical ...
... cingulate cortex than typical controls on an occulomotor spatial working memory task. This body of research may help to explain the lack of consistent evidence of abnormal frontal lobe structures; rather than specific structural abnormalities, perhaps the deficits seen in autism result from atypical ...
Optimization of neuronal cultures derived from human
... neuronal cultures isolated from E18 rat embryos were seeded in 96-well plates (Greiner) coated with poly-D-lysine with or without laminin. For some experiments, iCell Neurons or rat neurons were cultured with rat or human astrocytes (Lonza) grown as a monolayer. iCell Neurons and rat neurons were se ...
... neuronal cultures isolated from E18 rat embryos were seeded in 96-well plates (Greiner) coated with poly-D-lysine with or without laminin. For some experiments, iCell Neurons or rat neurons were cultured with rat or human astrocytes (Lonza) grown as a monolayer. iCell Neurons and rat neurons were se ...
Lecture 6 - School of Computing | University of Leeds
... Last time... biological neural networks We introduced biological neural networks. We found complexity at every level, from the sub-cellular to the entire brain. We realised that even with a limited understanding, cartoon models can be derived for some functions of neurons (action potentials, synapt ...
... Last time... biological neural networks We introduced biological neural networks. We found complexity at every level, from the sub-cellular to the entire brain. We realised that even with a limited understanding, cartoon models can be derived for some functions of neurons (action potentials, synapt ...
Central nervous system
... postsynaptic potential(EPSP) in postsynaptic neuron when: * many presynaptic excitatory terminals are stimulated simultaneously * or when single presynaptic terminal is stimulated repeatedly. 5-electricale property: The electrical properties of the synapse are the EPSP and IPSP which are already. ...
... postsynaptic potential(EPSP) in postsynaptic neuron when: * many presynaptic excitatory terminals are stimulated simultaneously * or when single presynaptic terminal is stimulated repeatedly. 5-electricale property: The electrical properties of the synapse are the EPSP and IPSP which are already. ...
3680Lecture13 - U of L Class Index
... • It is the brain actively reconfiguring itself by changing the way signals propagate through networks • It is a form of very fast, very transient plasticity ...
... • It is the brain actively reconfiguring itself by changing the way signals propagate through networks • It is a form of very fast, very transient plasticity ...
Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Pyramidal Cells
... 2003; Wilbrecht et al., 2010). Conversely, most of the studies on structural plasticity to date have investigated spine plasticity of LV neurons (Hofer et al., 2009; Trachtenberg et al., 2002; Wilbrecht et al., 2010). LV is a major output projection layer of the cortex and in the somatosensory syste ...
... 2003; Wilbrecht et al., 2010). Conversely, most of the studies on structural plasticity to date have investigated spine plasticity of LV neurons (Hofer et al., 2009; Trachtenberg et al., 2002; Wilbrecht et al., 2010). LV is a major output projection layer of the cortex and in the somatosensory syste ...
Optogenetic Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ofMRI
... the same location. After allowing animal recovery time and opsin expression time, the animal was scanned using a 7T small animal. Animals were intubated with the tracheal tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and ...
... the same location. After allowing animal recovery time and opsin expression time, the animal was scanned using a 7T small animal. Animals were intubated with the tracheal tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and ...
Save
... Broca,Werniche,Kussmaul) , can be identified with the consciousness formation that can be interpreted as a sort of constant,continous and simultaneous low-noise effect. When the cortex receives sufficient afferent impulses, it is said to be aroused or activated. That is, a critical number of cortica ...
... Broca,Werniche,Kussmaul) , can be identified with the consciousness formation that can be interpreted as a sort of constant,continous and simultaneous low-noise effect. When the cortex receives sufficient afferent impulses, it is said to be aroused or activated. That is, a critical number of cortica ...
Powerpoint version
... Nerve cells have a Na+K+ pump and selective permeability to Na+and K+ that set up a potential Na+K+ pump transports 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ in. ...
... Nerve cells have a Na+K+ pump and selective permeability to Na+and K+ that set up a potential Na+K+ pump transports 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ in. ...
Document
... Neuroanatomy Handout #3: Brain Structures • Pons (B) – lies on each side of the medulla (ventral and anterior). – along with the medulla, contains the reticular formation and raphe system, which work together to increase arousal and readiness of other parts of the brain ...
... Neuroanatomy Handout #3: Brain Structures • Pons (B) – lies on each side of the medulla (ventral and anterior). – along with the medulla, contains the reticular formation and raphe system, which work together to increase arousal and readiness of other parts of the brain ...