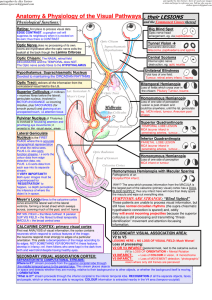
Chapter 3—The Brain and Behavior
... The midbrain is involved in the relay of information between the brain and the hindbrain and forebrain. A midbrain structure called the reticular formation is involved in stereotyped patterns of behavior. The highest region of the brain is called the forebrain. A forebrain structure that plays impo ...
... The midbrain is involved in the relay of information between the brain and the hindbrain and forebrain. A midbrain structure called the reticular formation is involved in stereotyped patterns of behavior. The highest region of the brain is called the forebrain. A forebrain structure that plays impo ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Cranial and spinal nerves form from neural crest cells that have split off from the developing neural tube. The cranial (superior) part of the neural tube expands and develops into the brain. The caudal (inferior) part of the neural tube forms the spinal cord. ...
... Cranial and spinal nerves form from neural crest cells that have split off from the developing neural tube. The cranial (superior) part of the neural tube expands and develops into the brain. The caudal (inferior) part of the neural tube forms the spinal cord. ...
Document
... Dr Alexandrowicz kindly called my attention to the presence of a number of pits, located just distally to the ischio-meropodite, mero-carpopodite and carpo-propodite joints of Homarus and Palinurus. It was observed that the location of these pits is such that they are covered by their joint membrane ...
... Dr Alexandrowicz kindly called my attention to the presence of a number of pits, located just distally to the ischio-meropodite, mero-carpopodite and carpo-propodite joints of Homarus and Palinurus. It was observed that the location of these pits is such that they are covered by their joint membrane ...
Hansen Neuropathy: Still a Possible Diagnosis in the Investigation
... Hansen’s disease1,4 and upper limb nerves are the most frequently affected. Skin involvement progresses with disfiguring lesions, responsible for the stigmatizing nature of this disease. Despite the aetiological agent - Mycobacterium leprae – having been identified more than a century ago, little is ...
... Hansen’s disease1,4 and upper limb nerves are the most frequently affected. Skin involvement progresses with disfiguring lesions, responsible for the stigmatizing nature of this disease. Despite the aetiological agent - Mycobacterium leprae – having been identified more than a century ago, little is ...
Pudendal Nerve Entrapment Syndrome
... The perception is that much remains to be done in the disclosure of its existence and to publicize the centres which can be used for proper treatment. ...
... The perception is that much remains to be done in the disclosure of its existence and to publicize the centres which can be used for proper treatment. ...
Physiological Psychology
... and processing of information is called the integrative function of the nervous system. Thus, if a person places a hand on a hot stove, the desired instantaneous response is to lift the hand. And other associated responses follow, such as moving the entire body away from the stove, and perhaps even ...
... and processing of information is called the integrative function of the nervous system. Thus, if a person places a hand on a hot stove, the desired instantaneous response is to lift the hand. And other associated responses follow, such as moving the entire body away from the stove, and perhaps even ...
Copy of PNS philadelphia
... skull. These recordings contain information from large populations of neurons that can be decoded by a computer. Other forms of BCI require the implantation of an array of electrodes smaller than a postage stamp in the arm and hand area of the motor cortex. This form of BCI, while more invasive, is ...
... skull. These recordings contain information from large populations of neurons that can be decoded by a computer. Other forms of BCI require the implantation of an array of electrodes smaller than a postage stamp in the arm and hand area of the motor cortex. This form of BCI, while more invasive, is ...
Skeletal System
... movement of the joints Ruffini corpuscles are slowly adapting stretch receptors that are ideal for measuring the positions of non-moving joints and the stretch of joints that undergo slow, sustained movements ...
... movement of the joints Ruffini corpuscles are slowly adapting stretch receptors that are ideal for measuring the positions of non-moving joints and the stretch of joints that undergo slow, sustained movements ...
Autonomic nervous system
... the pupils, micturition (urination), and sexual arousal. Whereas most of its actions are involuntary, some, such as breathing, work in tandem with the conscious mind. It is classically divided into two subsystems: the parasympathetic nervous system and sympathetic nervous system.[1][2] Relatively re ...
... the pupils, micturition (urination), and sexual arousal. Whereas most of its actions are involuntary, some, such as breathing, work in tandem with the conscious mind. It is classically divided into two subsystems: the parasympathetic nervous system and sympathetic nervous system.[1][2] Relatively re ...
Biology - Chpt 14- The Nervous System
... What is a synapse? A synapse is a junction between two neurons across which electrical signals pass. The human body contains up to 500 trillion synapses. presynaptic cell ...
... What is a synapse? A synapse is a junction between two neurons across which electrical signals pass. The human body contains up to 500 trillion synapses. presynaptic cell ...
14. Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... cauda equina (“horse’s tail”) is the name for the collection of nerves in the vertebral column that continue to travel through the vertebral column below the conus medullaris. The cauda equina forms as a result of the fact that the spinal cord stops growing in length at about age four, even though t ...
... cauda equina (“horse’s tail”) is the name for the collection of nerves in the vertebral column that continue to travel through the vertebral column below the conus medullaris. The cauda equina forms as a result of the fact that the spinal cord stops growing in length at about age four, even though t ...
IRONS vol 14.indd
... The scapula floats on the chest wall on a bed of muscles. Shoulder girdle muscles by means of trapezius, levator scapulae, rhoimboid major et minor and serratus anterior support the scapula, participate during the hand movement and these muscles, both stabilize the arm to the body and move the arm a ...
... The scapula floats on the chest wall on a bed of muscles. Shoulder girdle muscles by means of trapezius, levator scapulae, rhoimboid major et minor and serratus anterior support the scapula, participate during the hand movement and these muscles, both stabilize the arm to the body and move the arm a ...
ch13
... area of the skin that provides sensory input to the CNS via one pair of spinal nerves or the trigeminal nerve. ...
... area of the skin that provides sensory input to the CNS via one pair of spinal nerves or the trigeminal nerve. ...
Spinal_Cord_Power_Point
... area of the skin that provides sensory input to the CNS via one pair of spinal nerves or the trigeminal nerve. ...
... area of the skin that provides sensory input to the CNS via one pair of spinal nerves or the trigeminal nerve. ...
Electrical Communication #2
... The action potential races down the axon and depolarizes the terminal. This causes voltage-gated Ca++ channels at the terminal to open. Since the calcium concentration is 5 mM outside the cell and 0.1 µM inside, calcium rushes in. (FYI: lots of calcium inside the cell is a bad thing. That’s why th ...
... The action potential races down the axon and depolarizes the terminal. This causes voltage-gated Ca++ channels at the terminal to open. Since the calcium concentration is 5 mM outside the cell and 0.1 µM inside, calcium rushes in. (FYI: lots of calcium inside the cell is a bad thing. That’s why th ...
Homeostasis and Development of Homeostats
... eyes, ears, nose, mouth and skin. The CNS sends out appropriate signal to control motor functions. The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. The communication occurs through the release of transmitter substance into the synapses triggere ...
... eyes, ears, nose, mouth and skin. The CNS sends out appropriate signal to control motor functions. The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. The communication occurs through the release of transmitter substance into the synapses triggere ...
The Special Senses
... • Taste researchers have known for many years that these tongue maps are wrong. The maps arose early in the 20th century as a result of a misinterpretation of research reported in the late 1800s, and they have been almost impossible to purge from the literature. In reality, all qualities of taste ca ...
... • Taste researchers have known for many years that these tongue maps are wrong. The maps arose early in the 20th century as a result of a misinterpretation of research reported in the late 1800s, and they have been almost impossible to purge from the literature. In reality, all qualities of taste ca ...
Muscle Twitches - Mount Carmel Academy
... When the action potential ends, calcium ions are immediately reabsorbed into the SR storage areas, and the muscle cell relaxes and settles back to its original ...
... When the action potential ends, calcium ions are immediately reabsorbed into the SR storage areas, and the muscle cell relaxes and settles back to its original ...
Muscles - Part 3
... When the action potential ends, calcium ions are immediately reabsorbed into the SR storage areas, and the muscle cell relaxes and settles back to its original length. ...
... When the action potential ends, calcium ions are immediately reabsorbed into the SR storage areas, and the muscle cell relaxes and settles back to its original length. ...
NEURAL REGULATION OF RESPIRATION LEARNING
... – I neurons in its mid region – E neurons at its rostral and caudal ends These neurons are inactive during quiet breathing. Expiration center is activated when activity and ...
... – I neurons in its mid region – E neurons at its rostral and caudal ends These neurons are inactive during quiet breathing. Expiration center is activated when activity and ...
neuropathy classification
... Particular nerve Plexus Nerve root level Proximal weakness results in an inability to squat or to rise unassisted from a chair. ...
... Particular nerve Plexus Nerve root level Proximal weakness results in an inability to squat or to rise unassisted from a chair. ...
The Dellon Approach to Neurolysis in the Neuropathy Patient with
... injure the lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf, which is sometimes present. The deep fascia is palpated to identify the common peroneal nerve. This fascia is lifted and then incised to identify the CPN. This nerve often has a yellowish color and appears like a lipoma. Only the epineurium should be g ...
... injure the lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf, which is sometimes present. The deep fascia is palpated to identify the common peroneal nerve. This fascia is lifted and then incised to identify the CPN. This nerve often has a yellowish color and appears like a lipoma. Only the epineurium should be g ...
Brain and Nervous System Overview
... transmitter (excitatory or inhibitory) (i.e. ACH acetylcholine or GABA) Each vesicle contains ~10,000 ACH and are passed to postsynaptic site through exocytosis in < 100 microsec. Transmitter causes change in post-synaptic membrane permeability leading to firing (excitation) or hyperpolorization (in ...
... transmitter (excitatory or inhibitory) (i.e. ACH acetylcholine or GABA) Each vesicle contains ~10,000 ACH and are passed to postsynaptic site through exocytosis in < 100 microsec. Transmitter causes change in post-synaptic membrane permeability leading to firing (excitation) or hyperpolorization (in ...