THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the narrow gap between pre- and postsynapt ...
... neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the narrow gap between pre- and postsynapt ...
SENSORY INNERVATION OF HEAD
... Cervical plexus (C2-C4) anterior and lateral; dorsal primary rami posterior side ...
... Cervical plexus (C2-C4) anterior and lateral; dorsal primary rami posterior side ...
Slide 1
... the same affect • Addiction: the need to continue obtaining and using a substance; no free choice • Withdrawal: physical symptoms that occur upon stopping the drug ...
... the same affect • Addiction: the need to continue obtaining and using a substance; no free choice • Withdrawal: physical symptoms that occur upon stopping the drug ...
Central Nervous System
... • Myelinated axons – Plasma membrane of Schwann cells or Oligodendrocytes repeatedly wraps around a segment of an axon to form the myelin sheath – Myelin is a whitish, fatty (protein-lipid), segmented sheath around most long axons – It functions to: • Protect the axon • Electrically insulate fibers ...
... • Myelinated axons – Plasma membrane of Schwann cells or Oligodendrocytes repeatedly wraps around a segment of an axon to form the myelin sheath – Myelin is a whitish, fatty (protein-lipid), segmented sheath around most long axons – It functions to: • Protect the axon • Electrically insulate fibers ...
Neuroscience Course Conference
... c. What might be the side effects of such a drug? 3. Although gNa increases as a graded function of membrane depolarization (Fig. 9-6 of textbook), the action potential has a discrete voltage threshold. Why? 4. During epileptic seizures, massive synchronous bursts of activity in cortical neurons cau ...
... c. What might be the side effects of such a drug? 3. Although gNa increases as a graded function of membrane depolarization (Fig. 9-6 of textbook), the action potential has a discrete voltage threshold. Why? 4. During epileptic seizures, massive synchronous bursts of activity in cortical neurons cau ...
Applicator - Research - Vanderbilt University
... •Little change in potassium and sodium concentration levels in extracellular and intracellular fluids of the brain. These electrolytes are important to the function of many systems, homeostasis, and iron regulation in the body and play a role in nerve stimulation. ...
... •Little change in potassium and sodium concentration levels in extracellular and intracellular fluids of the brain. These electrolytes are important to the function of many systems, homeostasis, and iron regulation in the body and play a role in nerve stimulation. ...
Psy101 Brain.lst
... Explain the anatomy of a neuron including: dendrite, soma, axon, myelin sheath, axon terminal, terminal buttons/synaptic vesicles and synapse. Give an example of how a message travels through the neuron. ...
... Explain the anatomy of a neuron including: dendrite, soma, axon, myelin sheath, axon terminal, terminal buttons/synaptic vesicles and synapse. Give an example of how a message travels through the neuron. ...
THE WORKING OF THE HUMAN BRAIN
... Blocks the receptors on the axons of neurons and inhibits them from firing Also connected with the reward mechanisms in the brain and is responsible for pleasant feelings ...
... Blocks the receptors on the axons of neurons and inhibits them from firing Also connected with the reward mechanisms in the brain and is responsible for pleasant feelings ...
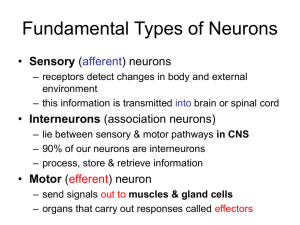
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... sequential opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels down entire length of axon • Nerve signal (nondecremental) travels at 2m/sec ...
... sequential opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels down entire length of axon • Nerve signal (nondecremental) travels at 2m/sec ...
Cell Structure: From an Information Processing View
... central nervous system to the effector organs (such as muscles and glands) are called motor (or efferent) neurons ...
... central nervous system to the effector organs (such as muscles and glands) are called motor (or efferent) neurons ...
The Nervous System - Science with Mr. Enns
... It is the most complex thing in the universe. It contains roughly 100 billion neurons. Each neuron connects with 100,000 others. The brain uses 1/3 of the food we eat each day. The fastest supercomputer in the world is nothing compared to the average brain. ...
... It is the most complex thing in the universe. It contains roughly 100 billion neurons. Each neuron connects with 100,000 others. The brain uses 1/3 of the food we eat each day. The fastest supercomputer in the world is nothing compared to the average brain. ...
The Nervous System workbooklet
... The brain has billions of neurons that receive, analyse, and store information about internal and external conditions. It is also the source of conscious and unconscious thoughts, moods, and emotions. Four major brain divisions govern its main functions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellu ...
... The brain has billions of neurons that receive, analyse, and store information about internal and external conditions. It is also the source of conscious and unconscious thoughts, moods, and emotions. Four major brain divisions govern its main functions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellu ...
successful transplantation of motoneurons into the peripheral nerve
... stained with both b-tubulin III and islet-1 by the number of nuclei. In the dissociated ventral spinal cord cells, 82.9 ± 2.1% of the cells were positive for both b-tubulin III and islet-1. With the transplantation of 200,000 cells in group A and 1 million cells in group B, we estimate that an avera ...
... stained with both b-tubulin III and islet-1 by the number of nuclei. In the dissociated ventral spinal cord cells, 82.9 ± 2.1% of the cells were positive for both b-tubulin III and islet-1. With the transplantation of 200,000 cells in group A and 1 million cells in group B, we estimate that an avera ...
Membrane potential
... channels in the membrane to open • As a result of ion flow through these channels, the inside of neuron briefly ...
... channels in the membrane to open • As a result of ion flow through these channels, the inside of neuron briefly ...
Neuro 16 Neurotransmitters Student
... GABAergic neurons of caudate nucleus and putamen project to substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Reduced concentrations in patients with Huntington’s chorea: ...
... GABAergic neurons of caudate nucleus and putamen project to substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Reduced concentrations in patients with Huntington’s chorea: ...
Therapeutic techniques
... bladder, amongst other problems. While specific procedures may require general anesthesia, other procedures can be performed with only sedation and local anesthetic blocks. Because of the small incisions that are made with this technique, many horses are able to return to athletic usefulness much fa ...
... bladder, amongst other problems. While specific procedures may require general anesthesia, other procedures can be performed with only sedation and local anesthetic blocks. Because of the small incisions that are made with this technique, many horses are able to return to athletic usefulness much fa ...
DESIRED RESULTS (STAGE 1) - Anoka
... The parts and functions of the endocrine system central nervous system peripheral nervous system The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will n ...
... The parts and functions of the endocrine system central nervous system peripheral nervous system The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will n ...
ANS_jh - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Simplified pathway: sensory neurons to spinothalamic tract to thalamus to cerebral cortex Visceral pain is induced by stretching, infection and cramping of internal organs but seldom by cutting (e.g. cutting off a colon ...
... Simplified pathway: sensory neurons to spinothalamic tract to thalamus to cerebral cortex Visceral pain is induced by stretching, infection and cramping of internal organs but seldom by cutting (e.g. cutting off a colon ...
Worksheet - Humble ISD
... There are 3 types of neurons, they are _______________, ______________, & _______________. The ______________ neuron carries impulses from the brain to muscles or glands. The _________________ neuron connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense o ...
... There are 3 types of neurons, they are _______________, ______________, & _______________. The ______________ neuron carries impulses from the brain to muscles or glands. The _________________ neuron connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense o ...
Tissues of the Body
... movement leading to heart beat. These are also under involuntary control ...
... movement leading to heart beat. These are also under involuntary control ...
No Slide Title
... Are action potentials always propagated between cells? Different action potentials from varying neurons can simultaneously influence the neuron they collectively synapse with to create ________ ___________ ...
... Are action potentials always propagated between cells? Different action potentials from varying neurons can simultaneously influence the neuron they collectively synapse with to create ________ ___________ ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-29
... from skin/muscle, visceral from organs 2. Sensory neuron enters dorsal part of spinal cord to synapse on gray matter neuron 3. Information integration by interneurons (not required for reflexes) 4. Motor neurons exit ventral part of spinal cord 5. Effector (muscle, gland) responds Anatomy of the Spi ...
... from skin/muscle, visceral from organs 2. Sensory neuron enters dorsal part of spinal cord to synapse on gray matter neuron 3. Information integration by interneurons (not required for reflexes) 4. Motor neurons exit ventral part of spinal cord 5. Effector (muscle, gland) responds Anatomy of the Spi ...
Nervous System
... the central nervous system (CNS); the connecting nerve processes to effectors and receptors serve as the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Special sense receptors provide for taste, smell, sight, hearing, and balance. Nerves carry all messages exchanged between the CNS and the rest of the body. CNS: ...
... the central nervous system (CNS); the connecting nerve processes to effectors and receptors serve as the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Special sense receptors provide for taste, smell, sight, hearing, and balance. Nerves carry all messages exchanged between the CNS and the rest of the body. CNS: ...