Antipyretic-analgesic and antiinflammatory drugs
... temporary loss of sensation without a loss of consciousness. (2) Unlike general anesthetics, they normally do not cause central nervous system (CNS) depression. ...
... temporary loss of sensation without a loss of consciousness. (2) Unlike general anesthetics, they normally do not cause central nervous system (CNS) depression. ...
Cranial Nerves
... 1. Motor innervation to muscles of face, eyes, tongue, jaw and two neck muscles. 2. Somatosensory information from skin and muscles of face and TMJ, and special sensory information (olfactory, visual, auditory, vestibular, taste, and visceral sensations) 3. Parasympathetic regulation of heart rate, ...
... 1. Motor innervation to muscles of face, eyes, tongue, jaw and two neck muscles. 2. Somatosensory information from skin and muscles of face and TMJ, and special sensory information (olfactory, visual, auditory, vestibular, taste, and visceral sensations) 3. Parasympathetic regulation of heart rate, ...
Slide ()
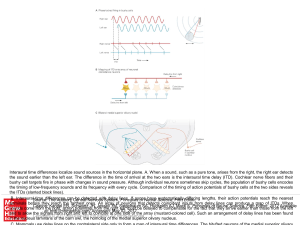
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
13-2nd, 3rd, 4th & 6th cranial nerves
... It passes through cavernous sinus, lying below and lateral to the internal carotid artery. Then it enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. It supplies; the lateral rectus muscle which rotates the eye ball laterally ; (abduction). ...
... It passes through cavernous sinus, lying below and lateral to the internal carotid artery. Then it enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. It supplies; the lateral rectus muscle which rotates the eye ball laterally ; (abduction). ...
Neuroscience Flash Cards, Second Edition
... cell enwraps a single internodal region of axon with a myelin sheath. Unmyelinated axons (small primary sensory axons, most postganglionic autonomic axons) are protected by a layer of Schwann cell cytoplasm. CNS axons are myelinated by oligodendrocytes; a single oligodendrocyte extends processes to ...
... cell enwraps a single internodal region of axon with a myelin sheath. Unmyelinated axons (small primary sensory axons, most postganglionic autonomic axons) are protected by a layer of Schwann cell cytoplasm. CNS axons are myelinated by oligodendrocytes; a single oligodendrocyte extends processes to ...
Nervous System 1
... • The end of one neuron is not connected to the next. There is always a small gap between them. The gap is called a synapse. • When an impulse reaches the end of an axon, a chemical is produced. The chemical diffuses across the gap. It starts off an impulse in the next neuron . • Only one end of a n ...
... • The end of one neuron is not connected to the next. There is always a small gap between them. The gap is called a synapse. • When an impulse reaches the end of an axon, a chemical is produced. The chemical diffuses across the gap. It starts off an impulse in the next neuron . • Only one end of a n ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... Curare, a poison certain So. American Indians have applied to hunting-dart tips, occupies and blocks ACh receptor sites, leaving the neurotransmitter unable to affect the muscles. The animal is paralyzed. ...
... Curare, a poison certain So. American Indians have applied to hunting-dart tips, occupies and blocks ACh receptor sites, leaving the neurotransmitter unable to affect the muscles. The animal is paralyzed. ...
Chapter 40
... The vertebrate nervous system has two main divisions: CNS and PNS A. The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord B. The PNS is made up of sensory receptors and nerves 1. Afferent nerves are sensory 2. Efferent nerves innervate muscles or glands and are motor a) The PNS can be divided into the soma ...
... The vertebrate nervous system has two main divisions: CNS and PNS A. The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord B. The PNS is made up of sensory receptors and nerves 1. Afferent nerves are sensory 2. Efferent nerves innervate muscles or glands and are motor a) The PNS can be divided into the soma ...
Synergy between Transplantation of Olig2
... roles in the treatment of SCI. In this study, the MBP-T cells, which can express IFN-, IL-10, and IL-13 after activation in vitro, were passively immunized to spinal cord injured rats within one day after SCI. The NSCs, which infected with lentivirus expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP-NSCs) ...
... roles in the treatment of SCI. In this study, the MBP-T cells, which can express IFN-, IL-10, and IL-13 after activation in vitro, were passively immunized to spinal cord injured rats within one day after SCI. The NSCs, which infected with lentivirus expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP-NSCs) ...
Peripheric nervous system. Vegetative nervous system
... long axons are directed to the organs; 2) the second type – afferent cells have processes of equal length; their long dendrites and axon form synapses with the I and III types of cells in the neughbouring ganglia; 3) the third type are associated or intercalated cells; they connect several cells of ...
... long axons are directed to the organs; 2) the second type – afferent cells have processes of equal length; their long dendrites and axon form synapses with the I and III types of cells in the neughbouring ganglia; 3) the third type are associated or intercalated cells; they connect several cells of ...
nervous system - Cloudfront.net
... What is the function of the nervous system? • The nervous system is made up of the structures that control actions and reactions of the body in response to stimuli in the environment. • The nervous system has two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). ...
... What is the function of the nervous system? • The nervous system is made up of the structures that control actions and reactions of the body in response to stimuli in the environment. • The nervous system has two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). ...
Biology 13A
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
Biology 4 Practice Exam Chapter 16 – Autonomic Nervous System 1
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
chapter32_part2
... framework for neurons, insulate neuron axons, assist neurons metabolically, and protect the brain from injury and disease. • Because neuroglia have essential roles in assisting neurons, diseases that impair neuroglia impair the function of the nervous system. • Unlike neurons, most types of neurogli ...
... framework for neurons, insulate neuron axons, assist neurons metabolically, and protect the brain from injury and disease. • Because neuroglia have essential roles in assisting neurons, diseases that impair neuroglia impair the function of the nervous system. • Unlike neurons, most types of neurogli ...
Peripheral Nervous System - cK-12
... under your control, such as waving your hand or kicking a ball. The girl pictured below (Figure 1.6) is using her somatic nervous system to control the muscles needed to play the violin. Her brain sends messages to motor neurons that move her hands so she can play. Without the messages from her brai ...
... under your control, such as waving your hand or kicking a ball. The girl pictured below (Figure 1.6) is using her somatic nervous system to control the muscles needed to play the violin. Her brain sends messages to motor neurons that move her hands so she can play. Without the messages from her brai ...
Nervous System
... that carries the signal to the next cell. Length of neurons varies depending on their location. Neurons located in CNS could be a few millimeter long but some of the neurons in PNS could be more than a meter long. In a normal human body, there are about two billion neurons, approximately 1 billion i ...
... that carries the signal to the next cell. Length of neurons varies depending on their location. Neurons located in CNS could be a few millimeter long but some of the neurons in PNS could be more than a meter long. In a normal human body, there are about two billion neurons, approximately 1 billion i ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... 1. Motor neuron 2. Sensory neuron 3. Interneuron B. Schwann Cells 1. neurolemma 2. PNS cells 1. Glial cells types and functions : 1. Oligodendrocytes 2. Astrocytes 3. Microglia 4. Ependyma C. Nerve cell impulse transmission: the electricity! 1. Essentially the same as described in muscle impulse. 2. ...
... 1. Motor neuron 2. Sensory neuron 3. Interneuron B. Schwann Cells 1. neurolemma 2. PNS cells 1. Glial cells types and functions : 1. Oligodendrocytes 2. Astrocytes 3. Microglia 4. Ependyma C. Nerve cell impulse transmission: the electricity! 1. Essentially the same as described in muscle impulse. 2. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... between neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the narrow gap between pre- and po ...
... between neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the narrow gap between pre- and po ...
1 • In the animals of highly developed organization consisting of
... silver impregnation is performed, fine fibrils appear around the nucleus very densely, and run in all directions in cell body and through there from dendrites into dendrites and from cell body into the neurite; these are called neurofibrils. • Dendrites: These are protoplasmic processes, radiating f ...
... silver impregnation is performed, fine fibrils appear around the nucleus very densely, and run in all directions in cell body and through there from dendrites into dendrites and from cell body into the neurite; these are called neurofibrils. • Dendrites: These are protoplasmic processes, radiating f ...
CH3
... The medulla is the most caudal portion of brain and is rostral to the spinal cord The medulla contains part of the reticular formation The nuclei of the medulla control vital functions such as regulation of the cardiovascular system, breathing, and skeletal muscle tone ...
... The medulla is the most caudal portion of brain and is rostral to the spinal cord The medulla contains part of the reticular formation The nuclei of the medulla control vital functions such as regulation of the cardiovascular system, breathing, and skeletal muscle tone ...
Pathology of the Peripheral Nervous System
... if injury to the neuron or axon is sufficiently sever, there will be rapid disintegration and death of the axon Histo: globules of myelin accompanied by simulatneous loss of the axon identical to Wallerian degeneration Regeneration occurs (no gliosis in PNS) regenerative clusters – small group ...
... if injury to the neuron or axon is sufficiently sever, there will be rapid disintegration and death of the axon Histo: globules of myelin accompanied by simulatneous loss of the axon identical to Wallerian degeneration Regeneration occurs (no gliosis in PNS) regenerative clusters – small group ...
Biology 231
... dendrites – short, branched receiving portion of neuron axon – single, long sending portion of neuron synapse – site where neuron communicates with another cell releases a chemical neurotransmitter (eg. acetylcholine) sensory neuron – axon sends signals to the CNS motor neuron – axon sends signals a ...
... dendrites – short, branched receiving portion of neuron axon – single, long sending portion of neuron synapse – site where neuron communicates with another cell releases a chemical neurotransmitter (eg. acetylcholine) sensory neuron – axon sends signals to the CNS motor neuron – axon sends signals a ...