In vitro studies of limb regeneration in adult Diemictylus
... the quality of the results. In ganglionated explants cultured for 4 days (Fig. 3) the greatest density in the population of blastema cells is seen near the implanted ganglion; the cells were contiguous to one another (little intercellular space) and they exhibited numerous mitotic figures. This effe ...
... the quality of the results. In ganglionated explants cultured for 4 days (Fig. 3) the greatest density in the population of blastema cells is seen near the implanted ganglion; the cells were contiguous to one another (little intercellular space) and they exhibited numerous mitotic figures. This effe ...
Structural changes of the human superior cervical
... Key words: human superior cervical ganglion; sympathetic neuron; apoptosis; ischemic stroke; TUNEL method. Summary. Objective. The sympathetic nervous system participates in the modulation of cerebrovascular autoregulation. The most important source of sympathetic innervation of the cerebral arterie ...
... Key words: human superior cervical ganglion; sympathetic neuron; apoptosis; ischemic stroke; TUNEL method. Summary. Objective. The sympathetic nervous system participates in the modulation of cerebrovascular autoregulation. The most important source of sympathetic innervation of the cerebral arterie ...
The Evaluation of Weakness in the
... influx prevents quanta release Decreased number of MEPP’s of normal amplitude Decrement to low frequency rep stim due to many muscle fibers activated near-threshold so decreased release is miniscule but significant Post-exercise facilitation due to increased Ca++ in cell resulting in increased ...
... influx prevents quanta release Decreased number of MEPP’s of normal amplitude Decrement to low frequency rep stim due to many muscle fibers activated near-threshold so decreased release is miniscule but significant Post-exercise facilitation due to increased Ca++ in cell resulting in increased ...
SPINAL CORD II
... limb. Cells of origin extend from coccygeal to L1 segment. Fibres mostly crossed. Pathway has two neurons. 1st osrder in dorsal root ganglion 2nd in spinal cord. Axons of 2nd order neurons runs over superior cerebellar peduncle to enter the cerebellum. Concerned with coordinated movement and posture ...
... limb. Cells of origin extend from coccygeal to L1 segment. Fibres mostly crossed. Pathway has two neurons. 1st osrder in dorsal root ganglion 2nd in spinal cord. Axons of 2nd order neurons runs over superior cerebellar peduncle to enter the cerebellum. Concerned with coordinated movement and posture ...
“visual pathway and its lesions” dr.tasneem
... Behind the lens and in front of the retina is a chamber called the vitreous body, which contains a clear, gelatinous fluid called vitreous humor. Light rays pass through the vitreous before reaching the retina. The retina lines the back two-thirds of the eye and is responsible for the wide field of ...
... Behind the lens and in front of the retina is a chamber called the vitreous body, which contains a clear, gelatinous fluid called vitreous humor. Light rays pass through the vitreous before reaching the retina. The retina lines the back two-thirds of the eye and is responsible for the wide field of ...
Biologically active peptides in molluscs
... At all times, biologists have been fascinated by the extraordinary variety of living forms. From the time when Lucretius asked: "How can there be this infinite variety of things and what is behind this incredible variety of shapes and sizes?", philosophers asked themselves this important question ov ...
... At all times, biologists have been fascinated by the extraordinary variety of living forms. From the time when Lucretius asked: "How can there be this infinite variety of things and what is behind this incredible variety of shapes and sizes?", philosophers asked themselves this important question ov ...
NERVOUS SYSTEMS – FUNCTION AT THE CELLULAR LEVEL
... A single receiving (post-synaptic) neuron can have 1000’s of synapses with different incoming (pre-synaptic) axon terminals - each synapse is either excitatory or inhibitory ...
... A single receiving (post-synaptic) neuron can have 1000’s of synapses with different incoming (pre-synaptic) axon terminals - each synapse is either excitatory or inhibitory ...
The NeuronDoctrine: A Revision of Functional
... The mitral cell and its interneurons, by contrast, appear as specialized neurons with multiple functions. In order to identify these functions we need to free the term "functional unit" from its association with the entire neuron. We can then propose that a functional unit may be defined in the most ...
... The mitral cell and its interneurons, by contrast, appear as specialized neurons with multiple functions. In order to identify these functions we need to free the term "functional unit" from its association with the entire neuron. We can then propose that a functional unit may be defined in the most ...
Neuron-Glia Interactions of Rat Hippocampal Cells in vitro: Glial
... Video-enhanced dtyerential interference microscopy. For video microscopy, hippocampal cells were harvested on E20 and plated in glass coverslip microcultures pretreated with Matrigel. After 24 hr in vitro, the medium was changed to L15 medium supplemented with horse serum (10%) and glucose (8 mM), a ...
... Video-enhanced dtyerential interference microscopy. For video microscopy, hippocampal cells were harvested on E20 and plated in glass coverslip microcultures pretreated with Matrigel. After 24 hr in vitro, the medium was changed to L15 medium supplemented with horse serum (10%) and glucose (8 mM), a ...
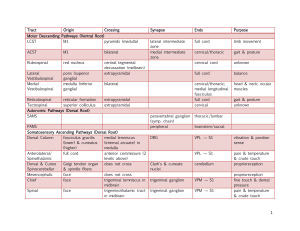
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... treatment: Na channel inhibition to tamper exitotoxicity mitochondria failing → oxidative stress → not enough ATP → defective axonal transport → not interacting with postsynaptic partners → loss of trophic factors → presynaptic die back → stress → don't buffer calcium well → activate secondary messe ...
... treatment: Na channel inhibition to tamper exitotoxicity mitochondria failing → oxidative stress → not enough ATP → defective axonal transport → not interacting with postsynaptic partners → loss of trophic factors → presynaptic die back → stress → don't buffer calcium well → activate secondary messe ...
chapt07_lecture
... 1. Myelin sheath in the PNS a. All axons in the PNS are surrounded by a sheath of Schwann cells called the neurilemma, or sheath of Schwann. b. These cells wrap around the axon to form the myelin sheath in the PNS. c. Gaps between Schwann cells, called nodes of Ranvier, are left open. ...
... 1. Myelin sheath in the PNS a. All axons in the PNS are surrounded by a sheath of Schwann cells called the neurilemma, or sheath of Schwann. b. These cells wrap around the axon to form the myelin sheath in the PNS. c. Gaps between Schwann cells, called nodes of Ranvier, are left open. ...
Module 5 – Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nerves The Spinal Cord
... Terminates in a cone shaped structure à fibrous connective tissue extending from the conus medullaris to anchor the spinal cord to the coccyx Divided into 31 segments: à Cervical (C1 – C8) à Thoracic (T1 – T12) à Lumbar (L1 – L5) à Sacral (S1 – S5) à Coccygeal (Co1) Lumbar, sacral, and coccy ...
... Terminates in a cone shaped structure à fibrous connective tissue extending from the conus medullaris to anchor the spinal cord to the coccyx Divided into 31 segments: à Cervical (C1 – C8) à Thoracic (T1 – T12) à Lumbar (L1 – L5) à Sacral (S1 – S5) à Coccygeal (Co1) Lumbar, sacral, and coccy ...
Axonal Localization of Integrins in the CNS Is Neuronal Type and
... The regenerative ability of CNS axons decreases with age, however, this ability remains largely intact in PNS axons throughout adulthood. These differences are likely to correspond with agerelated silencing of proteins necessary for axon growth and elongation. In previous studies, it has been shown ...
... The regenerative ability of CNS axons decreases with age, however, this ability remains largely intact in PNS axons throughout adulthood. These differences are likely to correspond with agerelated silencing of proteins necessary for axon growth and elongation. In previous studies, it has been shown ...
15_QuizShowQuestions
... a. It coordinates daily cycles of activity that are linked to the day/night cycle. b. Its output adjusts the activities of the hypothalamic nuclei, the pineal gland, and the reticular formation. c. It is one of the ventral nuclei of the ...
... a. It coordinates daily cycles of activity that are linked to the day/night cycle. b. Its output adjusts the activities of the hypothalamic nuclei, the pineal gland, and the reticular formation. c. It is one of the ventral nuclei of the ...
Bridging Areas of Injury in the Spinal Cord
... distal ones in tissue viability, types of degenerating and regenerating axons, blood-brain barrier deficiency, number of macrophages/microglia, and blood circulation, as examples. New initiatives have begun to reduce CSPG in areas of CNS injury to potentially improve axonal regeneration (Lemons and ...
... distal ones in tissue viability, types of degenerating and regenerating axons, blood-brain barrier deficiency, number of macrophages/microglia, and blood circulation, as examples. New initiatives have begun to reduce CSPG in areas of CNS injury to potentially improve axonal regeneration (Lemons and ...
Assisted morphogenesis: glial control of dendrite
... gap junction proteins connexin 26 and connexin 43 [23]. Glia-derived cues are known to play important roles in axon guidance, affecting the shapes of axons by defining axonal extension paths [24]. Recent evidence suggests that these same glia-derived axon guidance cues can also act on dendrites [25] ...
... gap junction proteins connexin 26 and connexin 43 [23]. Glia-derived cues are known to play important roles in axon guidance, affecting the shapes of axons by defining axonal extension paths [24]. Recent evidence suggests that these same glia-derived axon guidance cues can also act on dendrites [25] ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... • The Central Nervous System • The Peripheral Nervous System • The Somatic Nervous System • The Autonomic Nervous System • The Sympathetic Nervous System • The Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
... • The Central Nervous System • The Peripheral Nervous System • The Somatic Nervous System • The Autonomic Nervous System • The Sympathetic Nervous System • The Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
Glial heterogeneity: the increasing complexity of the brain
... traverse the parenchyma irregularly, oligodendroglial processes point into all directions. The functional characterization of oligodendroglial heterogeneity is still in its infancy. They are equipped with a variety of receptors to sense the extracellular level of transmitters released by neurones [1 ...
... traverse the parenchyma irregularly, oligodendroglial processes point into all directions. The functional characterization of oligodendroglial heterogeneity is still in its infancy. They are equipped with a variety of receptors to sense the extracellular level of transmitters released by neurones [1 ...
PDF here
... active degeneration, was first observed at day 80 and continued through death (Fig. 4). The numbers of large motor neurons did not decrease, however, until the 100-day time point. Quantitative analysis of a-motor neurons was performed both as mean number of a-motor neurons per section, and as an est ...
... active degeneration, was first observed at day 80 and continued through death (Fig. 4). The numbers of large motor neurons did not decrease, however, until the 100-day time point. Quantitative analysis of a-motor neurons was performed both as mean number of a-motor neurons per section, and as an est ...
Pharynx
... earlier years of childhood, probably in response to upper respiratory tract infection. Maximum bulk is obtained at the age of 3-6 years, thereafter, some regression in size is to be expected, and in old age it atrophies. ...
... earlier years of childhood, probably in response to upper respiratory tract infection. Maximum bulk is obtained at the age of 3-6 years, thereafter, some regression in size is to be expected, and in old age it atrophies. ...
Pharyngobasilar Fascia
... earlier years of childhood, probably in response to upper respiratory tract infection. Maximum bulk is obtained at the age of 3-6 years, thereafter, some regression in size is to be expected, and in old age it atrophies. ...
... earlier years of childhood, probably in response to upper respiratory tract infection. Maximum bulk is obtained at the age of 3-6 years, thereafter, some regression in size is to be expected, and in old age it atrophies. ...
Understanding-Psychology-8th-Edition-Morris-Test-Bank
... A teacher grading papers opens the door of the room in which she has been working and becomes aware of loud rock music coming from her son's radio. When she asks him to turn it off, he asks why she is just noticing it now when he's had it on for over 20 minutes. Which of the following psychological ...
... A teacher grading papers opens the door of the room in which she has been working and becomes aware of loud rock music coming from her son's radio. When she asks him to turn it off, he asks why she is just noticing it now when he's had it on for over 20 minutes. Which of the following psychological ...
The Nervous System (2)
... – Fused pair of cerebral ganglia (brain) – Paired ventral nerve cord – Fused ganglion in each segment along the ventral nerve cord Lund University / Faculty of Science / Department of Biology / BIO B02 – Zoologi ...
... – Fused pair of cerebral ganglia (brain) – Paired ventral nerve cord – Fused ganglion in each segment along the ventral nerve cord Lund University / Faculty of Science / Department of Biology / BIO B02 – Zoologi ...